מידע על Codelab זה
1. סקירה כללית
מהו Document AI?
Document AI היא פלטפורמה שמאפשרת לחלץ תובנות מהמסמכים שלכם. בבסיס, הספרייה מציעה רשימה הולכת וגדלה של מעבדי מסמכים (שנקראים גם מנתחנים או מפרידים, בהתאם לפונקציונליות שלהם).
יש שתי דרכים לנהל מעבדים של Document AI:
- באופן ידני, במסוף האינטרנט.
- באופן פרוגרמטי, באמצעות Document AI API.
לפניכם צילום מסך לדוגמה שבו מוצגת רשימת המעבדים, גם ממסוף האינטרנט וגם מקוד Python:
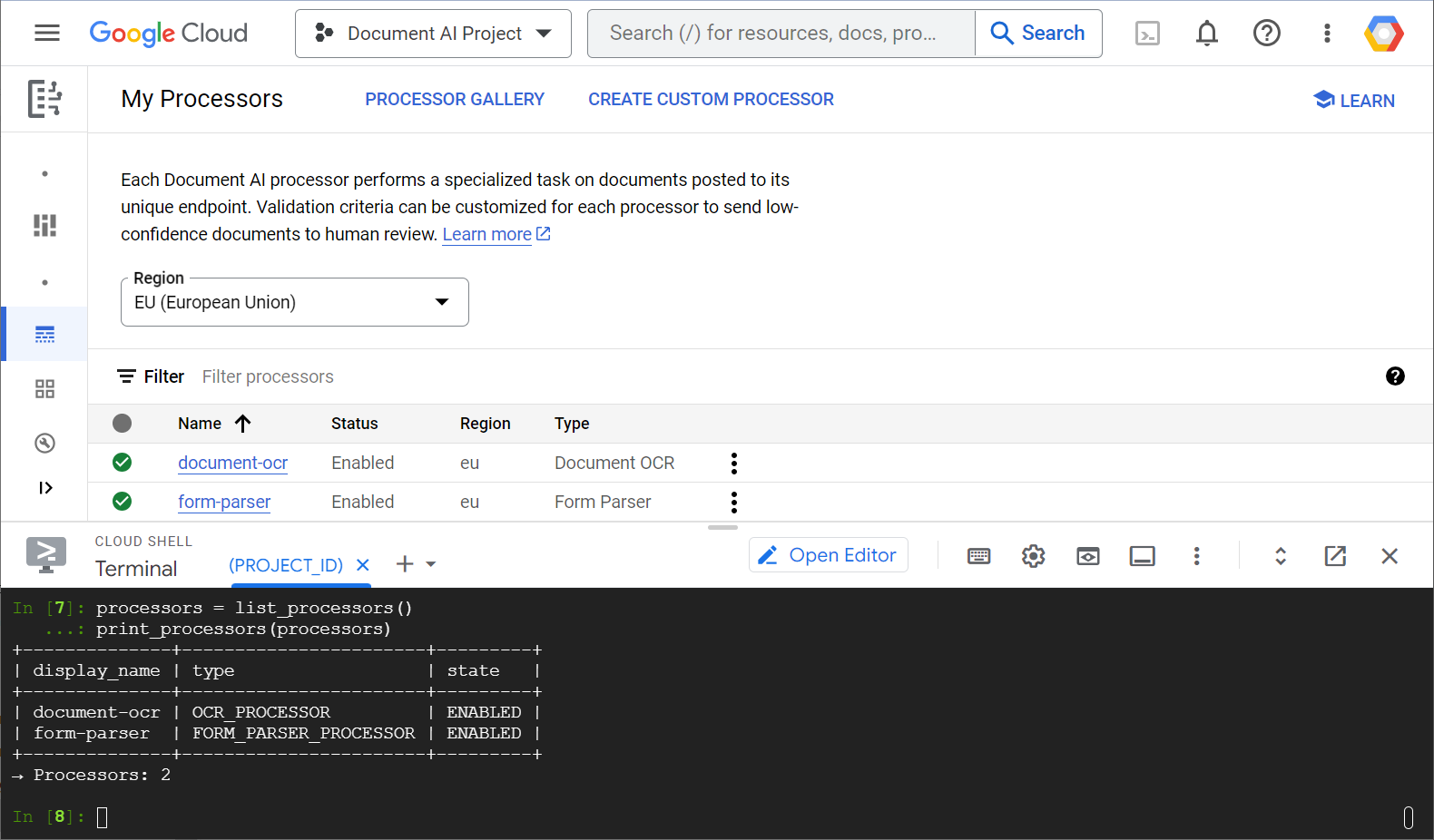
בשיעור ה-Lab הזה נתמקד בניהול מעבדי Document AI באופן פרוגרמטי באמצעות ספריית הלקוח של Python.
