1. 准备工作
ARCore 是用于在移动设备上构建增强现实 (AR) 应用的平台。借助不同的 API,ARCore 可以让用户的设备观察和接收关于其环境的信息,并与这些信息进行交互。
在此 Codelab 中,您将构建一个使用 ARCore Depth API 的简单 AR 应用。
前提条件
此 Codelab 的目标受众是了解基本 AR 概念的开发者。
构建内容

您将构建一个应用,该应用利用每一帧的深度图像来视觉呈现场景的几何形状,并为放置的虚拟物品呈现遮挡效果。您将完成以下具体步骤:
- 检查手机是否支持 Depth API
- 检索每一帧的深度图像
- 以多种方式可视化深度信息(参见以上动画)
- 利用深度来提升应用中的遮挡效果的真实感
- 学习如何妥善处理不支持 Depth API 的手机
所需条件
硬件要求
- 受支持的 ARCore 设备,通过 USB 线连接到开发机器。此设备还必须支持 Depth API。请参阅此受支持设备的列表。Depth API 仅适用于 Android。
- 为此设备启用 USB 调试。
软件要求
- ARCore SDK 1.18.0 或更高版本。
- 安装了 Android Studio(v3.0 或更高版本)的开发机器。
2. ARCore 和 Depth API
Depth API 使用受支持设备的 RGB 摄像头创建深度图(也称为深度图像)。您可以使用深度图提供的信息让虚拟对象准确显示在真实对象的前面或后面,从而打造逼真的沉浸式用户体验。
利用 ARCore Depth API,您可以访问与 ARCore 的会话提供的每一帧匹配的深度图像。每个像素都体现从相机到环境的距离测量值,让您的 AR 应用更加逼真。
Depth API 背后的关键功能是遮挡:数字对象相对于真实对象准确显示的能力。这样会让这些对象看起来像是与用户处于同一环境中一样。
此 Codelab 将指导您构建一款简单的 AR 应用,该应用使用深度图像呈现虚拟对象位于现实表面后的遮挡效果,并从视觉呈现检测到的空间的几何形状。
3.进行设置
设置开发机器
- 使用 USB 线将 ARCore 设备连接到计算机。确保您的设备允许执行 USB 调试。
- 打开一个终端并运行
adb devices,如下所示:
adb devices List of devices attached <DEVICE_SERIAL_NUMBER> device
<DEVICE_SERIAL_NUMBER> 是您的设备独有的字符串。请确保仅看到恰好一台设备后再继续。
下载并安装代码
- 您可以克隆代码库:
git clone https://github.com/googlecodelabs/arcore-depth
或者下载 ZIP 文件并解压缩:
- 启动 Android Studio,然后点击 Open an existing Android Studio project。
- 找到将之前下载的 ZIP 文件解压缩到的目录,然后打开
depth_codelab_io2020目录。
这是一个单 Gradle 项目,包含多个模块。如果 Android Studio 左上角的相应位置尚未显示“Project”窗格,请从下拉菜单中点击 Projects。
结果应如下所示:
| 此项目包含以下模块:
|
您将在 part0_work 模块中进行修改。我们还提供了 Codelab 的各个部分的完整解决方案。每个模块都是一个可构建的应用。
4.运行起始应用
- 点击 Run > Run…> 'part0_work'。在显示的 Select Deployment Target 对话框中,您的设备应列在 Connected Devices 下。
- 选择您的设备,然后点击 OK。Android Studio 将构建初始应用并在您的设备上运行该应用。
- 该应用将请求摄像头权限。点按 Allow 以继续。
| 如何使用该应用
|
目前,您的应用非常简单,几乎无法感知现实场景的几何形状。
例如,如果您将 Android 小人放到椅子后面,则渲染效果为小人看起来悬停在它前面,这是因为应用并不知道椅子在那里并且应该藏起 Android 小人。



为解决此问题,我们将使用 Depth API 来改善该应用中的沉浸感和真实感。
5. 检查 Depth API 是否受支持(第 1 部分)
ARCore Depth API 仅可在部分受支持的设备上运行。在使用这些深度图像将功能集成到应用中之前,您必须先确保该应用在受支持的设备上运行。
向 DepthCodelabActivity 中添加一个新的私有成员函数(充当指示当前设备是否支持深度的标志):
private boolean isDepthSupported;
我们可以在 onResume() 函数中填充该标志,该函数中创建了一个新 Session。
找到现有代码:
// Creates the ARCore session.
session = new Session(/* context= */ this);
将代码更新为以下代码:
// Creates the ARCore session.
session = new Session(/* context= */ this);
Config config = session.getConfig();
isDepthSupported = session.isDepthModeSupported(Config.DepthMode.AUTOMATIC);
if (isDepthSupported) {
config.setDepthMode(Config.DepthMode.AUTOMATIC);
} else {
config.setDepthMode(Config.DepthMode.DISABLED);
}
session.configure(config);
现在此 AR Session 已配置妥当,应用也知道是否可以使用基于深度的功能。
您还应该告知用户此 Session 是否使用深度。
向信息提示控件再添加一条消息。它会显示在屏幕底部:
// Add this line at the top of the file, with the other messages.
