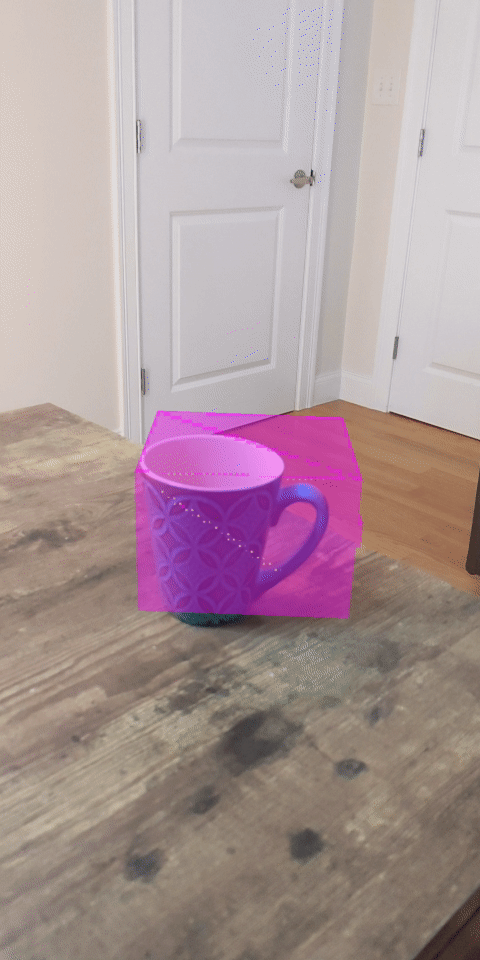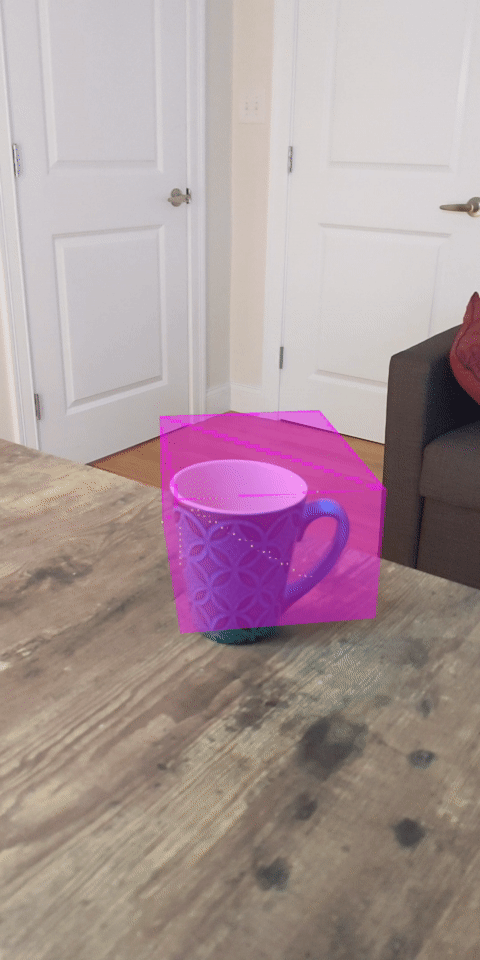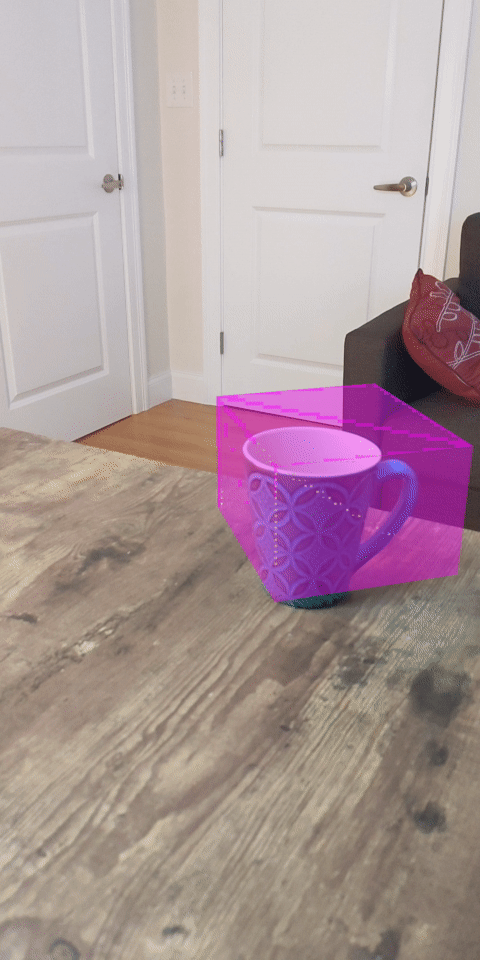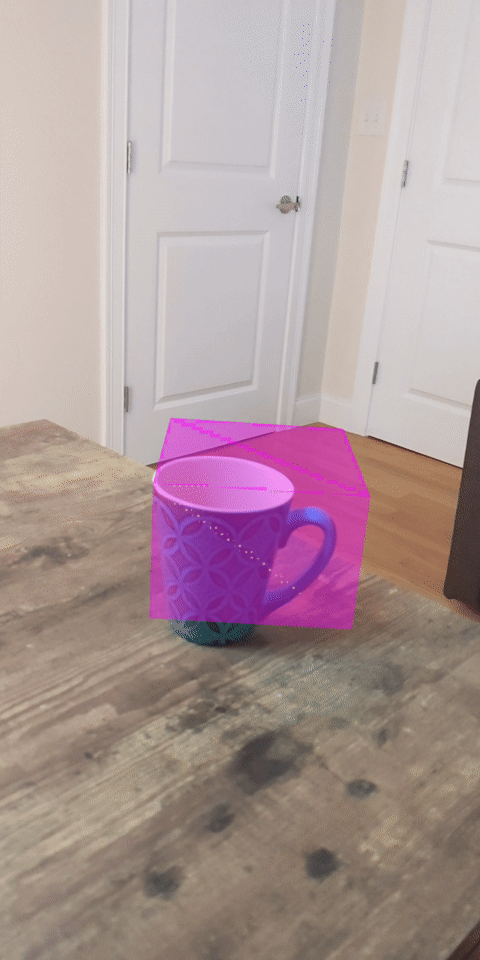
1. บทนำ
ARCore เป็นแพลตฟอร์มสำหรับสร้างแอป Augmented Reality (AR) ในอุปกรณ์เคลื่อนที่ ARCore Depth API ของ Google ให้สิทธิ์เข้าถึงรูปภาพความลึกแต่ละเฟรมในเซสชัน ARCore ภาพแต่ละพิกเซลในระดับลึกจะแสดงการวัดระยะทางจากกล้องไปยังสภาพแวดล้อม
Raw Depth API จะให้รูปภาพที่มีความลึกที่ไม่ผ่านการดำเนินการกรองพื้นที่หน้าจอซึ่งออกแบบมาให้ใช้งานได้อย่างลื่นไหลและสอดแทรกผลลัพธ์ ค่าเหล่านี้มีความถูกต้องทางเรขาคณิตมากกว่า แต่ก็อาจมีข้อมูลที่ขาดหายไปและไม่สอดคล้องกับรูปภาพจากกล้องที่เกี่ยวข้องน้อยลง
Codelab นี้แสดงวิธีใช้ Raw Depth API เพื่อทำการวิเคราะห์เรขาคณิต 3 มิติของฉาก คุณจะได้สร้างแอปที่เปิดใช้ AR แบบง่ายๆ โดยใช้ข้อมูลดิบที่มีความลึกในการตรวจจับและแสดงภาพเรขาคณิตของโลก
Depth และ Raw Depth API รองรับเฉพาะในอุปกรณ์ที่เปิดใช้ ARCore บางส่วนเท่านั้น Depth API ใช้งานได้ใน Android เท่านั้น
สิ่งที่คุณจะสร้าง
ใน Codelab นี้ คุณจะได้สร้างแอปที่ใช้ภาพความลึกแบบดิบสำหรับแต่ละเฟรมเพื่อทำการวิเคราะห์ทางเรขาคณิตของโลกรอบตัวคุณ แอปนี้จะ:
- ตรวจสอบว่าอุปกรณ์เป้าหมายรองรับความลึกหรือไม่
- ดึงรูปภาพความลึกที่เป็นข้อมูลดิบของเฟรมกล้องแต่ละเฟรม
- ฉายภาพความลึกดิบอีกครั้งเป็นจุด 3 มิติ และกรองจุดเหล่านั้นตามความเชื่อมั่นและเรขาคณิต
- ใช้ระบบคลาวด์ที่มีจุดความลึกแบบข้อมูลดิบเพื่อแบ่งกลุ่มวัตถุ 3 มิติที่สนใจ
|
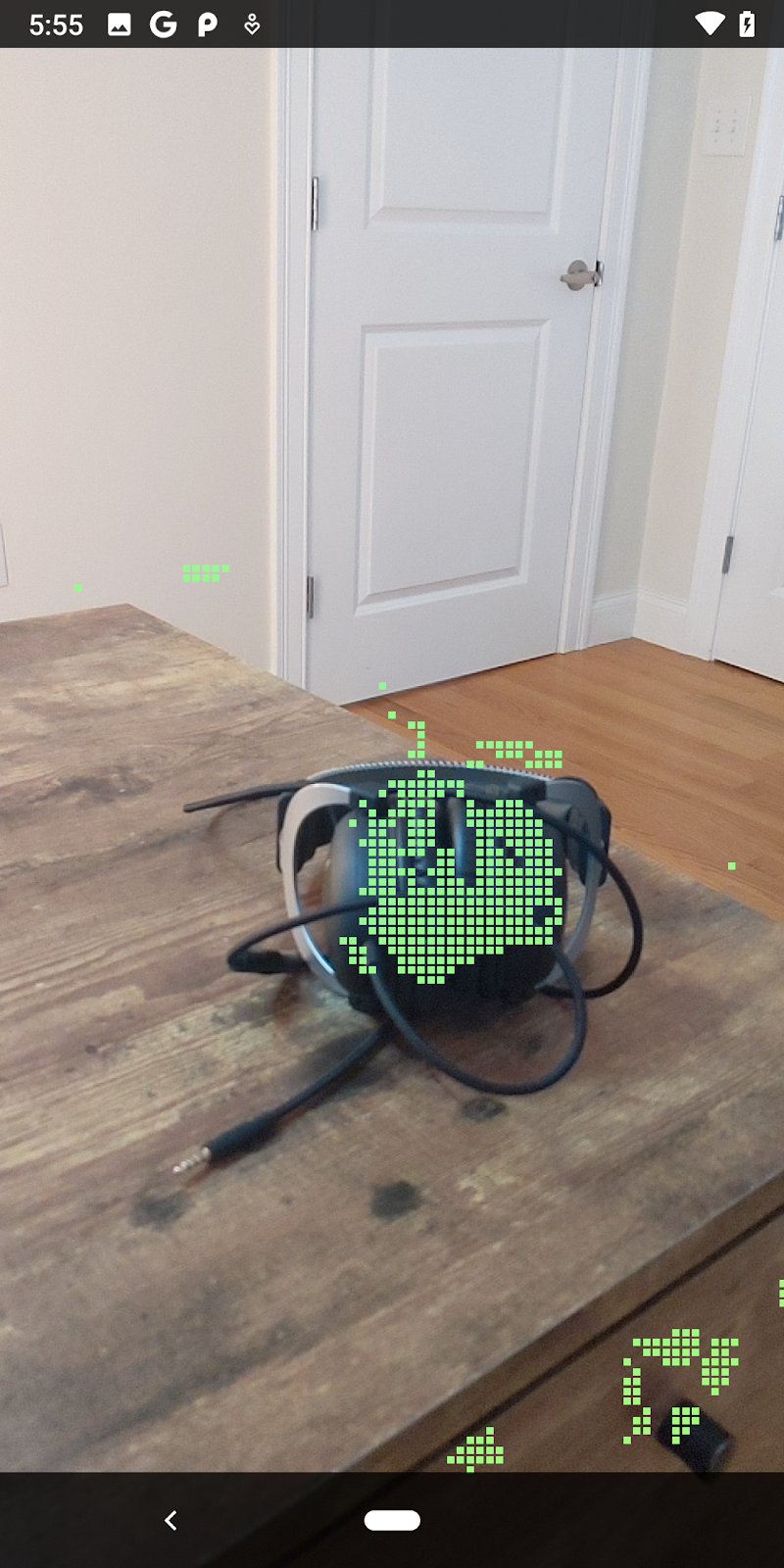
ดูตัวอย่างสิ่งที่คุณจะสร้าง |
หมายเหตุ: หากพบปัญหาระหว่างการใช้งาน ให้ข้ามไปยังส่วนสุดท้ายเพื่อดูเคล็ดลับในการแก้ปัญหาบางอย่าง
2. ข้อกำหนดเบื้องต้น
คุณจะต้องใช้ฮาร์ดแวร์และซอฟต์แวร์เฉพาะเพื่อทำงาน Codelab นี้ให้เสร็จสมบูรณ์
ข้อกำหนดเกี่ยวกับฮาร์ดแวร์
- อุปกรณ์ที่รองรับ ARCore ที่เปิดใช้การแก้ไขข้อบกพร่องผ่าน USB และเชื่อมต่อกับเครื่องพัฒนาผ่านสาย USB อุปกรณ์นี้ต้องรองรับ Depth API ด้วย
ข้อกำหนดของซอฟต์แวร์
- ARCore SDK 1.31.0 ขึ้นไป
- เครื่องพัฒนาซอฟต์แวร์ที่ติดตั้ง Android Studio (เวอร์ชัน 4.0.1 ขึ้นไป)
3. ตั้งค่า
ตั้งค่าเครื่องสำหรับการพัฒนา
เชื่อมต่ออุปกรณ์ ARCore กับคอมพิวเตอร์ผ่านสาย USB ตรวจสอบว่าอุปกรณ์ของคุณอนุญาตให้แก้ไขข้อบกพร่อง USB เปิดเทอร์มินัลและเรียกใช้ adb devices ตามที่แสดงด้านล่าง
adb devices List of devices attached <DEVICE_SERIAL_NUMBER> device
<DEVICE_SERIAL_NUMBER> จะเป็นสตริงเฉพาะสำหรับอุปกรณ์ของคุณ โปรดตรวจสอบว่าคุณเห็นอุปกรณ์รุ่นเดียวเท่านั้นก่อนดำเนินการต่อ
ดาวน์โหลดและติดตั้งโค้ด
คุณจะโคลนที่เก็บได้ด้วยวิธีการต่อไปนี้
git clone https://github.com/googlecodelabs/arcore-rawdepthapi
หรือดาวน์โหลดไฟล์ ZIP และแตกข้อมูลออกมา
ทำตามขั้นตอนต่อไปนี้เพื่อเริ่มต้นใช้งานโค้ด
- เปิด Android Studio แล้วเลือกเปิดโปรเจ็กต์ Android Studio ที่มีอยู่
- ไปที่ไดเรกทอรีในเครื่องที่คุณจัดเก็บไฟล์ ZIP แบบความลึกเป็นไฟล์ข้อมูล RAW
- ดับเบิลคลิกไดเรกทอรี
arcore_rawdepthapi_codelab
ไดเรกทอรี arcore_rawdepthapi_codelab เป็นโปรเจ็กต์ Gradle เดียวที่มีหลายโมดูล หากแผงโครงการที่ด้านซ้ายบนของ Android Studio ยังไม่ปรากฏในแผงโครงการ ให้คลิกโครงการจากเมนูแบบเลื่อนลง
ผลลัพธ์ที่ได้ควรมีลักษณะดังนี้
| โครงการนี้มีโมดูลต่อไปนี้:
|
คุณจะได้ทำงานในโมดูล part0_work นอกจากนี้ยังมีโซลูชันที่สมบูรณ์สำหรับแต่ละส่วนของ Codelab แต่ละโมดูลคือแอปที่บิลด์ได้
4. เรียกใช้แอปเริ่มต้น
ทำตามขั้นตอนต่อไปนี้เพื่อเรียกใช้แอปเริ่มต้นสำหรับขอบเขตข้อมูลดิบ
- ไปที่เรียกใช้ > เรียกใช้... "part0_work"
- ในกล่องโต้ตอบเลือกเป้าหมายการทำให้ใช้งานได้ ให้เลือกอุปกรณ์ของคุณจากรายการอุปกรณ์ที่เชื่อมต่อ แล้วคลิกตกลง
Android Studio จะสร้างแอปเริ่มต้นและเรียกใช้บนอุปกรณ์ของคุณ
| เมื่อเรียกใช้แอปเป็นครั้งแรก แอปจะขอสิทธิ์ใช้กล้อง แตะอนุญาตเพื่อดำเนินการต่อ |
| ขณะนี้แอปไม่ได้ดำเนินการใดๆ ซึ่งเป็นแอปพลิเคชัน AR ขั้นพื้นฐานที่สุดที่แสดงมุมมองกล้องของฉาก แต่ไม่ได้ดำเนินการใดๆ โค้ดที่มีอยู่จะคล้ายกับตัวอย่าง Hello AR ที่เผยแพร่ด้วย ARCore SDK |
ถัดไป คุณจะใช้ API ความลึกแบบ Raw เพื่อดึงข้อมูลเรขาคณิตของฉากรอบตัวคุณ
5. ตั้งค่า Raw Depth API (ส่วนที่ 1)
ตรวจสอบว่าอุปกรณ์เป้าหมายรองรับความลึก