מה יוצג לכם
- איך מגדירים את הסביבה
- איך מאחזרים סוגי מעבדים
- איך יוצרים מעבדים
- איך מציגים רשימה של מעבדי פרויקטים
- איך משתמשים במעבדים
- איך מפעילים או משביתים מעבדים
- איך מנהלים גרסאות מעבדים
- איך מוחקים מעבדים
מה צריך להכין
סקר
איך תוכלו להשתמש במדריך הזה?
איזה דירוג מגיע לדעתך לחוויית השימוש שלך ב-Python?
מהו הדירוג המתאים לחוויית השימוש שלך בשירותי Google Cloud?
2. הגדרה ודרישות
הגדרת סביבה בקצב אישי
- נכנסים למסוף Google Cloud ויוצרים פרויקט חדש או משתמשים מחדש בפרויקט קיים. אם עדיין אין לכם חשבון Gmail או חשבון Google Workspace, עליכם ליצור חשבון.

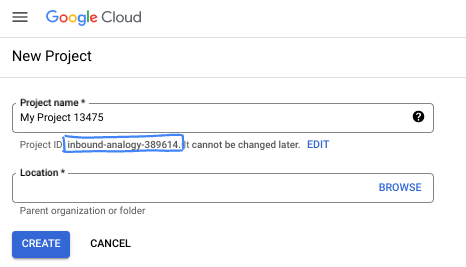
- שם הפרויקט הוא השם המוצג של המשתתפים בפרויקט. זוהי מחרוזת תווים שלא משמשת את Google APIs. תמיד אפשר לעדכן אותו.
- מזהה הפרויקט הוא ייחודי לכל הפרויקטים ב-Google Cloud ואי אפשר לשנות אותו אחרי שמגדירים אותו. מסוף Cloud יוצר מחרוזת ייחודית באופן אוטומטי. בדרך כלל לא משנה מה המחרוזת הזו. ברוב ה-codelabs תצטרכו להפנות למזהה הפרויקט (בדרך כלל מזהים אותו בתור
PROJECT_ID). אם המזהה שנוצר לא מוצא חן בעיניכם, תוכלו ליצור מזהה אקראי אחר. לחלופין, אפשר לנסות כתובת משלכם ולבדוק אם היא זמינה. לא ניתן לשנות את השם אחרי השלב הזה, והוא יישאר למשך כל תקופת הפרויקט. - לידיעתכם, יש ערך שלישי, מספר פרויקט, שמשתמשים בו בחלק מממשקי ה-API. מידע נוסף על כל שלושת הערכים האלה זמין במסמכי התיעוד.
- בשלב הבא, כדי להשתמש במשאבים או ב-API של Cloud, תצטרכו להפעיל את החיוב במסוף Cloud. השלמת הקודלאב הזה לא תעלה הרבה, אם בכלל. כדי להשבית את המשאבים ולמנוע חיובים אחרי סיום המדריך, אפשר למחוק את המשאבים שיצרתם או למחוק את הפרויקט. משתמשים חדשים ב-Google Cloud זכאים להשתתף בתוכנית תקופת ניסיון בחינם בסך 300$.
הפעלת Cloud Shell
אפשר להפעיל את Google Cloud מרחוק מהמחשב הנייד, אבל במעבדה הזו תשתמשו ב-Cloud Shell, סביבת שורת פקודה שפועלת ב-Cloud.
הפעלת Cloud Shell
- במסוף Cloud, לוחצים על Activate Cloud Shell
 .
.