private static final String DEPTH_NOT_AVAILABLE_MESSAGE = "[Depth not supported on this device]";
在 onDrawFrame() 中,您可以根据需要显示此消息:
// Add this if-statement above messageSnackbarHelper.showMessage(this, messageToShow).
if (!isDepthSupported) {
messageToShow += "\n" + DEPTH_NOT_AVAILABLE_MESSAGE;
}
如果在不支持深度的设备上运行此应用,您刚刚添加的消息会显示在底部:

接下来,您将更新该应用以调用 Depth API,并检索每一帧的深度图像。
6.检索深度图像(第 2 部分)
Depth API 捕获设备环境的 3D 观察结果,并将包含这些数据的深度图像返回到您的应用。深度图像中的每个像素均代表从设备相机到现实环境的距离测量值。
现在,您将使用这些深度图像来提升应用的渲染和视觉呈现效果。第一步是检索每一帧的深度图像,并绑定该纹理,以供 GPU 使用。
首先,在项目中添加一个新类。DepthTextureHandler 负责检索给定 ARCore 帧的深度图像。
添加以下文件:
src/main/java/com/google/ar/core/codelab/depth/DepthTextureHandler.java
package com.google.ar.core.codelab.depth;
import static android.opengl.GLES20.GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE;
import static android.opengl.GLES20.GL_TEXTURE_2D;
import static android.opengl.GLES20.GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER;
import static android.opengl.GLES20.GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER;
import static android.opengl.GLES20.GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S;
import static android.opengl.GLES20.GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T;
import static android.opengl.GLES20.GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE;
import static android.opengl.GLES20.glBindTexture;
import static android.opengl.GLES20.glGenTextures;
import static android.opengl.GLES20.glTexImage2D;
import static android.opengl.GLES20.glTexParameteri;
import static android.opengl.GLES30.GL_LINEAR;
import static android.opengl.GLES30.GL_RG;
import static android.opengl.GLES30.GL_RG8;
import android.media.Image;
import com.google.ar.core.Frame;
import com.google.ar.core.exceptions.NotYetAvailableException;
/** Handle RG8 GPU texture containing a DEPTH16 depth image. */
public final class DepthTextureHandler {
private int depthTextureId = -1;
private int depthTextureWidth = -1;
private int depthTextureHeight = -1;
/**
* Creates and initializes the depth texture. This method needs to be called on a
* thread with a EGL context attached.
*/
public void createOnGlThread() {
int[] textureId = new int[1];
glGenTextures(1, textureId, 0);
depthTextureId = textureId[0];
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, depthTextureId);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
}
/**
* Updates the depth texture with the content from acquireDepthImage().
* This method needs to be called on a thread with an EGL context attached.
*/
public void update(final Frame frame) {
try {
Image depthImage = frame.acquireDepthImage();
depthTextureWidth = depthImage.getWidth();
depthTextureHeight = depthImage.getHeight();
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, depthTextureId);
glTexImage2D(
GL_TEXTURE_2D,
0,
GL_RG8,
depthTextureWidth,
depthTextureHeight,
0,
GL_RG,
GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE,
depthImage.getPlanes()[0].getBuffer());
depthImage.close();
} catch (NotYetAvailableException e) {
// This normally means that depth data is not available yet.
}
}
public int getDepthTexture() {
return depthTextureId;
}
public int getDepthWidth() {
return depthTextureWidth;
}
public int getDepthHeight() {
return depthTextureHeight;
}
}
现在,您将此类的一个实例添加到 DepthCodelabActivity,确保您能够轻松访问每一帧的深度图像的副本。
在 DepthCodelabActivity.java 中,将新类的一个实例添加为私有成员变量:
private final DepthTextureHandler depthTexture = new DepthTextureHandler();
接下来,更新 onSurfaceCreated() 方法以初始化此纹理,以供 GPU 着色器使用:
// Put this at the top of the "try" block in onSurfaceCreated().
depthTexture.createOnGlThread();
最后,您想使用最新的深度图像填充每个帧中的这种纹理,可以通过针对从 session 检索到的最新帧调用上面创建的 update() 方法完成。
由于此应用是并不强制支持深度,因此仅在使用深度时才使用此调用。
// Add this just after "frame" is created inside onDrawFrame().
if (isDepthSupported) {
depthTexture.update(frame);
}
现在,您有了随着每一帧更新的深度图像,准备好提供给着色器使用。
不过,应用的行为并没有发生任何变化。现在,您将使用深度图像来改进应用。
7. 渲染深度图像(第 3 部分)
现在,您有了深度图像,想看看效果如何。在本部分中,您将向应用添加一个按钮,以呈现每一帧的深度。
添加新的着色器
有多种方法可以查看深度图像。以下着色器提供了简单的色彩映射视觉呈现。
| 添加新的 .vert 着色器在 Android Studio 中:
|
在新文件中,添加以下代码:
src/main/assets/shaders/background_show_depth_map.vert
attribute vec4 a_Position;
attribute vec2 a_TexCoord;
varying vec2 v_TexCoord;
void main() {
v_TexCoord = a_TexCoord;
gl_Position = a_Position;
}
重复上述步骤,在同一目录添加 fragment 着色器,并将其命名为 background_show_depth_map.frag。
将以下代码添加到这个新文件中:
src/main/assets/shaders/background_show_depth_map.frag
precision mediump float;
uniform sampler2D u_Depth;
varying vec2 v_TexCoord;
const highp float kMaxDepth = 8000.0; // In millimeters.