อุปกรณ์ที่รองรับ ARCore บางอย่างอาจเรียกใช้ Depth API ได้ ตรวจสอบว่าอุปกรณ์เป้าหมายรองรับความลึกก่อนที่จะเพิ่มฟังก์ชันลงในแอปภายในฟังก์ชัน onResume() ของ RawDepthCodelabActivity.java ที่มีการสร้างเซสชันใหม่
ค้นหารหัสที่มีอยู่
// Create the ARCore session.
session = new Session(/* context= */ this);
โปรดอัปเดตเพื่อให้แอปพลิเคชันทำงานบนอุปกรณ์ที่รองรับ Depth API ได้เท่านั้น
// Create the ARCore session.
session = new Session(/* context= */ this);
if (!session.isDepthModeSupported(Config.DepthMode.RAW_DEPTH_ONLY)) {
message =
"This device does not support the ARCore Raw Depth API. See" +
"https://developers.google.com/ar/devices for
a list of devices that do.";
}
เปิดใช้ความลึกของไฟล์ข้อมูล RAW
Raw Depth API ให้รูปภาพความลึกที่ไม่เรียบเนียน และรูปภาพระดับความเชื่อมั่นที่สอดคล้องกันซึ่งมีความเชื่อมั่นด้านความลึกสำหรับแต่ละพิกเซลในรูปภาพที่มีความลึกแบบ RAW เปิดใช้ความลึกของไฟล์ข้อมูล RAW โดยการอัปเดตโค้ดต่อไปนี้ใต้ข้อความลองจับที่คุณเพิ่งแก้ไข
try {
// ************ New code to add ***************
// Enable raw depth estimation and auto focus mode while ARCore is running.
Config config = session.getConfig();
config.setDepthMode(Config.DepthMode.RAW_DEPTH_ONLY);
config.setFocusMode(Config.FocusMode.AUTO);
session.configure(config);
// ************ End new code to add ***************
session.resume();
} catch (CameraNotAvailableException e) {
messageSnackbarHelper.showError(this, "Camera not available. Try restarting the app.");
session = null;
return;
}
ตอนนี้เซสชัน AR ได้รับการกำหนดค่าอย่างเหมาะสมแล้ว และแอปก็จะใช้ฟีเจอร์ที่อิงตามความลึกได้
เรียกใช้ Depth API
ถัดไป ให้เรียก Depth API เพื่อเรียกข้อมูลรูปภาพความลึกของแต่ละเฟรม สรุปข้อมูลความลึกไว้ในคลาสใหม่โดยการสร้างไฟล์ใหม่ คลิกขวาที่โฟลเดอร์ rawdepth แล้วเลือก New > Java Class การดำเนินการนี้จะสร้างไฟล์เปล่า เพิ่มข้อมูลต่อไปนี้ในชั้นเรียนนี้
src/main/java/com/google/ar/core/codelab/rawdepth/DepthData.java
package com.google.ar.core.codelab.rawdepth;
import android.media.Image;
import android.opengl.Matrix;
import com.google.ar.core.Anchor;
import com.google.ar.core.CameraIntrinsics;
import com.google.ar.core.Frame;
import com.google.ar.core.exceptions.NotYetAvailableException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.ByteOrder;
import java.nio.FloatBuffer;
import java.nio.ShortBuffer;
/**
* Convert depth data from ARCore depth images to 3D pointclouds. Points are added by calling the
* Raw Depth API, and reprojected into 3D space.
*/
public class DepthData {
public static final int FLOATS_PER_POINT = 4; // X,Y,Z,confidence.
}
คลาสนี้ใช้เพื่อแปลงรูปภาพความลึกเป็น Pointcloud Pointcloud แสดงเรขาคณิตของฉากพร้อมด้วยรายการจุดที่แต่ละจุดมีพิกัด 3 มิติ (x, y, z) และค่าความเชื่อมั่นในช่วง 0 ถึง 1
เพิ่มการเรียกใช้เพื่อป้อนข้อมูลค่าเหล่านี้โดยใช้ Raw Depth API โดยเพิ่มเมธอด create() ที่ด้านล่างของคลาส วิธีนี้จะค้นหารูปภาพความลึกและความเชื่อมั่นล่าสุด ซึ่งจัดเก็บ Pointcloud ที่ได้ รูปภาพความลึกและความเชื่อมั่นจะมีข้อมูลที่ตรงกัน
public static FloatBuffer create(Frame frame, Anchor cameraPoseAnchor) {
try {
Image depthImage = frame.acquireRawDepthImage16Bits();
Image confidenceImage = frame.acquireRawDepthConfidenceImage();
// Retrieve the intrinsic camera parameters corresponding to the depth image to
// transform 2D depth pixels into 3D points. See more information about the depth values
// at
// https://developers.google.com/ar/develop/java/depth/overview#understand-depth-values.
final CameraIntrinsics intrinsics = frame.getCamera().getTextureIntrinsics();
float[] modelMatrix = new float[16];
cameraPoseAnchor.getPose().toMatrix(modelMatrix, 0);
final FloatBuffer points = convertRawDepthImagesTo3dPointBuffer(
depthImage, confidenceImage, intrinsics, modelMatrix);
depthImage.close();
confidenceImage.close();
return points;
} catch (NotYetAvailableException e) {
// This normally means that depth data is not available yet.
// This is normal, so you don't have to spam the logcat with this.