אם זו הפעם הראשונה שאתם מפעילים את Cloud Shell, יוצג מסך ביניים עם תיאור של השירות. אם יוצג מסך ביניים, לוחצים על המשך.
תהליך ההקצאה וההתחברות ל-Cloud Shell אמור להימשך רק כמה רגעים.
המכונה הווירטואלית הזו כוללת את כל הכלים הנדרשים לפיתוח. יש בה ספריית בית בנפח מתמיד של 5GB והיא פועלת ב-Google Cloud, משפרת מאוד את ביצועי הרשת ואת האימות. אפשר לבצע את רוב העבודה בקודלאב הזה, אם לא את כולה, באמצעות דפדפן.
אחרי שתתחברו ל-Cloud Shell, אמורה להופיע הודעה על כך שהאימות בוצע והפרויקט מוגדר לפי מזהה הפרויקט שלכם.
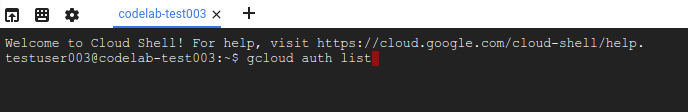
- מריצים את הפקודה הבאה ב-Cloud Shell כדי לוודא שהאימות בוצע:
gcloud auth list
פלט הפקודה
Credentialed Accounts
ACTIVE ACCOUNT
* <my_account>@<my_domain.com>
To set the active account, run:
$ gcloud config set account `ACCOUNT`
- מריצים את הפקודה הבאה ב-Cloud Shell כדי לוודא שפקודת gcloud מכירה את הפרויקט:
gcloud config list project
פלט הפקודה
[core] project = <PROJECT_ID>
אם לא, אפשר להגדיר אותו באמצעות הפקודה הבאה:
gcloud config set project <PROJECT_ID>
פלט הפקודה
Updated property [core/project].
3. הגדרת הסביבה
לפני שמתחילים להשתמש ב-Document AI, מריצים את הפקודה הבאה ב-Cloud Shell כדי להפעיל את Document AI API:
gcloud services enable documentai.googleapis.com
התוצאה אמורה להיראות כך:
Operation "operations/..." finished successfully.
עכשיו אפשר להשתמש ב-Document AI!
עוברים לספריית הבית:
cd ~
יוצרים סביבה וירטואלית של Python כדי לבודד את יחסי התלות:
virtualenv venv-docai
מפעילים את הסביבה הווירטואלית:
source venv-docai/bin/activate
מתקינים את IPython, את ספריית הלקוח של Document AI ואת python-tabulate (שתשמשים להדפסה יפה של תוצאות הבקשה):
pip install ipython google-cloud-documentai tabulate
התוצאה אמורה להיראות כך:
... Installing collected packages: ..., tabulate, ipython, google-cloud-documentai Successfully installed ... google-cloud-documentai-2.15.0 ...
עכשיו אתם מוכנים להשתמש בספריית הלקוח של Document AI.
מגדירים את משתני הסביבה הבאים:
export PROJECT_ID=$(gcloud config get-value core/project)
# Choose "us" or "eu"
export API_LOCATION="us"
מעכשיו, צריך להשלים את כל השלבים באותו סשן.