float GetDepthMillimeters(vec4 depth_pixel_value) {
return 255.0 * (depth_pixel_value.r + depth_pixel_value.g * 256.0);
}
// Returns an interpolated color in a 6 degree polynomial interpolation.
vec3 GetPolynomialColor(in float x,
in vec4 kRedVec4, in vec4 kGreenVec4, in vec4 kBlueVec4,
in vec2 kRedVec2, in vec2 kGreenVec2, in vec2 kBlueVec2) {
// Moves the color space a little bit to avoid pure red.
// Removes this line for more contrast.
x = clamp(x * 0.9 + 0.03, 0.0, 1.0);
vec4 v4 = vec4(1.0, x, x * x, x * x * x);
vec2 v2 = v4.zw * v4.z;
return vec3(
dot(v4, kRedVec4) + dot(v2, kRedVec2),
dot(v4, kGreenVec4) + dot(v2, kGreenVec2),
dot(v4, kBlueVec4) + dot(v2, kBlueVec2)
);
}
// Returns a smooth Percept colormap based upon the Turbo colormap.
vec3 PerceptColormap(in float x) {
const vec4 kRedVec4 = vec4(0.55305649, 3.00913185, -5.46192616, -11.11819092);
const vec4 kGreenVec4 = vec4(0.16207513, 0.17712472, 15.24091500, -36.50657960);
const vec4 kBlueVec4 = vec4(-0.05195877, 5.18000081, -30.94853351, 81.96403246);
const vec2 kRedVec2 = vec2(27.81927491, -14.87899417);
const vec2 kGreenVec2 = vec2(25.95549545, -5.02738237);
const vec2 kBlueVec2 = vec2(-86.53476570, 30.23299484);
const float kInvalidDepthThreshold = 0.01;
return step(kInvalidDepthThreshold, x) *
GetPolynomialColor(x, kRedVec4, kGreenVec4, kBlueVec4,
kRedVec2, kGreenVec2, kBlueVec2);
}
void main() {
vec4 packed_depth = texture2D(u_Depth, v_TexCoord.xy);
highp float depth_mm = GetDepthMillimeters(packed_depth);
highp float normalized_depth = depth_mm / kMaxDepth;
vec4 depth_color = vec4(PerceptColormap(normalized_depth), 1.0);
gl_FragColor = depth_color;
}
接下来,更新 BackgroundRenderer 类,以使用位于 src/main/java/com/google/ar/core/codelab/common/rendering/BackgroundRenderer.java 中的这些新着色器。
在类的顶部添加这些着色器的文件路径。
// Add these under the other shader names at the top of the class.
private static final String DEPTH_VERTEX_SHADER_NAME = "shaders/background_show_depth_map.vert";
private static final String DEPTH_FRAGMENT_SHADER_NAME = "shaders/background_show_depth_map.frag";
向 BackgroundRenderer 类添加更多成员变量,因为它将运行两个着色器。
// Add to the top of file with the rest of the member variables.
private int depthProgram;
private int depthTextureParam;
private int depthTextureId = -1;
private int depthQuadPositionParam;
private int depthQuadTexCoordParam;
添加新方法来填充以下字段:
// Add this method below createOnGlThread().
public void createDepthShaders(Context context, int depthTextureId) throws IOException {
int vertexShader =
ShaderUtil.loadGLShader(
TAG, context, GLES20.GL_VERTEX_SHADER, DEPTH_VERTEX_SHADER_NAME);
int fragmentShader =
ShaderUtil.loadGLShader(
TAG, context, GLES20.GL_FRAGMENT_SHADER, DEPTH_FRAGMENT_SHADER_NAME);
depthProgram = GLES20.glCreateProgram();
GLES20.glAttachShader(depthProgram, vertexShader);
GLES20.glAttachShader(depthProgram, fragmentShader);
GLES20.glLinkProgram(depthProgram);
GLES20.glUseProgram(depthProgram);
ShaderUtil.checkGLError(TAG, "Program creation");
depthTextureParam = GLES20.glGetUniformLocation(depthProgram, "u_Depth");
ShaderUtil.checkGLError(TAG, "Program parameters");
depthQuadPositionParam = GLES20.glGetAttribLocation(depthProgram, "a_Position");
depthQuadTexCoordParam = GLES20.glGetAttribLocation(depthProgram, "a_TexCoord");
this.depthTextureId = depthTextureId;
}
添加以下方法,对每一帧使用这些着色器进行绘制:
// Put this at the bottom of the file.
public void drawDepth(@NonNull Frame frame) {
if (frame.hasDisplayGeometryChanged()) {
frame.transformCoordinates2d(
Coordinates2d.OPENGL_NORMALIZED_DEVICE_COORDINATES,
quadCoords,
Coordinates2d.TEXTURE_NORMALIZED,
quadTexCoords);
}
if (frame.getTimestamp() == 0 || depthTextureId == -1) {
return;
}
// Ensure position is rewound before use.
quadTexCoords.position(0);
// No need to test or write depth, the screen quad has arbitrary depth, and is expected
// to be drawn first.