}
return null;
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
โค้ดยังจัดเก็บจุดยึดของกล้องในตอนนี้ เพื่อให้สามารถเปลี่ยนข้อมูลความลึกเป็นพิกัดโลกได้โดยการเรียกใช้เมธอดช่วย convertRawDepthImagesTo3dPointBuffer() เมธอดตัวช่วยนี้จะนำแต่ละพิกเซลในรูปภาพลึกและใช้ภายในกล้องเพื่อยกเลิกการฉายภาพความลึกไปยังจุด 3 มิติที่สัมพันธ์กับกล้อง จากนั้นจะใช้จุดยึดกล้องเพื่อแปลงตำแหน่งของจุดให้เป็นพิกัดโลก แต่ละพิกเซลที่มีอยู่จะถูกแปลงเป็นจุด 3 มิติ (เป็นหน่วยเมตร) และจัดเก็บไว้ควบคู่กับความเชื่อมั่นของจุด 3 มิติ
เพิ่มเมธอด Helper ต่อไปนี้ไปยัง DepthData.java
/** Apply camera intrinsics to convert depth image into a 3D pointcloud. */
private static FloatBuffer convertRawDepthImagesTo3dPointBuffer(
Image depth, Image confidence, CameraIntrinsics cameraTextureIntrinsics, float[] modelMatrix) {
// Java uses big endian so change the endianness to ensure
// that the depth data is in the correct byte order.
final Image.Plane depthImagePlane = depth.getPlanes()[0];
ByteBuffer depthByteBufferOriginal = depthImagePlane.getBuffer();
ByteBuffer depthByteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(depthByteBufferOriginal.capacity());
depthByteBuffer.order(ByteOrder.LITTLE_ENDIAN);
while (depthByteBufferOriginal.hasRemaining()) {
depthByteBuffer.put(depthByteBufferOriginal.get());
}
depthByteBuffer.rewind();
ShortBuffer depthBuffer = depthByteBuffer.asShortBuffer();
final Image.Plane confidenceImagePlane = confidence.getPlanes()[0];
ByteBuffer confidenceBufferOriginal = confidenceImagePlane.getBuffer();
ByteBuffer confidenceBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(confidenceBufferOriginal.capacity());
confidenceBuffer.order(ByteOrder.LITTLE_ENDIAN);
while (confidenceBufferOriginal.hasRemaining()) {
confidenceBuffer.put(confidenceBufferOriginal.get());
}
confidenceBuffer.rewind();
// To transform 2D depth pixels into 3D points, retrieve the intrinsic camera parameters
// corresponding to the depth image. See more information about the depth values at
// https://developers.google.com/ar/develop/java/depth/overview#understand-depth-values.
final int[] intrinsicsDimensions = cameraTextureIntrinsics.getImageDimensions();
final int depthWidth = depth.getWidth();
final int depthHeight = depth.getHeight();
final float fx =
cameraTextureIntrinsics.getFocalLength()[0] * depthWidth / intrinsicsDimensions[0];
final float fy =
cameraTextureIntrinsics.getFocalLength()[1] * depthHeight / intrinsicsDimensions[1];
final float cx =
cameraTextureIntrinsics.getPrincipalPoint()[0] * depthWidth / intrinsicsDimensions[0];
final float cy =
cameraTextureIntrinsics.getPrincipalPoint()[1] * depthHeight / intrinsicsDimensions[1];
// Allocate the destination point buffer. If the number of depth pixels is larger than
// `maxNumberOfPointsToRender` we uniformly subsample. The raw depth image may have
// different resolutions on different devices.
final float maxNumberOfPointsToRender = 20000;
int step = (int) Math.ceil(Math.sqrt(depthWidth * depthHeight / maxNumberOfPointsToRender));
FloatBuffer points = FloatBuffer.allocate(depthWidth / step * depthHeight / step * FLOATS_PER_POINT);
float[] pointCamera = new float[4];
float[] pointWorld = new float[4];
for (int y = 0; y < depthHeight; y += step) {
for (int x = 0; x < depthWidth; x += step) {
// Depth images are tightly packed, so it's OK to not use row and pixel strides.
int depthMillimeters = depthBuffer.get(y * depthWidth + x); // Depth image pixels are in mm.
if (depthMillimeters == 0) {
// Pixels with value zero are invalid, meaning depth estimates are missing from
// this location.
continue;
}
final float depthMeters = depthMillimeters / 1000.0f; // Depth image pixels are in mm.
// Retrieve the confidence value for this pixel.
final byte confidencePixelValue =
confidenceBuffer.get(
y * confidenceImagePlane.getRowStride()
+ x * confidenceImagePlane.getPixelStride());
final float confidenceNormalized = ((float) (confidencePixelValue & 0xff)) / 255.0f;
// Unproject the depth into a 3D point in camera coordinates.
pointCamera[0] = depthMeters * (x - cx) / fx;
pointCamera[1] = depthMeters * (cy - y) / fy;
pointCamera[2] = -depthMeters;
pointCamera[3] = 1;
// Apply model matrix to transform point into world coordinates.
Matrix.multiplyMV(pointWorld, 0, modelMatrix, 0, pointCamera, 0);
points.put(pointWorld[0]); // X.
points.put(pointWorld[1]); // Y.
points.put(pointWorld[2]); // Z.
points.put(confidenceNormalized);
}
}
points.rewind();
return points;
}
รับข้อมูลความลึกไฟล์ดิบล่าสุดของแต่ละเฟรม
แก้ไขแอปเพื่อดึงข้อมูลความลึกและปรับแนวให้ตรงกับพิกัดโลกสำหรับท่าทางแต่ละท่า
ใน RawDepthCodelabActivity.java ให้ค้นหาบรรทัดที่มีอยู่ในเมธอด onDrawFrame() ดังต่อไปนี้
Frame frame = session.update();
Camera camera = frame.getCamera();
// If the frame is ready, render the camera preview image to the GL surface.
backgroundRenderer.draw(frame);
เพิ่มบรรทัดต่อไปนี้ที่ด้านล่าง
// Retrieve the depth data for this frame.
FloatBuffer points = DepthData.create(frame, session.createAnchor(camera.getPose()));
if (points == null) {
return;
}
if (messageSnackbarHelper.isShowing() && points != null) {
messageSnackbarHelper.hide(this);
}
6. แสดงข้อมูลความลึก (ส่วนที่ 2)
เมื่อคุณมี Pointcloud สำหรับดูระดับความลึกให้เล่นแล้ว ก็ถึงเวลาดูว่าข้อมูลมีลักษณะอย่างไรบนหน้าจอ
เพิ่มโหมดแสดงภาพเพื่อแสดงภาพจุดความลึก
เพิ่มโหมดแสดงภาพเพื่อแสดงภาพจุดความลึก
ขั้นแรก ให้เพิ่มคลาสใหม่เพื่อให้มีตรรกะการแสดงผล คลาสนี้จะดำเนินการ OpenGL เพื่อเริ่มต้นตัวปรับแสงเงาเพื่อแสดงภาพ Pointcloud ของความลึก
| เพิ่มคลาส DepthRenderer
|
สร้างชั้นเรียนนี้ด้วยรหัสต่อไปนี้
src/main/java/com/google/ar/core/codelab/common/rendering/DepthRenderer.java
package com.google.ar.core.codelab.common.rendering;
import android.content.Context;
import android.opengl.GLES20;
import android.opengl.Matrix;
import com.google.ar.core.Camera;
import com.google.ar.core.codelab.rawdepth.DepthData;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.FloatBuffer;
public class DepthRenderer {
private static final String TAG = DepthRenderer.class.getSimpleName();
// Shader names.
private static final String VERTEX_SHADER_NAME = "shaders/depth_point_cloud.vert";
private static final String FRAGMENT_SHADER_NAME = "shaders/depth_point_cloud.frag";
public static final int BYTES_PER_FLOAT = Float.SIZE / 8;
private static final int BYTES_PER_POINT = BYTES_PER_FLOAT * DepthData.FLOATS_PER_POINT;
private static final int INITIAL_BUFFER_POINTS = 1000;
private int arrayBuffer;
private int arrayBufferSize;
private int programName;
private int positionAttribute;
private int modelViewProjectionUniform;
private int pointSizeUniform;
private int numPoints = 0;
public DepthRenderer() {}
public void createOnGlThread(Context context) throws IOException {
ShaderUtil.checkGLError(TAG, "Bind");
int[] buffers = new int[1];
GLES20.glGenBuffers(1, buffers, 0);
arrayBuffer = buffers[0];
GLES20.glBindBuffer(GLES20.GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, arrayBuffer);
arrayBufferSize = INITIAL_BUFFER_POINTS * BYTES_PER_POINT;
GLES20.glBufferData(GLES20.GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, arrayBufferSize, null, GLES20.GL_DYNAMIC_DRAW);
GLES20.glBindBuffer(GLES20.GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, 0);
ShaderUtil.checkGLError(TAG, "Create");
int vertexShader =
ShaderUtil.loadGLShader(TAG, context, GLES20.GL_VERTEX_SHADER, VERTEX_SHADER_NAME);
int fragmentShader =
ShaderUtil.loadGLShader(TAG, context, GLES20.GL_FRAGMENT_SHADER, FRAGMENT_SHADER_NAME);
programName = GLES20.glCreateProgram();
GLES20.glAttachShader(programName, vertexShader);
GLES20.glAttachShader(programName, fragmentShader);
GLES20.glLinkProgram(programName);
GLES20.glUseProgram(programName);
ShaderUtil.checkGLError(TAG, "Program");
positionAttribute = GLES20.glGetAttribLocation(programName, "a_Position");
modelViewProjectionUniform = GLES20.glGetUniformLocation(programName, "u_ModelViewProjection");
// Sets the point size, in pixels.
pointSizeUniform = GLES20.glGetUniformLocation(programName, "u_PointSize");
ShaderUtil.checkGLError(TAG, "Init complete");
}
}
แสดงผลข้อมูลความลึก
ถัดไป ให้ระบุแหล่งที่มาของตัวปรับแสงเงา เพิ่มเมธอด update() ต่อไปนี้ที่ด้านล่างของคลาส DepthRenderer วิธีนี้ใช้ข้อมูลความลึกล่าสุดเป็นอินพุตและคัดลอกข้อมูล Pointcloud ไปยัง GPU
/**
* Update the OpenGL buffer contents to the provided point. Repeated calls with the same point
* cloud will be ignored.
*/
public void update(FloatBuffer points) {
ShaderUtil.checkGLError(TAG, "Update");
GLES20.glBindBuffer(GLES20.GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, arrayBuffer);
// If the array buffer is not large enough to fit the new point cloud, resize it.
points.rewind();
numPoints = points.remaining() / DepthData.FLOATS_PER_POINT;
if (numPoints * BYTES_PER_POINT > arrayBufferSize) {
while (numPoints * BYTES_PER_POINT > arrayBufferSize) {
arrayBufferSize *= 2;
}
GLES20.glBufferData(GLES20.GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, arrayBufferSize, null, GLES20.GL_DYNAMIC_DRAW);
}
GLES20.glBufferSubData(
GLES20.GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, 0, numPoints * BYTES_PER_POINT, points);
GLES20.glBindBuffer(GLES20.GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, 0);
ShaderUtil.checkGLError(TAG, "Update complete");
}
วาดข้อมูลล่าสุดลงในหน้าจอโดยเพิ่มเมธอด draw() ไว้ที่ด้านล่างของชั้นเรียน DepthRenderer วิธีนี้จะใช้ข้อมูล Pointcloud 3 มิติและฉายกลับไปยังมุมมองกล้องเพื่อให้แสดงผลบนหน้าจอได้
/** Render the point cloud. The ARCore point cloud is given in world space. */
public void draw(Camera camera) {
float[] projectionMatrix = new float[16];
camera.getProjectionMatrix(projectionMatrix, 0, 0.1f, 100.0f);
float[] viewMatrix = new float[16];
camera.getViewMatrix(viewMatrix, 0);
float[] viewProjection = new float[16];
Matrix.multiplyMM(viewProjection, 0, projectionMatrix, 0, viewMatrix, 0);
ShaderUtil.checkGLError(TAG, "Draw");
GLES20.glUseProgram(programName);
GLES20.glEnableVertexAttribArray(positionAttribute);
GLES20.glBindBuffer(GLES20.GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, arrayBuffer);
GLES20.glVertexAttribPointer(positionAttribute, 4, GLES20.GL_FLOAT, false, BYTES_PER_POINT, 0);
GLES20.glUniformMatrix4fv(modelViewProjectionUniform, 1, false, viewProjection, 0);
// Set point size to 5 pixels.