מוודאים שמשתני הסביבה מוגדרים בצורה נכונה:
echo $PROJECT_ID
echo $API_LOCATION
בשלבים הבאים תשתמשו במתורגם Python אינטראקטיבי שנקרא IPython, שהתקנתם עכשיו. כדי להתחיל סשן, מריצים את הפקודה ipython ב-Cloud Shell:
ipython
התוצאה אמורה להיראות כך:
Python 3.12.3 (main, Feb 4 2025, 14:48:35) [GCC 13.3.0] Type 'copyright', 'credits' or 'license' for more information IPython 9.1.0 -- An enhanced Interactive Python. Type '?' for help. In [1]:
מעתיקים את הקוד הבא לסשן IPython:
import os
from typing import Iterator, MutableSequence, Optional, Sequence, Tuple
import google.cloud.documentai_v1 as docai
from tabulate import tabulate
PROJECT_ID = os.getenv("PROJECT_ID", "")
API_LOCATION = os.getenv("API_LOCATION", "")
assert PROJECT_ID, "PROJECT_ID is undefined"
assert API_LOCATION in ("us", "eu"), "API_LOCATION is incorrect"
# Test processors
document_ocr_display_name = "document-ocr"
form_parser_display_name = "form-parser"
test_processor_display_names_and_types = (
(document_ocr_display_name, "OCR_PROCESSOR"),
(form_parser_display_name, "FORM_PARSER_PROCESSOR"),
)
def get_client() -> docai.DocumentProcessorServiceClient:
client_options = {"api_endpoint": f"{API_LOCATION}-documentai.googleapis.com"}
return docai.DocumentProcessorServiceClient(client_options=client_options)
def get_parent(client: docai.DocumentProcessorServiceClient) -> str:
return client.common_location_path(PROJECT_ID, API_LOCATION)
def get_client_and_parent() -> Tuple[docai.DocumentProcessorServiceClient, str]:
client = get_client()
parent = get_parent(client)
return client, parent
עכשיו אתם מוכנים לשלוח את הבקשה הראשונה ולאחזר את סוגי המעבדים.
4. אחזור סוגי מעבדים
לפני שיוצרים מעבד בשלב הבא, צריך לאחזר את סוגי המעבדים הזמינים. אפשר לאחזר את הרשימה הזו באמצעות fetch_processor_types.
מוסיפים את הפונקציות הבאות לסשן IPython:
def fetch_processor_types() -> MutableSequence[docai.ProcessorType]:
client, parent = get_client_and_parent()
response = client.fetch_processor_types(parent=parent)
return response.processor_types
def print_processor_types(processor_types: Sequence[docai.ProcessorType]):
def sort_key(pt):
return (not pt.allow_creation, pt.category, pt.type_)
sorted_processor_types = sorted(processor_types, key=sort_key)
data = processor_type_tabular_data(sorted_processor_types)
headers = next(data)
colalign = next(data)
print(tabulate(data, headers, tablefmt="pretty", colalign=colalign))
print(f"→ Processor types: {len(sorted_processor_types)}")
def processor_type_tabular_data(
processor_types: Sequence[docai.ProcessorType],
) -> Iterator[Tuple[str, str, str, str]]:
def locations(pt):
return ", ".join(sorted(loc.location_id for loc in pt.available_locations))
yield ("type", "category", "allow_creation", "locations")
yield ("left", "left", "left", "left")
if not processor_types:
yield ("-", "-", "-", "-")
return
for pt in processor_types:
yield (pt.type_, pt.category, f"{pt.allow_creation}", locations(pt))
מציגים את סוגי המעבדים:
processor_types = fetch_processor_types()
print_processor_types(processor_types)
אמורה להופיע תוצאה שדומה לזו:
+--------------------------------------+-------------+----------------+-----------+ | type | category | allow_creation | locations | +--------------------------------------+-------------+----------------+-----------+ | CUSTOM_CLASSIFICATION_PROCESSOR | CUSTOM | True | eu, us | ... | FORM_PARSER_PROCESSOR | GENERAL | True | eu, us | | LAYOUT_PARSER_PROCESSOR | GENERAL | True | eu, us | | OCR_PROCESSOR | GENERAL | True | eu, us | | BANK_STATEMENT_PROCESSOR | SPECIALIZED | True | eu, us | | EXPENSE_PROCESSOR | SPECIALIZED | True | eu, us | ... +--------------------------------------+-------------+----------------+-----------+ → Processor types: 19
עכשיו יש לכם את כל המידע הדרוש כדי ליצור מעבדים בשלב הבא.
5. יצירת מעבדים
כדי ליצור מעבד, קוראים ל-create_processor עם שם מוצג וסוג מעבד.
מוסיפים את הפונקציה הבאה:
def create_processor(display_name: str, type: str) -> docai.Processor:
client, parent = get_client_and_parent()
processor = docai.Processor(display_name=display_name, type_=type)
return client.create_processor(parent=parent, processor=processor)
יוצרים את מעבדי הבדיקות:
separator = "=" * 80
for display_name, type in test_processor_display_names_and_types:
print(separator)
print(f"Creating {display_name} ({type})...")
try:
create_processor(display_name, type)
except Exception as err:
print(err)
print(separator)
print("Done")
התוצאה אמורה להיות:
================================================================================ Creating document-ocr (OCR_PROCESSOR)... ================================================================================ Creating form-parser (FORM_PARSER_PROCESSOR)... ================================================================================ Done
יצרתם מעבדים חדשים!