GLES20.glDisable(GLES20.GL_DEPTH_TEST);
GLES20.glDepthMask(false);
GLES20.glActiveTexture(GLES20.GL_TEXTURE0);
GLES20.glBindTexture(GLES20.GL_TEXTURE_2D, depthTextureId);
GLES20.glUseProgram(depthProgram);
GLES20.glUniform1i(depthTextureParam, 0);
// Set the vertex positions and texture coordinates.
GLES20.glVertexAttribPointer(
depthQuadPositionParam, COORDS_PER_VERTEX, GLES20.GL_FLOAT, false, 0, quadCoords);
GLES20.glVertexAttribPointer(
depthQuadTexCoordParam, TEXCOORDS_PER_VERTEX, GLES20.GL_FLOAT, false, 0, quadTexCoords);
// Draws the quad.
GLES20.glEnableVertexAttribArray(depthQuadPositionParam);
GLES20.glEnableVertexAttribArray(depthQuadTexCoordParam);
GLES20.glDrawArrays(GLES20.GL_TRIANGLE_STRIP, 0, 4);
GLES20.glDisableVertexAttribArray(depthQuadPositionParam);
GLES20.glDisableVertexAttribArray(depthQuadTexCoordParam);
// Restore the depth state for further drawing.
GLES20.glDepthMask(true);
GLES20.glEnable(GLES20.GL_DEPTH_TEST);
ShaderUtil.checkGLError(TAG, "BackgroundRendererDraw");
}
添加切换按钮
现在,您已经能够渲染深度图了,用一用吧!添加一个按钮,用于开启或关闭此渲染功能。
在 DepthCodelabActivity 文件的顶部,添加对要使用的按钮的导入操作:
import android.widget.Button;
更新相应类以添加一个布尔值成员,用于指示是否已开启深度渲染(默认情况下为关闭):
private boolean showDepthMap = false;
接下来,将控制 showDepthMap 布尔值的按钮添加到 onCreate() 方法的末尾:
final Button toggleDepthButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.toggle_depth_button);
toggleDepthButton.setOnClickListener(
view -> {
if (isDepthSupported) {
showDepthMap = !showDepthMap;
toggleDepthButton.setText(showDepthMap ? R.string.hide_depth : R.string.show_depth);
} else {
showDepthMap = false;
toggleDepthButton.setText(R.string.depth_not_available);
}
});
将以下字符串添加到 res/values/strings.xml 中:
<string translatable="false" name="show_depth">Show Depth</string>
<string translatable="false" name="hide_depth">Hide Depth</string>
<string translatable="false" name="depth_not_available">Depth Not Available</string>
在 res/layout/activity_main.xml 中的应用布局底部添加此按钮:
<Button