GLES20.glUniform1f(pointSizeUniform, 5.0f);
GLES20.glDrawArrays(GLES20.GL_POINTS, 0, numPoints);
GLES20.glDisableVertexAttribArray(positionAttribute);
GLES20.glBindBuffer(GLES20.GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, 0);
ShaderUtil.checkGLError(TAG, "Draw complete");
}
คุณกำหนดขนาดจุดเป็นขนาดต่างๆ ในหน่วยพิกเซลได้โดยใช้ตัวแปร pointSizeUniform มีการตั้งค่า pointSizeUniform เป็น 5 พิกเซลในแอปตัวอย่าง
เพิ่มตัวปรับแสงเงาใหม่
คุณดูความลึกและแสดงข้อมูลความลึกในแอปได้หลายวิธี ตรงนี้ให้เพิ่มตัวปรับแสงเงา 2-3 ตัว และสร้างภาพการแมปสีแบบง่ายๆ
เพิ่มตัวปรับแสงเงา .vert และ .frag ใหม่ในไดเรกทอรี src/main/assets/shaders/
| การเพิ่มตัวปรับแสงเงา .vert ใหม่ใน Android Studio ให้ทำดังนี้
|
เพิ่มโค้ดต่อไปนี้ในไฟล์ .vert ใหม่
src/main/assets/shaders/depth_point_cloud.vert
uniform mat4 u_ModelViewProjection;
uniform float u_PointSize;
attribute vec4 a_Position;
varying vec4 v_Color;
// Return an interpolated color in a 6 degree polynomial interpolation.
vec3 GetPolynomialColor(in float x,
in vec4 kRedVec4, in vec4 kGreenVec4, in vec4 kBlueVec4,
in vec2 kRedVec2, in vec2 kGreenVec2, in vec2 kBlueVec2) {
// Moves the color space a little bit to avoid pure red.
// Removes this line for more contrast.
x = clamp(x * 0.9 + 0.03, 0.0, 1.0);
vec4 v4 = vec4(1.0, x, x * x, x * x * x);
vec2 v2 = v4.zw * v4.z;
return vec3(
dot(v4, kRedVec4) + dot(v2, kRedVec2),
dot(v4, kGreenVec4) + dot(v2, kGreenVec2),
dot(v4, kBlueVec4) + dot(v2, kBlueVec2)
);
}
// Return a smooth Percept colormap based upon the Turbo colormap.
vec3 PerceptColormap(in float x) {
const vec4 kRedVec4 = vec4(0.55305649, 3.00913185, -5.46192616, -11.11819092);
const vec4 kGreenVec4 = vec4(0.16207513, 0.17712472, 15.24091500, -36.50657960);
const vec4 kBlueVec4 = vec4(-0.05195877, 5.18000081, -30.94853351, 81.96403246);
const vec2 kRedVec2 = vec2(27.81927491, -14.87899417);
const vec2 kGreenVec2 = vec2(25.95549545, -5.02738237);
const vec2 kBlueVec2 = vec2(-86.53476570, 30.23299484);
const float kInvalidDepthThreshold = 0.01;
return step(kInvalidDepthThreshold, x) *
GetPolynomialColor(x, kRedVec4, kGreenVec4, kBlueVec4,
kRedVec2, kGreenVec2, kBlueVec2);
}
void main() {
// Color the pointcloud by height.
float kMinHeightMeters = -2.0f;
float kMaxHeightMeters = 2.0f;
float normalizedHeight = clamp((a_Position.y - kMinHeightMeters) / (kMaxHeightMeters - kMinHeightMeters), 0.0, 1.0);
v_Color = vec4(PerceptColormap(normalizedHeight), 1.0);
gl_Position = u_ModelViewProjection * vec4(a_Position.xyz, 1.0);
gl_PointSize = u_PointSize;
}
ตัวปรับแสงเงานี้ใช้แผนที่สี Turbo สำหรับการแสดงภาพที่ดีขึ้น โดยมีขั้นตอนดังนี้
- ดึงข้อมูลระดับความสูงของแต่ละจุด (แกน y ในพิกัดโลก)
- คำนวณสีที่เชื่อมโยงกับระดับความสูงนั้น (แดง=ต่ำ, น้ำเงิน=สูง)
- คำนวณตำแหน่งหน้าจอของแต่ละจุด
- ตั้งค่าขนาด (เป็นพิกเซล) สำหรับแต่ละจุด ตามที่ระบุไว้ในเมธอด
DepthRenderer.update()
สร้างตัวปรับแสงเงา Fragment ในไดเรกทอรีเดียวกันและตั้งชื่อเป็น depth_point_cloud.frag โดยทำขั้นตอนเดียวกันซ้ำในส่วนนี้