בשלב הבא נסביר איך להציג את המעבדים.
6. הצגת מעבדי פרויקטים
הפונקציה list_processors מחזירה את הרשימה של כל המעבדים ששייכים לפרויקט.
מוסיפים את הפונקציות הבאות:
def list_processors() -> MutableSequence[docai.Processor]:
client, parent = get_client_and_parent()
response = client.list_processors(parent=parent)
return list(response.processors)
def print_processors(processors: Optional[Sequence[docai.Processor]] = None):
def sort_key(processor):
return processor.display_name
if processors is None:
processors = list_processors()
sorted_processors = sorted(processors, key=sort_key)
data = processor_tabular_data(sorted_processors)
headers = next(data)
colalign = next(data)
print(tabulate(data, headers, tablefmt="pretty", colalign=colalign))
print(f"→ Processors: {len(sorted_processors)}")
def processor_tabular_data(
processors: Sequence[docai.Processor],
) -> Iterator[Tuple[str, str, str]]:
yield ("display_name", "type", "state")
yield ("left", "left", "left")
if not processors:
yield ("-", "-", "-")
return
for processor in processors:
yield (processor.display_name, processor.type_, processor.state.name)
קוראים לפונקציות:
processors = list_processors()
print_processors(processors)
התוצאה אמורה להיות:
+--------------+-----------------------+---------+ | display_name | type | state | +--------------+-----------------------+---------+ | document-ocr | OCR_PROCESSOR | ENABLED | | form-parser | FORM_PARSER_PROCESSOR | ENABLED | +--------------+-----------------------+---------+ → Processors: 2
כדי לאחזר מעבד לפי השם המוצג שלו, מוסיפים את הפונקציה הבאה:
def get_processor(
display_name: str,
processors: Optional[Sequence[docai.Processor]] = None,
) -> Optional[docai.Processor]:
if processors is None:
processors = list_processors()
for processor in processors:
if processor.display_name == display_name:
return processor
return None
בודקים את הפונקציה:
processor = get_processor(document_ocr_display_name, processors)
assert processor is not None
print(processor)
התוצאה אמורה להיראות כך:
name: "projects/PROJECT_NUM/locations/LOCATION/processors/PROCESSOR_ID" type_: "OCR_PROCESSOR" display_name: "document-ocr" state: ENABLED ...
עכשיו אתם יודעים איך לקבל רשימה של מעבדי הפרויקטים ואיך לאחזר אותם לפי השמות המוצגים שלהם. בשלב הבא נסביר איך משתמשים במעבד.
7. שימוש במעבדים
יש שתי דרכים לעבד מסמכים:
- סינכרונית: קוראים ל-
process_documentכדי לנתח מסמך יחיד ולהשתמש בתוצאות ישירות. - באופן אסינכרוני: קוראים ל-
batch_process_documentsכדי להפעיל עיבוד באצווה במספר מסמכים או במסמכים גדולים.
מסמך הבדיקה ( PDF) הוא שאלון סרוק עם תשובות בכתב יד. מורידים אותו לספריית העבודה ישירות מהסשן של IPython:
!gsutil cp gs://cloud-samples-data/documentai/form.pdf .
בודקים את התוכן של ספריית העבודה:
!ls
אתם צריכים:
... form.pdf ... venv-docai ...
אפשר להשתמש בשיטה הסינכרנית process_document כדי לנתח קובץ מקומי. מוסיפים את הפונקציה הבאה:
def process_file(
processor: docai.Processor,
file_path: str,
mime_type: str,
) -> docai.Document:
client = get_client()
with open(file_path, "rb") as document_file:
document_content = document_file.read()
document = docai.RawDocument(content=document_content, mime_type=mime_type)
request = docai.ProcessRequest(raw_document=document, name=processor.name)
response = client.process_document(request)
return response.document
מאחר שהמסמך הוא שאלון, בוחרים את הכלי לניתוחי טפסים. בנוסף לחילוץ הטקסט (מודפס וידני), שכל המעבדים מבצעים, המעבד הכללי הזה מזהה שדות של טפסים.