android:id="@+id/toggle_depth_button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="20dp"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="@string/show_depth"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"/>
该按钮现在控制布尔值 showDepthMap 的值。使用此标志可以控制是否渲染深度图。
回到 DepthCodelabActivity 中的 onDrawFrame() 方法,添加以下代码:
// Add this snippet just under backgroundRenderer.draw(frame);
if (showDepthMap) {
backgroundRenderer.drawDepth(frame);
}
通过在 onSurfaceCreated() 中添加以下行,将深度纹理传递给 backgroundRenderer:
// Add to onSurfaceCreated() after backgroundRenderer.createonGlThread(/*context=*/ this);
backgroundRenderer.createDepthShaders(/*context=*/ this, depthTexture.getDepthTexture());
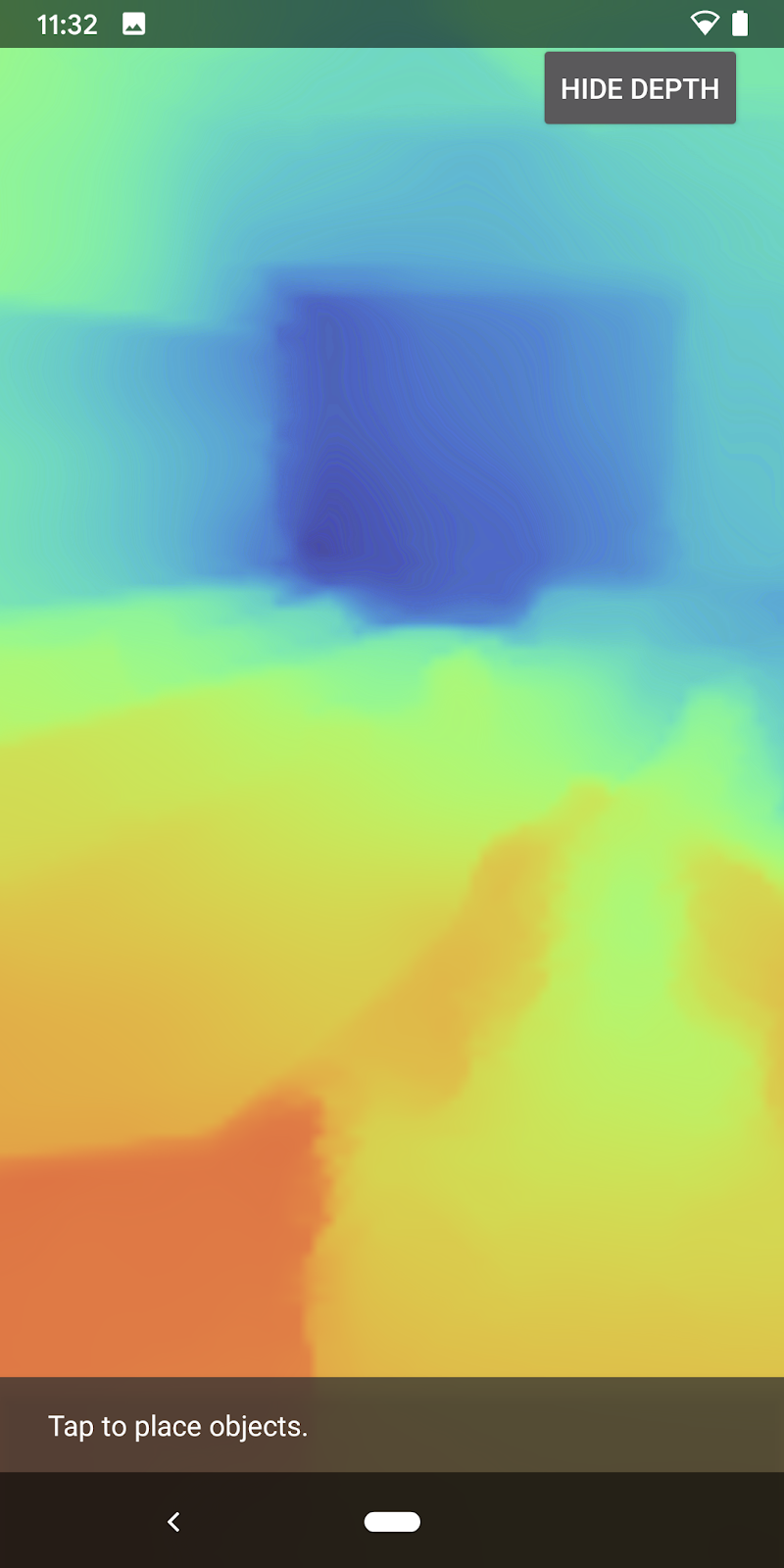
现在,您可以按屏幕右上角的按钮来查看每一帧的深度图像。
|
| ||
不支持 Depth API 时运行应用的效果 | 支持 Depth API 时运行应用的效果 | ||
[可选] 酷炫深度动画
应用目前直接显示深度图。红色像素表示邻近的区域,蓝色像素表示距离较远的区域。
|
|
可以通过多种方式传递深度信息。在本部分中,您将修改着色器,以定期闪烁深度,方法是修改着色器,仅显示指定距离范围(这个范围周期性远离相机)内的深度。
首先,将以下变量添加到 background_show_depth_map.frag 的顶部:
uniform float u_DepthRangeToRenderMm;
const float kDepthWidthToRenderMm = 350.0;
- 然后,在着色器的
main()函数中使用这些值过滤要使用深度值遮挡的像素。
// Add this line at the end of main().
gl_FragColor.a = clamp(1.0 - abs((depth_mm - u_DepthRangeToRenderMm) / kDepthWidthToRenderMm), 0.0, 1.0);
接下来,更新 BackgroundRenderer.java 以维持这些着色器参数。在该类的顶部添加以下字段:
private static final float MAX_DEPTH_RANGE_TO_RENDER_MM = 10000.0f;
private float depthRangeToRenderMm = 0.0f;
private int depthRangeToRenderMmParam;
在 createDepthShaders() 方法中,添加以下代码,以便将这些参数与着色器程序进行匹配:
depthRangeToRenderMmParam = GLES20.glGetUniformLocation(depthProgram, "u_DepthRangeToRenderMm");
- 最后,您可以在
drawDepth()方法中持续控制此范围。添加以下代码,以便每绘制一帧递增一次此范围。
// Enables alpha blending.
GLES20.glEnable(GLES20.GL_BLEND);
GLES20.glBlendFunc(GLES20.GL_SRC_ALPHA, GLES20.GL_ONE_MINUS_SRC_ALPHA);
// Updates range each time draw() is called.
depthRangeToRenderMm += 50.0f;
if (depthRangeToRenderMm > MAX_DEPTH_RANGE_TO_RENDER_MM) {
depthRangeToRenderMm = 0.0f;
}
// Passes latest value to the shader.