จากนั้นเพิ่มโค้ดต่อไปนี้ลงในไฟล์ใหม่นี้เพื่อแสดงจุดแต่ละจุดเป็นจุดยอดมุมเดี่ยวที่มีสีเดียวกันตามที่กำหนดไว้ในตัวปรับแสงเงา Vertex
src/main/assets/shaders/depth_point_cloud.frag
precision mediump float;
varying vec4 v_Color;
void main() {
gl_FragColor = v_Color;
}
หากต้องการใช้การแสดงผลนี้ ให้เพิ่มการโทรไปยังคลาส DepthRenderer ใน RawDepthCodelabActivity
src/main/java/com/google/ar/core/codelab/common/rendering/RawDepthCodelabActivity.java
import com.google.ar.core.codelab.common.rendering.DepthRenderer;
เพิ่มสมาชิกส่วนตัวถัดจาก backgroundRenderer ที่ด้านบนของชั้นเรียน
private final DepthRenderer depthRenderer = new DepthRenderer();
depthRenderer ต้องเริ่มต้นภายใน RawDepthCodelabActivity.onSurfaceCreated() เช่นเดียวกับ backgroundRenderer ที่มีอยู่
depthRenderer.createOnGlThread(/*context=*/ this);
เพิ่มโค้ดต่อไปนี้ไว้ที่ส่วนท้ายของบล็อกลองใช้ภายใน onDrawFrame เพื่อแสดงความลึกล่าสุดสำหรับเฟรมปัจจุบัน
// Visualize depth points.
depthRenderer.update(points);
depthRenderer.draw(camera);
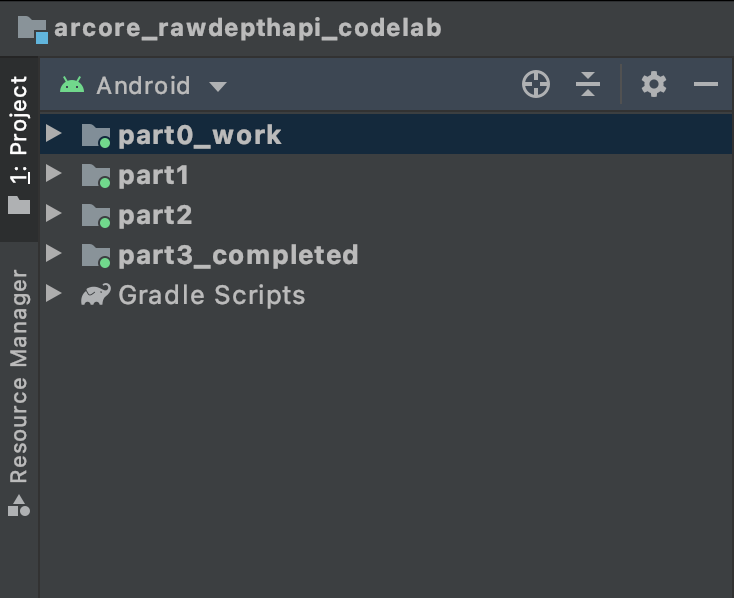
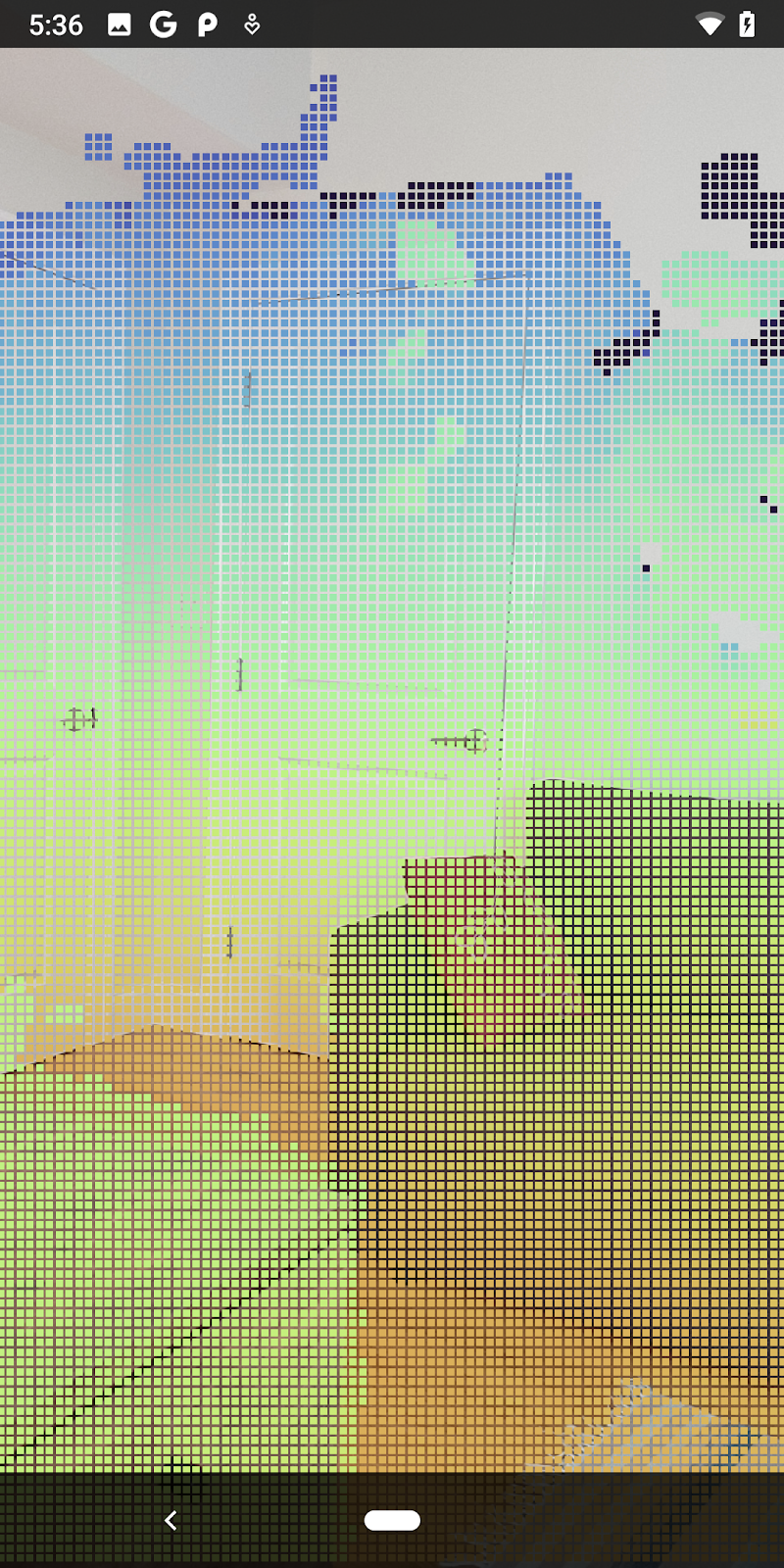
การเปลี่ยนแปลงเหล่านี้ทำให้แอปควรจะสร้างได้สำเร็จและแสดง Pointcloud ของความลึก
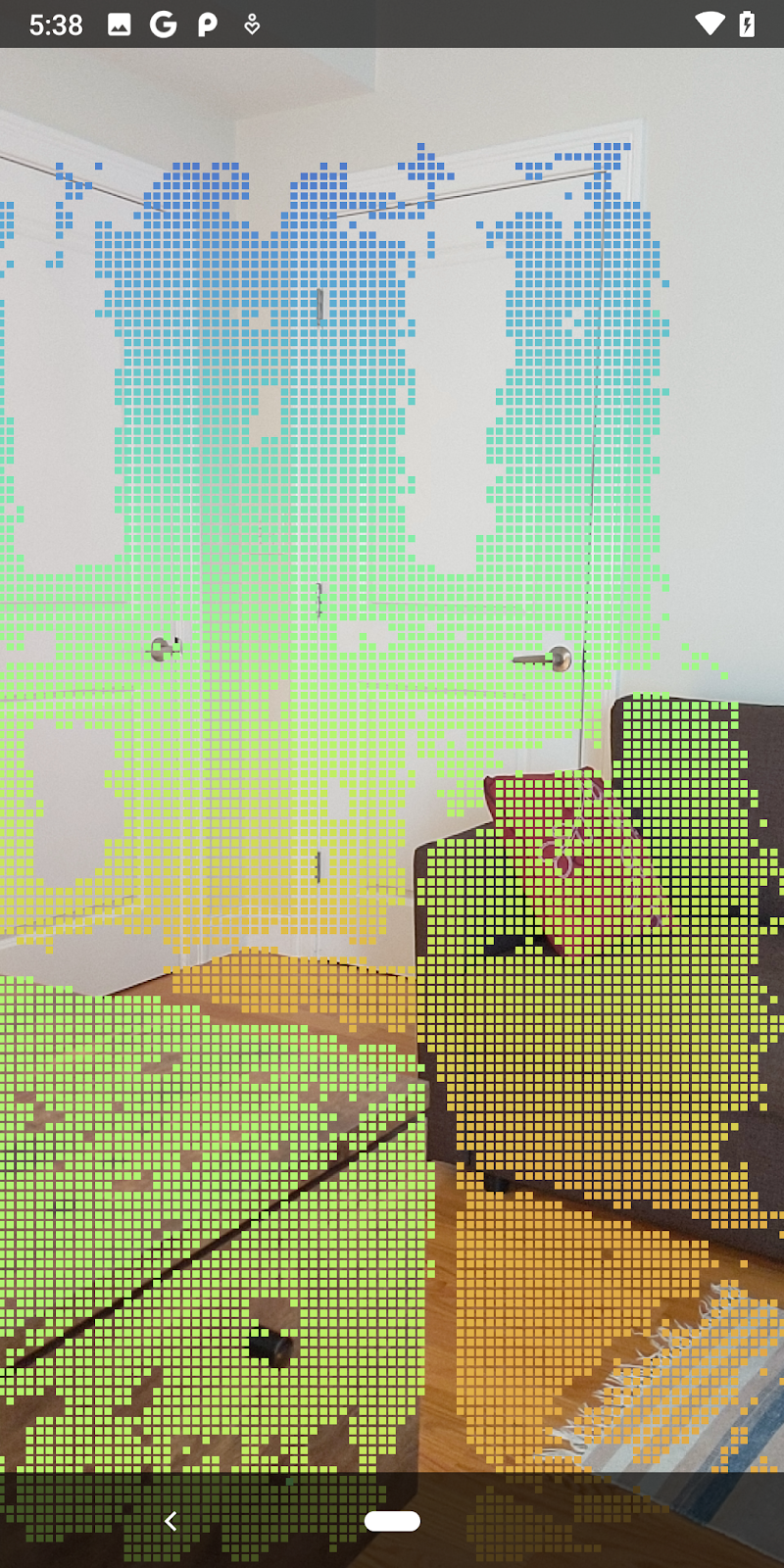
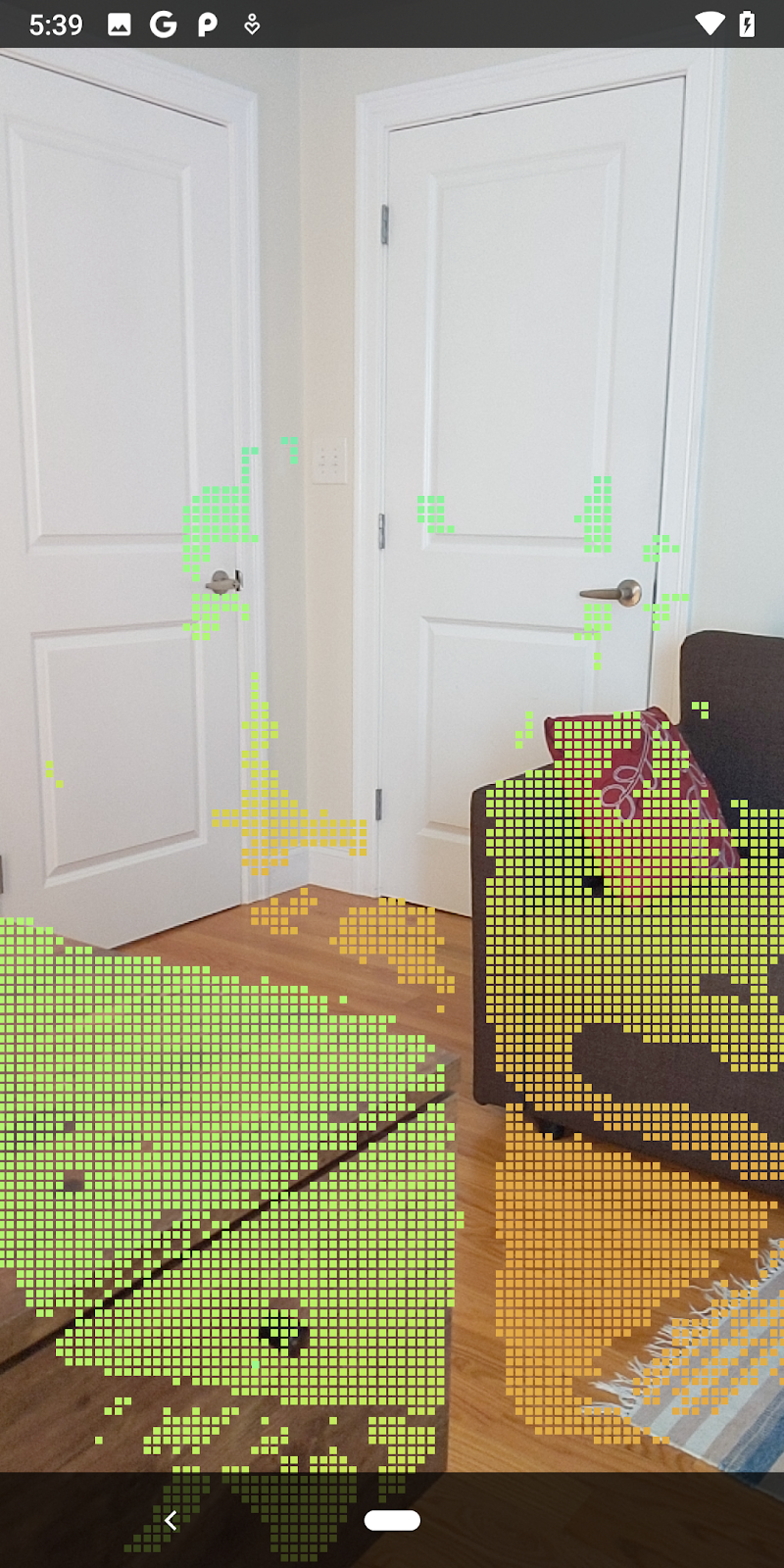
| ตัวอย่างการแสดงภาพ Pointcloud ของความลึกดิบ
|
7. วิเคราะห์เมฆแบบจุด 3 มิติ (ส่วนที่ 3)
คุณจะวิเคราะห์ข้อมูลความลึกได้เมื่อยืนยันได้ว่าข้อมูลดังกล่าวอยู่ในเซสชัน AR เครื่องมือสำคัญในการวิเคราะห์ความลึกคือค่าความเชื่อมั่นของแต่ละพิกเซล ใช้ค่าความเชื่อมั่นเพื่อวิเคราะห์เมฆแบบจุด 3 มิติ
เอาพิกเซลที่มีความเชื่อมั่นต่ำให้เป็นโมฆะ
คุณดึงข้อมูลค่าความเชื่อมั่นสำหรับพิกเซลความลึกแต่ละพิกเซลและบันทึกไว้ข้างๆ แต่ละจุดภายใน DepthData แล้ว แต่คุณยังไม่ได้ใช้พิกเซลดังกล่าว
ค่าของ confidenceNormalized อยู่ในช่วงตั้งแต่ 0 ถึง 1 โดย 0 หมายถึงความเชื่อมั่นต่ำ และ 1 หมายถึงความเชื่อมั่นเต็มที่ แก้ไขเมธอด convertRawDepthImagesTo3dPointBuffer() ในคลาส DepthData เพื่อหลีกเลี่ยงการบันทึกพิกเซลที่มีความเชื่อมั่นต่ำมากจนไม่มีประโยชน์
final float confidenceNormalized = ((float) (confidencePixelValue & 0xff)) / 255.0f;
// ******** New code to add ************
if (confidenceNormalized < 0.3) {
// Ignores "low-confidence" pixels.
continue;
}
// ******** End of new code to add *********
ลองใช้เกณฑ์ต่างๆ สำหรับระดับความเชื่อมั่นเพื่อดูจำนวนจุดความลึกที่เก็บไว้ในแต่ละระดับ
|
|
|
|
|
ความมั่นใจ >= 0.1 | ความมั่นใจ >= 0.3 | ความมั่นใจ >= 0.5 | ความมั่นใจ >= 0.7 | ความมั่นใจ >= 0.9 |
กรองพิกเซลตามระยะทาง
นอกจากนี้ยังกรองพิกเซลความลึกตามระยะทางได้ด้วย ขั้นตอนถัดไปเหล่านี้จะจัดการกับเรขาคณิตที่อยู่ใกล้กับกล้อง เพื่อการเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพการทำงาน คุณสามารถละเว้นจุดที่อยู่ไกลเกินไปได้
อัปเดตรหัสการตรวจสอบความเชื่อมั่นที่คุณเพิ่งเพิ่มด้วยข้อมูลต่อไปนี้
src/main/java/com/google/ar/core/codelab/rawdepth/DepthData.java
if (confidenceNormalized < 0.3 || depthMeters > 1.5) {
// Ignore "low-confidence" pixels or depth that is too far away.