בודקים את המסמך:
processor = get_processor(form_parser_display_name)
assert processor is not None
file_path = "./form.pdf"
mime_type = "application/pdf"
document = process_file(processor, file_path, mime_type)
כל המעבדים מריצים סבב ראשון של זיהוי תווים אופטי (OCR) במסמך. בודקים את הטקסט שזוהה על ידי תהליך ה-OCR:
document.text.split("\n")
אמורה להופיע הודעה דומה לזו:
['FakeDoc M.D.', 'HEALTH INTAKE FORM', 'Please fill out the questionnaire carefully. The information you provide will be used to complete', 'your health profile and will be kept confidential.', 'Date:', '9/14/19', 'Name:', 'Sally Walker', 'DOB: 09/04/1986', 'Address: 24 Barney Lane', 'City: Towaco', 'State: NJ Zip: 07082', 'Email: Sally, walker@cmail.com', '_Phone #: (906) 917-3486', 'Gender: F', 'Marital Status:', ... ]
מוסיפים את הפונקציות הבאות כדי להדפיס את שדות הטופס שזוהו:
def print_form_fields(document: docai.Document):
sorted_form_fields = form_fields_sorted_by_ocr_order(document)
data = form_field_tabular_data(sorted_form_fields, document)
headers = next(data)
colalign = next(data)
print(tabulate(data, headers, tablefmt="pretty", colalign=colalign))
print(f"→ Form fields: {len(sorted_form_fields)}")
def form_field_tabular_data(
form_fields: Sequence[docai.Document.Page.FormField],
document: docai.Document,
) -> Iterator[Tuple[str, str, str]]:
yield ("name", "value", "confidence")
yield ("right", "left", "right")
if not form_fields:
yield ("-", "-", "-")
return
for form_field in form_fields:
name_layout = form_field.field_name
value_layout = form_field.field_value
name = text_from_layout(name_layout, document)
value = text_from_layout(value_layout, document)
confidence = value_layout.confidence
yield (name, value, f"{confidence:.1%}")
מוסיפים גם את פונקציות התשתית הבאות:
def form_fields_sorted_by_ocr_order(
document: docai.Document,
) -> MutableSequence[docai.Document.Page.FormField]:
def sort_key(form_field):
# Sort according to the field name detected position
text_anchor = form_field.field_name.text_anchor
return text_anchor.text_segments[0].start_index if text_anchor else 0
fields = (field for page in document.pages for field in page.form_fields)
return sorted(fields, key=sort_key)
def text_from_layout(
layout: docai.Document.Page.Layout,
document: docai.Document,
) -> str:
full_text = document.text
segs = layout.text_anchor.text_segments
text = "".join(full_text[seg.start_index : seg.end_index] for seg in segs)
if text.endswith("\n"):
text = text[:-1]
return text
מדפיסים את שדות הטופס שזוהו:
print_form_fields(document)
אמורה להופיע הדפסה שדומה לזו:
+-----------------+-------------------------+------------+ | name | value | confidence | +-----------------+-------------------------+------------+ | Date: | 9/14/19 | 83.0% | | Name: | Sally Walker | 87.3% | | DOB: | 09/04/1986 | 88.5% | | Address: | 24 Barney Lane | 82.4% | | City: | Towaco | 90.0% | | State: | NJ | 89.4% | | Zip: | 07082 | 91.4% | | Email: | Sally, walker@cmail.com | 79.7% | | _Phone #: | walker@cmail.com | 93.2% | | | (906 | | | Gender: | F | 88.2% | | Marital Status: | Single | 85.2% | | Occupation: | Software Engineer | 81.5% | | Referred By: | None | 76.9% | ... +-----------------+-------------------------+------------+ → Form fields: 17
בודקים את שמות השדות והערכים שזוהו ( PDF). זהו החלק העליון של השאלון:

ניתחתם טופס שמכיל טקסט מודפס וגם טקסט בכתב יד. בנוסף, זיהית את השדות שלו ברמת סמך גבוהה. התוצאה היא שהפיקסלים שלכם הופכים לנתונים מובְנים.