GLES20.glUniform1f(depthRangeToRenderMmParam, depthRangeToRenderMm);
现在,深度将以动画的形式在场景中闪烁。

您可以随意更改此处提供的值,以使闪烁变慢、变快、变宽、变窄等。您还可以尝试采用其他的新方法来更改着色器,以呈现深度效果!
8. 借助 Depth API 实现遮挡效果(第 4 部分)
现在,您将在应用中处理对象遮挡关系。
遮挡是指虚拟对象因与相机之间存在真实物体而无法完整呈现时的情况。为了实现沉浸式 AR 体验,管理遮挡效果至关重要。
恰当地实时渲染虚拟对象,可提升增强现实场景的真实感和可信度。如需查看更多示例,请观看我们关于利用 Depth API 实现增强现实的视频。
在本部分中,您将更新应用,令其仅在可获得深度信息包括虚拟对象。
添加新的对象着色器
如上面几部分所述,您将添加新的着色器来支持深度信息。这一次,您可以复制现有的对象着色器,并添加遮挡功能。
请务必保留全部两个版本的对象着色器,以便应用在运行时可以决定是否支持深度。
在 src/main/assets/shaders 目录中为 object.vert 和 object.frag 着色器文件创建副本。
|
|
在 occlusion_object.vert 中,将以下变量添加到 main() 上方:
varying vec3 v_ScreenSpacePosition;
在 main() 底部设置以下变量:
v_ScreenSpacePosition = gl_Position.xyz / gl_Position.w;
在文件顶部 main() 上方添加以下变量,以更新 occlusion_object.frag:
varying vec3 v_ScreenSpacePosition;
uniform sampler2D u_Depth;
uniform mat3 u_UvTransform;
uniform float u_DepthTolerancePerMm;
uniform float u_OcclusionAlpha;
uniform float u_DepthAspectRatio;
- 在着色器中的
main()上方添加以下辅助函数,以便更轻松地处理深度信息。
float GetDepthMillimeters(in vec2 depth_uv) {
// Depth is packed into the red and green components of its texture.
// The texture is a normalized format, storing millimeters.
vec3 packedDepthAndVisibility = texture2D(u_Depth, depth_uv).xyz;
return dot(packedDepthAndVisibility.xy, vec2(255.0, 256.0 * 255.0));
}
// Returns linear interpolation position of value between min and max bounds.
// E.g., InverseLerp(1100, 1000, 2000) returns 0.1.
float InverseLerp(in float value, in float min_bound, in float max_bound) {
return clamp((value - min_bound) / (max_bound - min_bound), 0.0, 1.0);
}
// Returns a value between 0.0 (not visible) and 1.0 (completely visible)
// Which represents how visible or occluded is the pixel in relation to the
// depth map.
float GetVisibility(in vec2 depth_uv, in float asset_depth_mm) {
float depth_mm = GetDepthMillimeters(depth_uv);
// Instead of a hard z-buffer test, allow the asset to fade into the
// background along a 2 * u_DepthTolerancePerMm * asset_depth_mm
// range centered on the background depth.
float visibility_occlusion = clamp(0.5 * (depth_mm - asset_depth_mm) /
(u_DepthTolerancePerMm * asset_depth_mm) + 0.5, 0.0, 1.0);
// Depth close to zero is most likely invalid, do not use it for occlusions.
float visibility_depth_near = 1.0 - InverseLerp(
depth_mm, /*min_depth_mm=*/150.0, /*max_depth_mm=*/200.0);
// Same for very high depth values.
float visibility_depth_far = InverseLerp(
depth_mm, /*min_depth_mm=*/7500.0, /*max_depth_mm=*/8000.0);
float visibility =
max(max(visibility_occlusion, u_OcclusionAlpha),
max(visibility_depth_near, visibility_depth_far));
return visibility;
}
现在将 occlusion_object.frag 中的 main() 更新为深度感知型,并应用遮挡。在文件底部添加以下几行代码:
const float kMToMm = 1000.0;
float asset_depth_mm = v_ViewPosition.z * kMToMm * -1.;
vec2 depth_uvs = (u_UvTransform * vec3(v_ScreenSpacePosition.xy, 1)).xy;
gl_FragColor.a *= GetVisibility(depth_uvs, asset_depth_mm);
现在您已经有了新版本的对象着色器,接下来就可以修改渲染程序代码了。
呈现对象遮挡关系
接下来,为 src/main/java/com/google/ar/core/codelab/common/rendering/ObjectRenderer.java 中的 ObjectRenderer 类创建副本。
- 选择
ObjectRenderer类 - 右键点击 > Copy
- 选择 rendering 文件夹
- 右键点击 > Paste
- 将该类命名为
OcclusionObjectRenderer
现在,重命名后的新类应出现在同一文件夹中:
打开新创建的 OcclusionObjectRenderer.java,更改文件顶部的着色器路径:
private static final String VERTEX_SHADER_NAME = "shaders/occlusion_object.vert";
private static final String FRAGMENT_SHADER_NAME = "shaders/occlusion_object.frag";
- 在类的顶部添加下列与深度相关的成员变量以及其他变量:该变量可调整遮挡边框的锐度。
// Shader location: depth texture
private int depthTextureUniform;
// Shader location: transform to depth uvs
private int depthUvTransformUniform;
// Shader location: depth tolerance property
private int depthToleranceUniform;
// Shader location: maximum transparency for the occluded part.