continue;
}
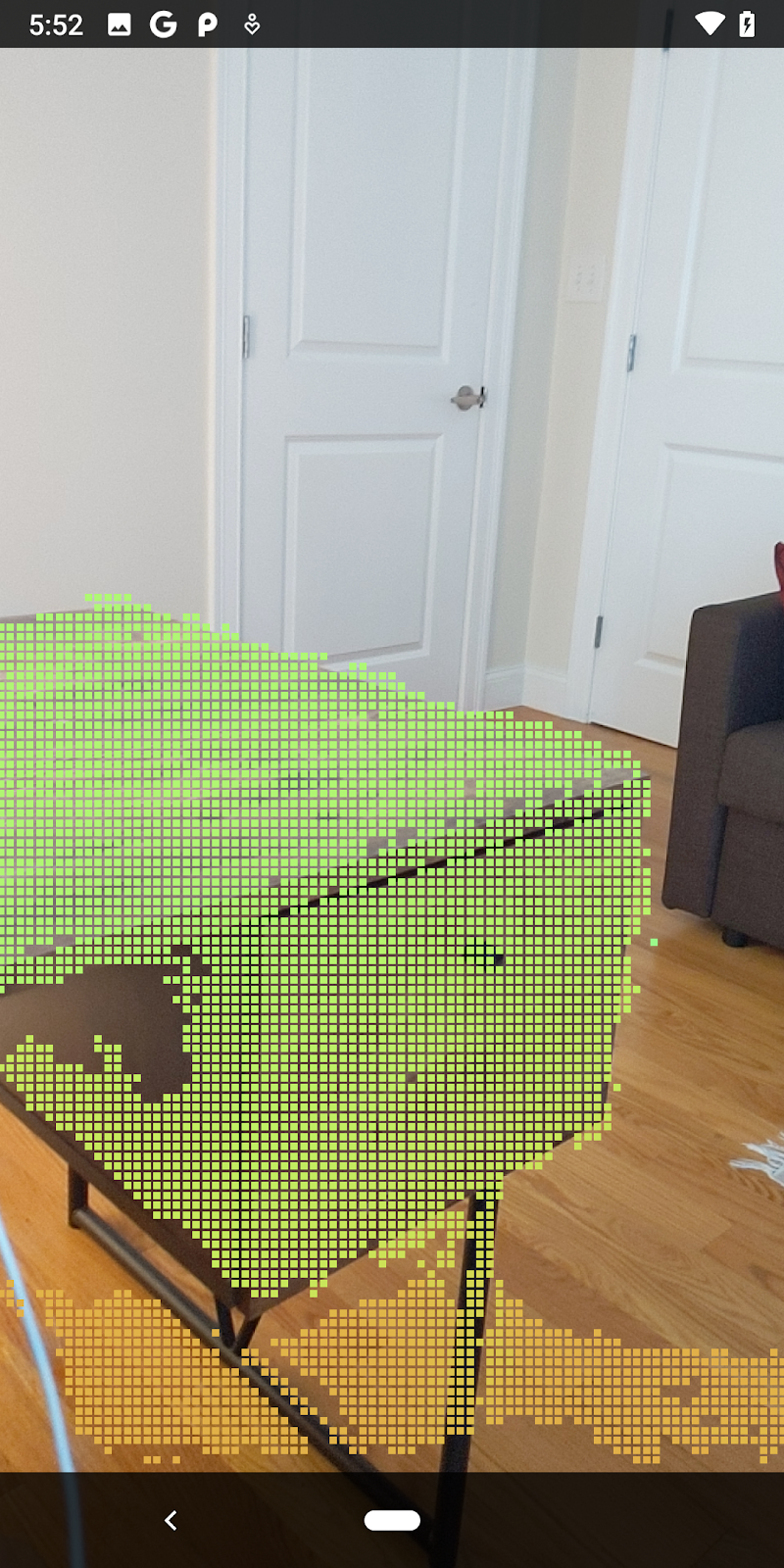
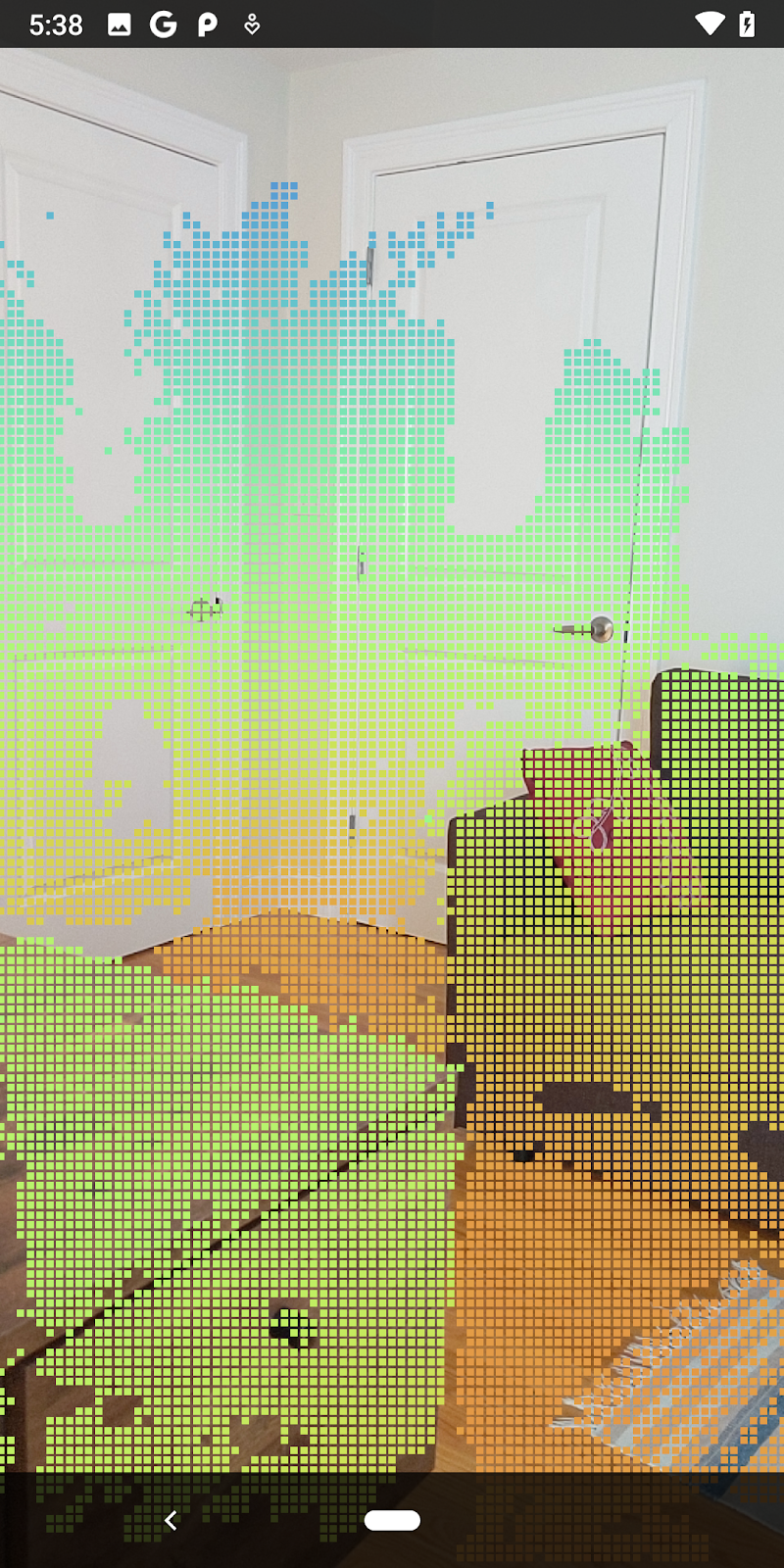
ตอนนี้คุณจะเห็นเฉพาะจุดความเชื่อมั่นสูงและช่วงปิด
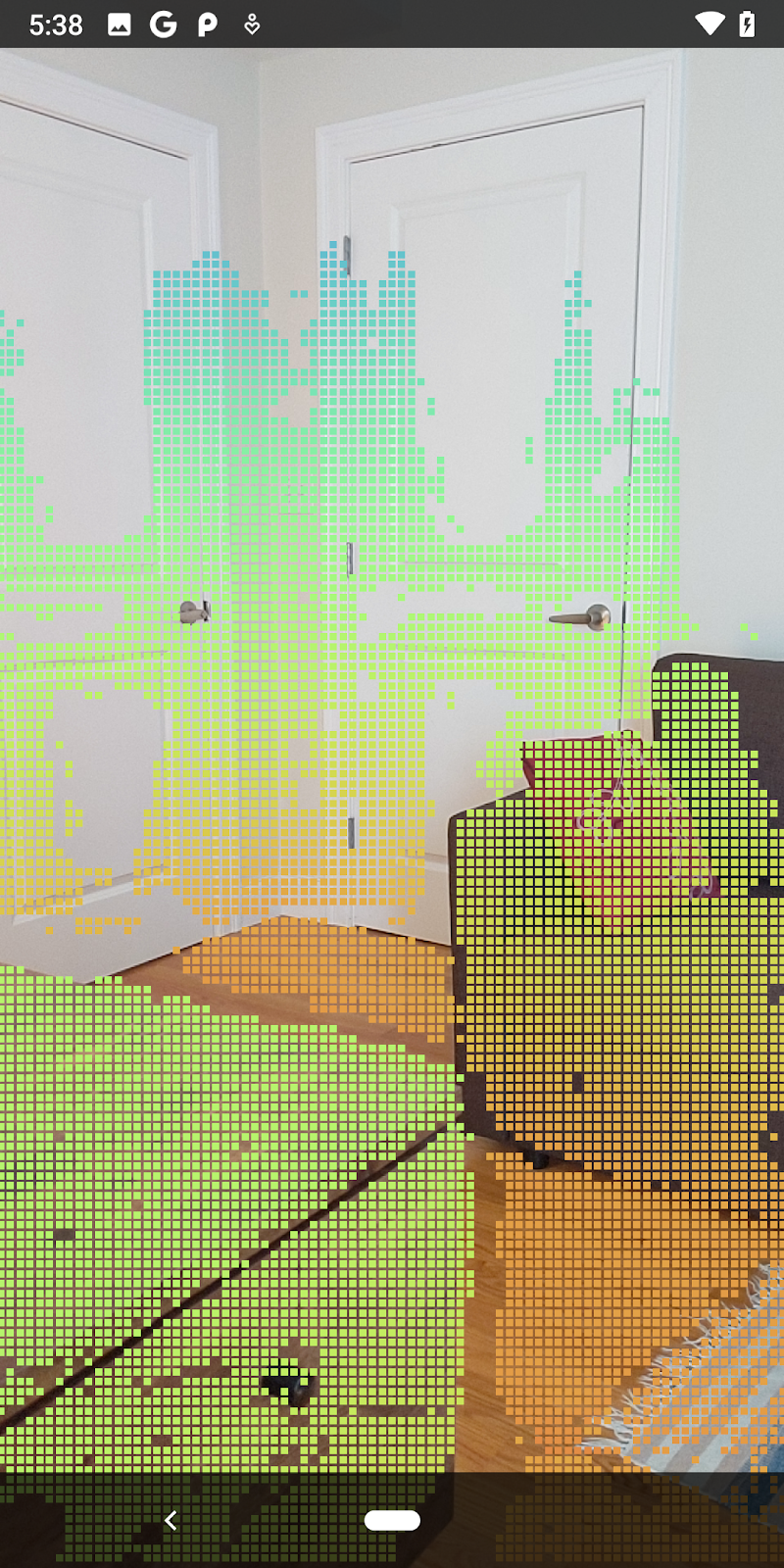
| การกรองระยะทางจำกัด Pointcloud ให้อยู่ห่างจากกล้องไม่เกิน 1.5 เมตร |
เปรียบเทียบจุด 3 มิติกับเครื่องบิน
คุณสามารถเปรียบเทียบจุด 3 มิติของเรขาคณิตกับระนาบต่างๆ และใช้จุดเหล่านั้นเพื่อกรองกัน เช่น นำจุดที่อยู่ใกล้กับระนาบ AR ที่สังเกตการณ์ออก
ขั้นตอนนี้จะเหลือเฉพาะ "ไม่ใช่ระนาบ" จุดที่มีแนวโน้มว่าจะแสดงพื้นผิวบนวัตถุในสภาพแวดล้อม เพิ่มเมธอด filterUsingPlanes() ที่ด้านล่างของชั้นเรียน DepthData เมธอดนี้จะทำซ้ำผ่านจุดที่มีอยู่ ตรวจสอบแต่ละจุดเทียบกับระนาบแต่ละระนาบ และทำให้จุดที่อยู่ใกล้กับระนาบ AR กลายเป็นโมฆะ ทำให้เหลือพื้นที่ที่ไม่ใช่ระนาบซึ่งไฮไลต์วัตถุในฉากนั้น
src/main/java/com/google/ar/core/codelab/rawdepth/DepthData.java
public static void filterUsingPlanes(FloatBuffer points, Collection<Plane> allPlanes) {
float[] planeNormal = new float[3];
// Allocate the output buffer.
int numPoints = points.remaining() / DepthData.FLOATS_PER_POINT;
// Check each plane against each point.
for (Plane plane : allPlanes) {
if (plane.getTrackingState() != TrackingState.TRACKING || plane.getSubsumedBy() != null) {
continue;
}
// Compute the normal vector of the plane.