8. הפעלה והשבתה של מעבדים
בעזרת disable_processor ו-enable_processor אפשר לקבוע אם ניתן להשתמש במעבד.
מוסיפים את הפונקציות הבאות:
def update_processor_state(processor: docai.Processor, enable_processor: bool):
client = get_client()
if enable_processor:
request = docai.EnableProcessorRequest(name=processor.name)
operation = client.enable_processor(request)
else:
request = docai.DisableProcessorRequest(name=processor.name)
operation = client.disable_processor(request)
operation.result() # Wait for operation to complete
def enable_processor(processor: docai.Processor):
update_processor_state(processor, True)
def disable_processor(processor: docai.Processor):
update_processor_state(processor, False)
משביתים את מעבד הניתוח של הטפסים ובודקים את המצב של המעבדים:
processor = get_processor(form_parser_display_name)
assert processor is not None
disable_processor(processor)
print_processors()
התוצאה אמורה להיות:
+--------------+-----------------------+----------+ | display_name | type | state | +--------------+-----------------------+----------+ | document-ocr | OCR_PROCESSOR | ENABLED | | form-parser | FORM_PARSER_PROCESSOR | DISABLED | +--------------+-----------------------+----------+ → Processors: 2
מפעילים מחדש את מעבד הניתוח של הטפסים:
enable_processor(processor)
print_processors()
התוצאה אמורה להיות:
+--------------+-----------------------+---------+ | display_name | type | state | +--------------+-----------------------+---------+ | document-ocr | OCR_PROCESSOR | ENABLED | | form-parser | FORM_PARSER_PROCESSOR | ENABLED | +--------------+-----------------------+---------+ → Processors: 2
בשלב הבא נסביר איך מנהלים גרסאות של מעבדים.
9. ניהול גרסאות של מעבדים
מעבדים יכולים להיות זמינים בכמה גרסאות. כדאי לעיין במאמרים בנושא השימוש בשיטות list_processor_versions ו-set_default_processor_version.
מוסיפים את הפונקציות הבאות:
def list_processor_versions(
processor: docai.Processor,
) -> MutableSequence[docai.ProcessorVersion]:
client = get_client()
response = client.list_processor_versions(parent=processor.name)
return list(response)
def get_sorted_processor_versions(
processor: docai.Processor,
) -> MutableSequence[docai.ProcessorVersion]:
def sort_key(processor_version: docai.ProcessorVersion):
return processor_version.name
versions = list_processor_versions(processor)
return sorted(versions, key=sort_key)
def print_processor_versions(processor: docai.Processor):
versions = get_sorted_processor_versions(processor)
default_version_name = processor.default_processor_version
data = processor_versions_tabular_data(versions, default_version_name)
headers = next(data)
colalign = next(data)
print(tabulate(data, headers, tablefmt="pretty", colalign=colalign))
print(f"→ Processor versions: {len(versions)}")
def processor_versions_tabular_data(
versions: Sequence[docai.ProcessorVersion],
default_version_name: str,
) -> Iterator[Tuple[str, str, str]]:
yield ("version", "display name", "default")
yield ("left", "left", "left")
if not versions:
yield ("-", "-", "-")
return
for version in versions:
mapping = docai.DocumentProcessorServiceClient.parse_processor_version_path(
version.name
)
processor_version = mapping["processor_version"]
is_default = "Y" if version.name == default_version_name else ""
yield (processor_version, version.display_name, is_default)
מציינים את הגרסאות הזמינות של מעבד ה-OCR:
processor = get_processor(document_ocr_display_name)
assert processor is not None
print_processor_versions(processor)
מוצגות גרסאות המעבד:
+--------------------------------+--------------------------+---------+ | version | display name | default | +--------------------------------+--------------------------+---------+ | pretrained-ocr-v1.0-2020-09-23 | Google Stable | | | pretrained-ocr-v1.1-2022-09-12 | Google Release Candidate | | | pretrained-ocr-v1.2-2022-11-10 | Google Release Candidate | | | pretrained-ocr-v2.0-2023-06-02 | Google Stable | Y | | pretrained-ocr-v2.1-2024-08-07 | Google Release Candidate | | +--------------------------------+--------------------------+---------+ → Processor versions: 5
עכשיו מוסיפים פונקציה לשינוי גרסת ברירת המחדל של המעבד:
def set_default_processor_version(processor: docai.Processor, version_name: str):
client = get_client()
request = docai.SetDefaultProcessorVersionRequest(
processor=processor.name,
default_processor_version=version_name,
)
operation = client.set_default_processor_version(request)
operation.result() # Wait for operation to complete
עוברים לגרסה האחרונה של המעבד:
processor = get_processor(document_ocr_display_name)
assert processor is not None
versions = get_sorted_processor_versions(processor)
new_version = versions[-1] # Latest version
set_default_processor_version(processor, new_version.name)
# Update the processor info
processor = get_processor(document_ocr_display_name)
assert processor is not None
print_processor_versions(processor)
מקבלים את ההגדרות של הגרסה החדשה:
+--------------------------------+--------------------------+---------+ | version | display name | default | +--------------------------------+--------------------------+---------+ | pretrained-ocr-v1.0-2020-09-23 | Google Stable | | | pretrained-ocr-v1.1-2022-09-12 | Google Release Candidate | | | pretrained-ocr-v1.2-2022-11-10 | Google Release Candidate | | | pretrained-ocr-v2.0-2023-06-02 | Google Stable | | | pretrained-ocr-v2.1-2024-08-07 | Google Release Candidate | Y | +--------------------------------+--------------------------+---------+ → Processor versions: 5
בשלב הבא, נציג את שיטת הניהול האולטימטיבית של מעבדים (מחיקה).
10. מחיקת מעבדים
לסיום, כדאי לבדוק איך משתמשים בשיטה delete_processor.
מוסיפים את הפונקציה הבאה:
def delete_processor(processor: docai.Processor):
client = get_client()
operation = client.delete_processor(name=processor.name)
operation.result() # Wait for operation to complete
מוחקים את מעבדי הבדיקה:
processors_to_delete = [dn for dn, _ in test_processor_display_names_and_types]
print("Deleting processors...")
for processor in list_processors():
if processor.display_name not in processors_to_delete:
continue
print(f" Deleting {processor.display_name}...")
delete_processor(processor)
print("Done\n")
print_processors()
התוצאה אמורה להיות:
Deleting processors... Deleting form-parser... Deleting document-ocr... Done +--------------+------+-------+ | display_name | type | state | +--------------+------+-------+ | - | - | - | +--------------+------+-------+ → Processors: 0
סיימתם את כל שיטות הניהול של המעבדים! כמעט סיימת...
11. מעולה!

למדתם איך לנהל מעבדים של Document AI באמצעות Python.
הסרת המשאבים
כדי לנקות את סביבת הפיתוח, ב-Cloud Shell:
- אם אתם עדיין בסשן IPython, חוזרים למסוף:
exit - מפסיקים להשתמש בסביבה הווירטואלית של Python:
deactivate - מוחקים את התיקייה של הסביבה הווירטואלית:
cd ~ ; rm -rf ./venv-docai
כדי למחוק את הפרויקט ב-Google Cloud, ב-Cloud Shell:
- אחזור של מזהה הפרויקט הנוכחי:
PROJECT_ID=$(gcloud config get-value core/project) - מוודאים שזהו הפרויקט שרוצים למחוק:
echo $PROJECT_ID - מוחקים את הפרויקט:
gcloud projects delete $PROJECT_ID
מידע נוסף
- אפשר לנסות את Document AI בדפדפן: https://cloud.google.com/document-ai/docs/drag-and-drop
- פרטי המעבד של Document AI: https://cloud.google.com/document-ai/docs/processors-list
- Python ב-Google Cloud: https://cloud.google.com/python
- ספריות לקוח של Cloud ל-Python: https://github.com/googleapis/google-cloud-python
רישיון
העבודה הזו בשימוש במסגרת רישיון Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 Generic.