private int occlusionAlphaUniform;
private int depthAspectRatioUniform;
private float[] uvTransform = null;
private int depthTextureId;
在类的顶部使用默认值创建这些成员变量:
// These values will be changed each frame based on the distance to the object.
private float depthAspectRatio = 0.0f;
private final float depthTolerancePerMm = 0.015f;
private final float occlusionsAlpha = 0.0f;
在 createOnGlThread() 方法中,初始化着色器的 uniform 参数:
// Occlusions Uniforms. Add these lines before the first call to ShaderUtil.checkGLError
// inside the createOnGlThread() method.
depthTextureUniform = GLES20.glGetUniformLocation(program, "u_Depth");
depthUvTransformUniform = GLES20.glGetUniformLocation(program, "u_UvTransform");
depthToleranceUniform = GLES20.glGetUniformLocation(program, "u_DepthTolerancePerMm");
occlusionAlphaUniform = GLES20.glGetUniformLocation(program, "u_OcclusionAlpha");
depthAspectRatioUniform = GLES20.glGetUniformLocation(program, "u_DepthAspectRatio");
- 通过更新
draw()方法,确保每次绘制时这些值都会更新:
// Add after other GLES20.glUniform calls inside draw().
GLES20.glActiveTexture(GLES20.GL_TEXTURE1);
GLES20.glBindTexture(GLES20.GL_TEXTURE_2D, depthTextureId);
GLES20.glUniform1i(depthTextureUniform, 1);
GLES20.glUniformMatrix3fv(depthUvTransformUniform, 1, false, uvTransform, 0);
GLES20.glUniform1f(depthToleranceUniform, depthTolerancePerMm);
GLES20.glUniform1f(occlusionAlphaUniform, occlusionsAlpha);
GLES20.glUniform1f(depthAspectRatioUniform, depthAspectRatio);
在 draw() 中添加以下几行代码以在渲染中启用混合模式,进而可以在遮挡虚拟对象时对其应用透明效果:
// Add these lines just below the code-block labeled "Enable vertex arrays"
GLES20.glEnable(GLES20.GL_BLEND);
GLES20.glBlendFunc(GLES20.GL_SRC_ALPHA, GLES20.GL_ONE_MINUS_SRC_ALPHA);
// Add these lines just above the code-block labeled "Disable vertex arrays"
GLES20.glDisable(GLES20.GL_BLEND);
GLES20.glDepthMask(true);
- 添加以下方法,以便
OcclusionObjectRenderer的调用程序可以提供深度信息。
// Add these methods at the bottom of the OcclusionObjectRenderer class.
public void setUvTransformMatrix(float[] transform) {
uvTransform = transform;
}
public void setDepthTexture(int textureId, int width, int height) {
depthTextureId = textureId;
depthAspectRatio = (float) width / (float) height;
}
控制对象遮挡
有了新的 OcclusionObjectRenderer 后,您可以将其添加到 DepthCodelabActivity,并选择何时以及如何应用遮挡呈现。
通过将 OcclusionObjectRenderer 的一个实例添加到 Activity 来启用此逻辑,以使 ObjectRenderer 和 OcclusionObjectRenderer 都是 DepthCodelabActivity 的成员:
// Add this include at the top of the file.
import com.google.ar.core.codelab.common.rendering.OcclusionObjectRenderer;
// Add this member just below the existing "virtualObject", so both are present.
private final OcclusionObjectRenderer occludedVirtualObject = new OcclusionObjectRenderer();
- 接下来,您可以根据当前设备是否支持 Depth API 来控制何时使用此
occludedVirtualObject。在onSurfaceCreated方法中添加以下代码行,并在下方配置virtualObject:
if (isDepthSupported) {
occludedVirtualObject.createOnGlThread(/*context=*/ this, "models/andy.obj", "models/andy.png");
occludedVirtualObject.setDepthTexture(
depthTexture.getDepthTexture(),
depthTexture.getDepthWidth(),
depthTexture.getDepthHeight());
occludedVirtualObject.setMaterialProperties(0.0f, 2.0f, 0.5f, 6.0f);
}
在不支持深度的设备上,系统会创建 occludedVirtualObject 实例,但不会使用它。在支持深度的手机上,会初始化两个版本的渲染程序,并在运行时决定绘制时使用哪个版本。
在 onDrawFrame() 方法中,找到以下现有代码:
virtualObject.updateModelMatrix(anchorMatrix, scaleFactor);
virtualObject.draw(viewmtx, projmtx, colorCorrectionRgba, OBJECT_COLOR);
将其替换为以下代码:
if (isDepthSupported) {
occludedVirtualObject.updateModelMatrix(anchorMatrix, scaleFactor);
occludedVirtualObject.draw(viewmtx, projmtx, colorCorrectionRgba, OBJECT_COLOR);
} else {
virtualObject.updateModelMatrix(anchorMatrix, scaleFactor);
virtualObject.draw(viewmtx, projmtx, colorCorrectionRgba, OBJECT_COLOR);
}
最后,请确保深度图像正确映射到输出渲染。由于深度图像与您的屏幕分辨率不同,可能宽高比也不同,因此纹理坐标在深度图像与相机图像之间可能存在差异。
- 在此文件的底部添加辅助方法
getTextureTransformMatrix()。此方法会返回一个转换矩阵,应用该矩阵后,可使屏幕空间 UV 坐标与用于渲染相机画面的四元纹理坐标正确匹配。此方法考虑了设备的屏幕方向。
private static float[] getTextureTransformMatrix(Frame frame) {
float[] frameTransform = new float[6];
float[] uvTransform = new float[9];
// XY pairs of coordinates in NDC space that constitute the origin and points along the two
// principal axes.