Pose planePose = plane.getCenterPose();
planePose.getTransformedAxis(1, 1.0f, planeNormal, 0);
// Filter points that are too close to the plane.
for (int index = 0; index < numPoints; ++index) {
// Retrieves the next point.
final float x = points.get(FLOATS_PER_POINT * index);
final float y = points.get(FLOATS_PER_POINT * index + 1);
final float z = points.get(FLOATS_PER_POINT * index + 2);
// Transform point to be in world coordinates, to match plane info.
float distance = (x - planePose.tx()) * planeNormal[0]
+ (y - planePose.ty()) * planeNormal[1]
+ (z - planePose.tz()) * planeNormal[2];
// Controls the size of objects detected.
// Smaller values mean smaller objects will be kept.
// Larger values will only allow detection of larger objects, but also helps reduce noise.
if (Math.abs(distance) > 0.03) {
continue; // Keep this point, since it's far enough away from the plane.
}
// Invalidate points that are too close to planar surfaces.
points.put(FLOATS_PER_POINT * index, 0);
points.put(FLOATS_PER_POINT * index + 1, 0);
points.put(FLOATS_PER_POINT * index + 2, 0);
points.put(FLOATS_PER_POINT * index + 3, 0);
}
}
}
คุณเพิ่มเมธอดนี้ลงใน RawDepthCodelabActivity ในเมธอด onDrawFrame ได้ ดังนี้
// ********** New code to add ************
// Filter the depth data.
DepthData.filterUsingPlanes(points, session.getAllTrackables(Plane.class));
// ********** End new code to add *******
// Visualize depth points.
depthRenderer.update(points);
depthRenderer.draw(camera);
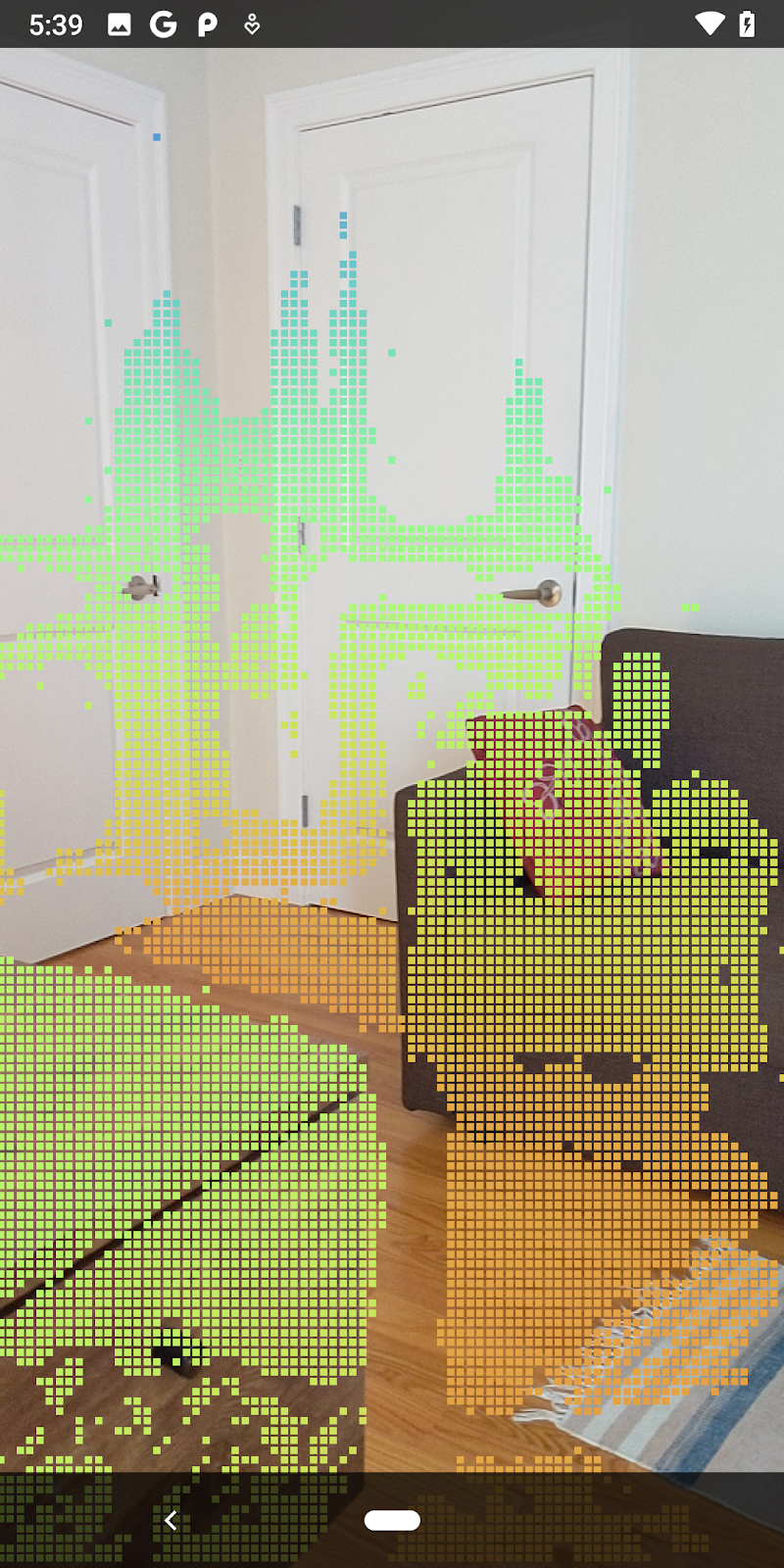
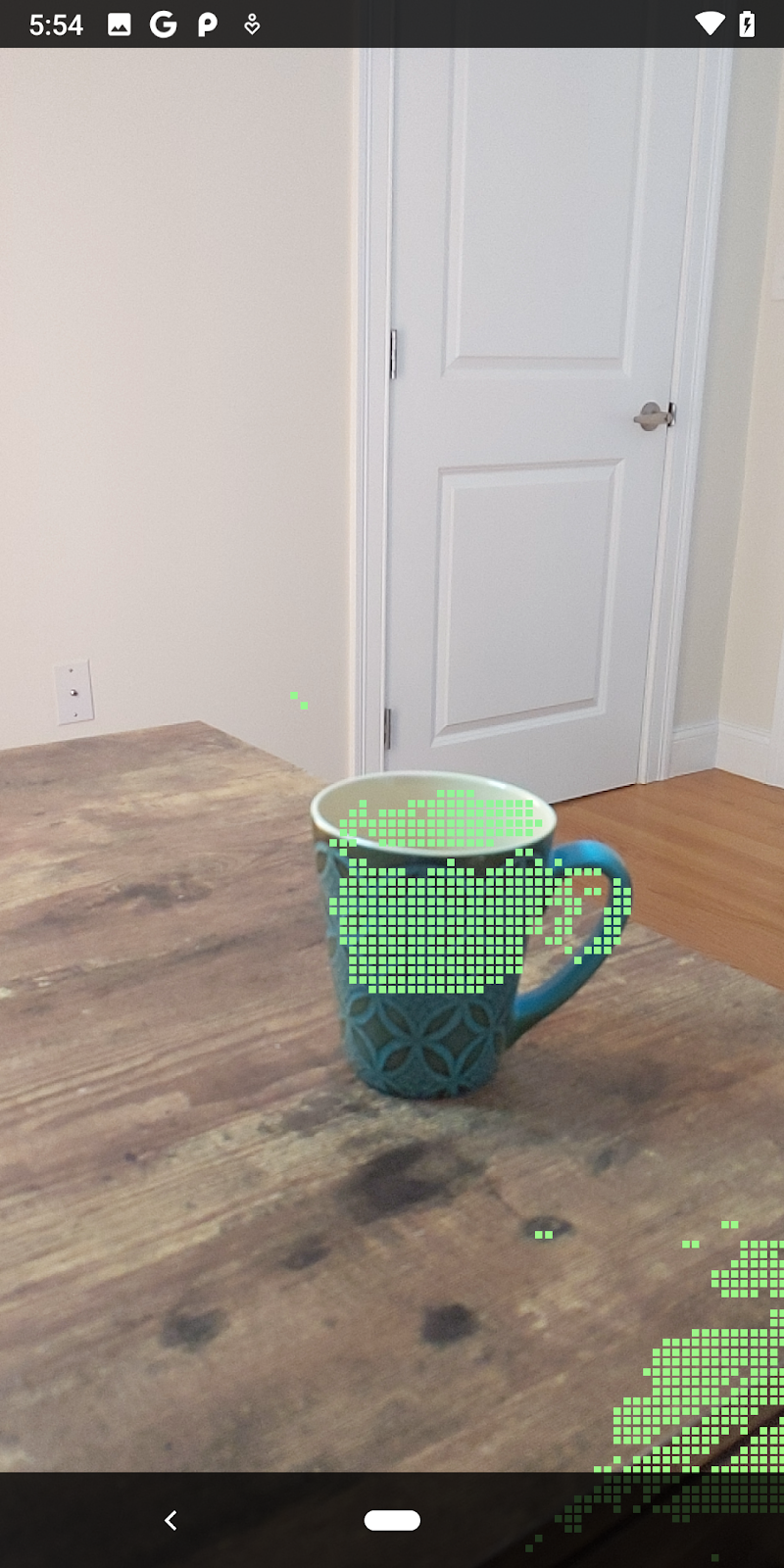
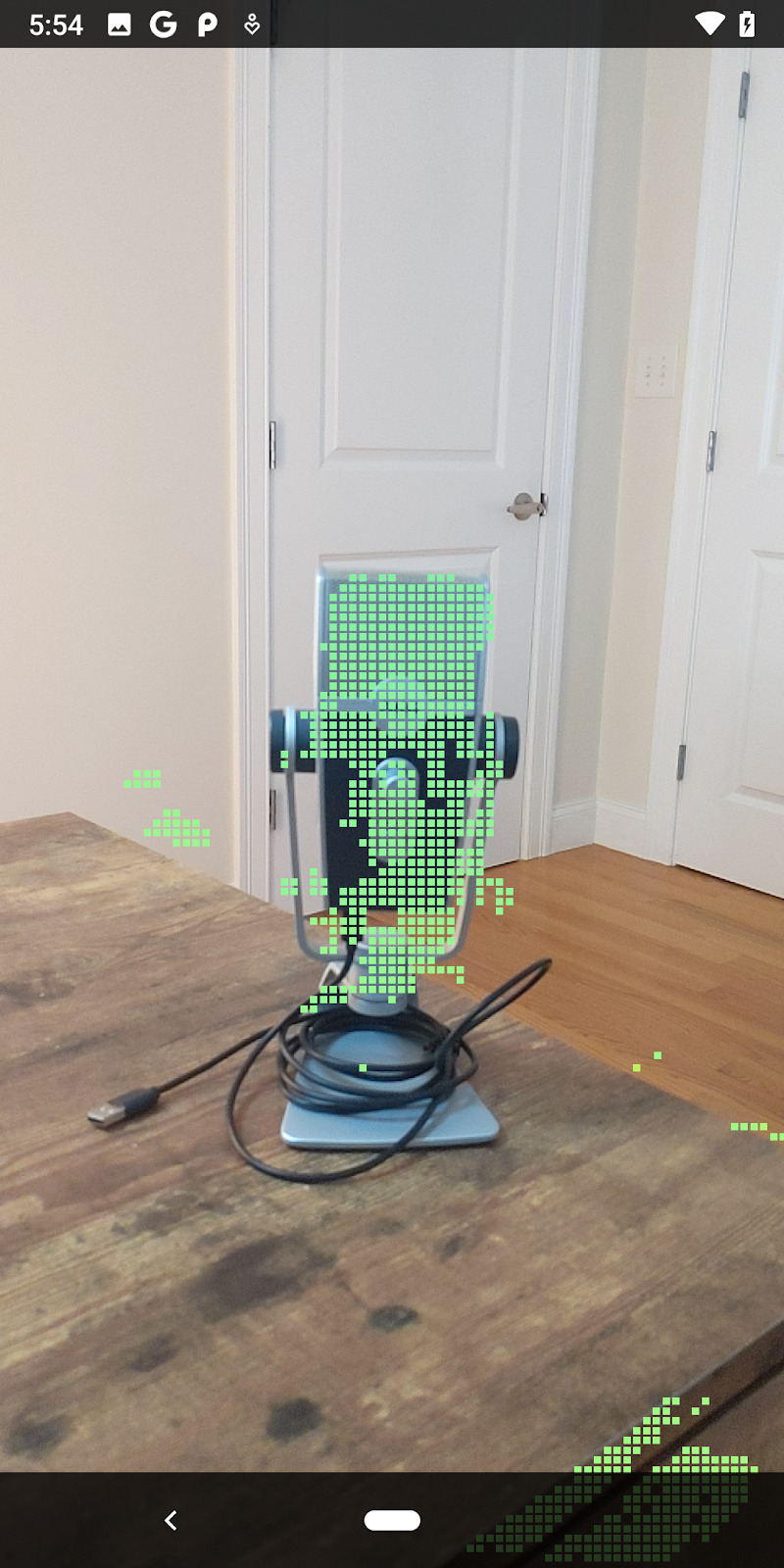
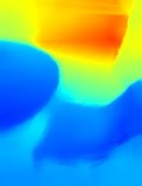
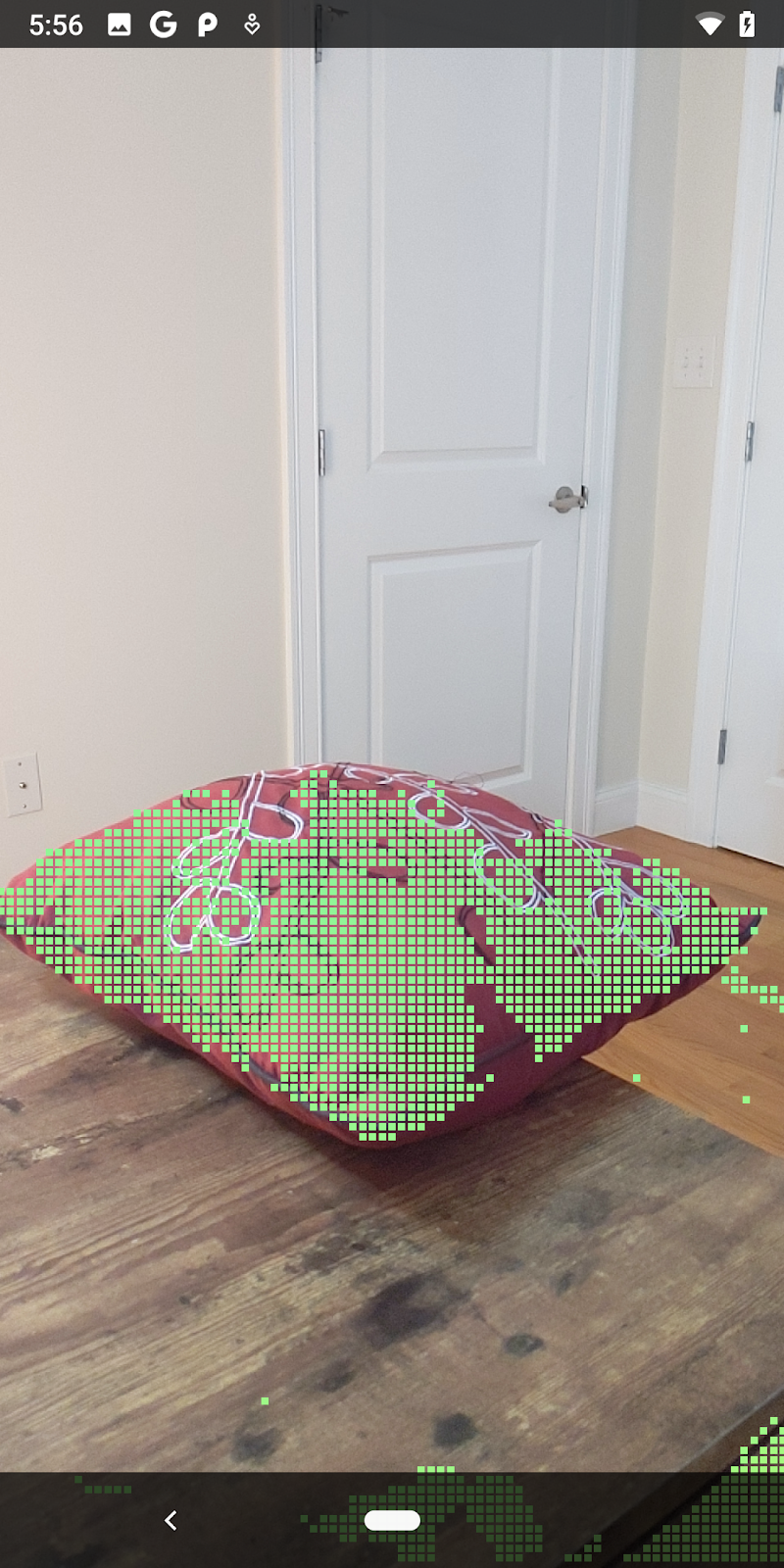
ตอนนี้การเรียกใช้ Codelab จะทำให้ระบบแสดงผลจุดบางส่วน จุดเหล่านี้แสดงถึงวัตถุในฉาก โดยไม่สนใจพื้นผิวราบที่วัตถุปรากฏอยู่ คุณใช้ข้อมูลเหล่านี้เพื่อประมาณขนาดและตำแหน่งของวัตถุได้โดยจัดกลุ่มจุดไว้ด้วยกัน
|
|
|
|
ถ้วยชา | ไมโครโฟน | หูฟัง | หมอน |
จุดคลัสเตอร์
Codelab นี้มีอัลกอริทึมคลัสเตอร์ Pointcloud ที่ง่ายมาก อัปเดต Codelab เพื่อจัดกลุ่ม Pointcloud ที่ดึงมาลงในคลัสเตอร์ที่กำหนดโดยกรอบล้อมรอบแบบแกน
src/main/java/com/google/ar/core/codelab/rawdepth/RawDepthCodelabActivity.java
import com.google.ar.core.codelab.common.helpers.AABB;
import com.google.ar.core.codelab.common.helpers.PointClusteringHelper;
import com.google.ar.core.codelab.common.rendering.BoxRenderer;
import java.util.List;
เพิ่ม BoxRenderer ลงในคลาสนี้ที่ด้านบนของไฟล์ พร้อมด้วยโหมดแสดงภาพอื่นๆ
private final BoxRenderer boxRenderer = new BoxRenderer();
ภายในเมธอด onSurfaceCreated() ให้เพิ่มค่าต่อไปนี้ควบคู่ไปกับโหมดแสดงภาพอื่นๆ
boxRenderer.createOnGlThread(/*context=*/this);
สุดท้าย ให้เพิ่มบรรทัดต่อไปนี้ไปยัง onDrawFrame() ภายใน RawDepthCodelabActivity เพื่อจัดกลุ่ม Pointcloud ที่ดึงมาไว้เป็นคลัสเตอร์และแสดงผลผลลัพธ์เป็นกรอบล้อมรอบแบบแกน
// Visualize depth points.
depthRenderer.update(points);
depthRenderer.draw(camera);
// ************ New code to add ***************
// Draw boxes around clusters of points.
PointClusteringHelper clusteringHelper = new PointClusteringHelper(points);
List<AABB> clusters = clusteringHelper.findClusters();
for (AABB aabb : clusters) {
boxRenderer.draw(aabb, camera);
}
// ************ End new code to add ***************
|
|
|
|
ถ้วยชา | ไมโครโฟน | หูฟัง | หมอน |
ตอนนี้คุณสามารถดึงข้อมูลความลึกแบบ Raw ผ่านเซสชัน ARCore, แปลงข้อมูลเชิงลึกเป็น Pointcloud 3 มิติ ตลอดจนดำเนินการกรองและการแสดงผลขั้นพื้นฐานในจุดเหล่านั้น
8. Build-Run-Test
สร้าง เรียกใช้ และทดสอบแอป
สร้างและเรียกใช้แอป
ทำตามขั้นตอนต่อไปนี้เพื่อสร้างและเรียกใช้แอป
- เสียบอุปกรณ์ที่รองรับ ARCore ผ่าน USB
- เรียกใช้โปรเจ็กต์ด้วยปุ่ม ► ในแถบเมนู
- รอให้แอปสร้างและทำให้ใช้งานได้ในอุปกรณ์ของคุณ
ครั้งแรกที่คุณพยายามทำให้แอปใช้งานได้ในอุปกรณ์ของคุณ คุณจะต้องดำเนินการต่อไปนี้
อนุญาตให้แก้ไขข้อบกพร่อง USB
ในอุปกรณ์ เลือก "ตกลง" เพื่อดำเนินการต่อ
ครั้งแรกที่เรียกใช้แอปในอุปกรณ์ ระบบจะถามว่าแอปมีสิทธิ์ใช้กล้องของอุปกรณ์หรือไม่ คุณต้องอนุญาตให้เข้าถึงเพื่อใช้ฟังก์ชัน AR ต่อไป
การทดสอบแอปของคุณ
เมื่อเรียกใช้แอป คุณทดสอบลักษณะการทำงานเบื้องต้นของแอปได้โดยถืออุปกรณ์ไว้ เคลื่อนไปรอบๆ พื้นที่ของคุณ และสแกนพื้นที่ช้าๆ พยายามรวบรวมข้อมูลอย่างน้อย 10 วินาทีและสแกนพื้นที่จากหลายๆ เส้นทางก่อนไปยังขั้นตอนถัดไป
9. ขอแสดงความยินดี
ขอแสดงความยินดี คุณได้สร้างและเรียกใช้แอป Augmented Reality แบบเจาะลึกแอปแรกโดยใช้ ARCore Raw Depth API ของ Google เรียบร้อยแล้ว เราตื่นเต้นที่จะได้เห็นสิ่งที่คุณจะสร้าง
10. การแก้ปัญหา
ตั้งค่าอุปกรณ์ Android เพื่อการพัฒนา
- เชื่อมต่ออุปกรณ์กับเครื่องพัฒนาซอฟต์แวร์ด้วยสาย USB หากคุณพัฒนาโดยใช้ Windows คุณอาจต้องติดตั้งไดรเวอร์ USB ที่เหมาะสมสำหรับอุปกรณ์ของคุณ
- ทำตามขั้นตอนต่อไปนี้เพื่อเปิดใช้การแก้ไขข้อบกพร่อง USB ในหน้าต่างตัวเลือกสำหรับนักพัฒนาแอป
- เปิดแอปการตั้งค่า
- หากอุปกรณ์ใช้ Android เวอร์ชัน 8.0 ขึ้นไป ให้เลือกระบบ
- เลื่อนไปด้านล่างแล้วเลือกเกี่ยวกับโทรศัพท์
- เลื่อนไปด้านล่างและแตะหมายเลขบิลด์ 7 ครั้ง
- กลับไปที่หน้าจอก่อนหน้า เลื่อนไปด้านล่าง แล้วแตะตัวเลือกสำหรับนักพัฒนาซอฟต์แวร์
- ในหน้าต่างตัวเลือกสำหรับนักพัฒนาซอฟต์แวร์ ให้เลื่อนลงเพื่อหาและเปิดใช้การแก้ไขข้อบกพร่อง USB
คุณสามารถดูข้อมูลโดยละเอียดเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับกระบวนการนี้ได้ที่เว็บไซต์นักพัฒนาซอฟต์แวร์ Android ของ Google
ความล้มเหลวของบิลด์ที่เกี่ยวข้องกับใบอนุญาต
หากเกิดความล้มเหลวในรุ่นที่เกี่ยวข้องกับใบอนุญาต (Failed to install the following Android SDK packages as some licences have not been accepted) คุณสามารถใช้คำสั่งต่อไปนี้เพื่อตรวจสอบและยอมรับใบอนุญาตเหล่านี้ได้
cd <path to Android SDK>
tools/bin/sdkmanager --licenses