float[] ndcBasis = {0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1};
// Temporarily store the transformed points into outputTransform.
frame.transformCoordinates2d(
Coordinates2d.OPENGL_NORMALIZED_DEVICE_COORDINATES,
ndcBasis,
Coordinates2d.TEXTURE_NORMALIZED,
frameTransform);
// Convert the transformed points into an affine transform and transpose it.
float ndcOriginX = frameTransform[0];
float ndcOriginY = frameTransform[1];
uvTransform[0] = frameTransform[2] - ndcOriginX;
uvTransform[1] = frameTransform[3] - ndcOriginY;
uvTransform[2] = 0;
uvTransform[3] = frameTransform[4] - ndcOriginX;
uvTransform[4] = frameTransform[5] - ndcOriginY;
uvTransform[5] = 0;
uvTransform[6] = ndcOriginX;
uvTransform[7] = ndcOriginY;
uvTransform[8] = 1;
return uvTransform;
}
getTextureTransformMatrix() 要求在文件顶部包含以下导入操作:
import com.google.ar.core.Coordinates2d;
您希望每次屏幕纹理发生变化时(例如,屏幕旋转时)都计算这些纹理坐标之间的转换。此功能有一定限制。
在文件顶部添加以下标志:
// Add this member at the top of the file.
private boolean calculateUVTransform = true;
- 在
onDrawFrame()中,检查在创建帧和相机后是否需要重新计算存储的转换:
// Add these lines inside onDrawFrame() after frame.getCamera().
if (frame.hasDisplayGeometryChanged() || calculateUVTransform) {
calculateUVTransform = false;
float[] transform = getTextureTransformMatrix(frame);
occludedVirtualObject.setUvTransformMatrix(transform);
}
执行这些更改后,您现在就可以运行应用并查看虚拟对象的遮挡效果了!
现在,该应用应该可以在所有手机上正常运行,并在手机支持深度功能时自动使用深度实现遮挡效果。
|
| ||
支持 Depth API 时运行应用的效果 | 不支持 Depth API 时运行应用的效果 | ||
9. [可选] 改善遮挡效果
上面实现的基于深度的遮挡方法可提供具有锐利边界的遮挡效果。当相机远离对象时,深度测量值的准确度会降低,这可能会导致出现视觉伪影。
要缓解这个问题,我们可以为遮挡测试添加额外的模糊处理,为隐藏的虚拟对象生成较平滑的边缘。
occlusion_object.frag
在 occlusion_object.frag 的顶部添加以下 uniform 变量:
uniform float u_OcclusionBlurAmount;
在着色器中,将这个辅助函数添加到 main() 上方,这会将内核模糊处理应用于遮挡采样:
float GetBlurredVisibilityAroundUV(in vec2 uv, in float asset_depth_mm) {
// Kernel used:
// 0 4 7 4 0
// 4 16 26 16 4
// 7 26 41 26 7
// 4 16 26 16 4
// 0 4 7 4 0
const float kKernelTotalWeights = 269.0;
float sum = 0.0;
vec2 blurriness = vec2(u_OcclusionBlurAmount,
u_OcclusionBlurAmount * u_DepthAspectRatio);
float current = 0.0;
current += GetVisibility(uv + vec2(-1.0, -2.0) * blurriness, asset_depth_mm);
current += GetVisibility(uv + vec2(+1.0, -2.0) * blurriness, asset_depth_mm);
current += GetVisibility(uv + vec2(-1.0, +2.0) * blurriness, asset_depth_mm);
current += GetVisibility(uv + vec2(+1.0, +2.0) * blurriness, asset_depth_mm);
current += GetVisibility(uv + vec2(-2.0, +1.0) * blurriness, asset_depth_mm);
current += GetVisibility(uv + vec2(+2.0, +1.0) * blurriness, asset_depth_mm);
current += GetVisibility(uv + vec2(-2.0, -1.0) * blurriness, asset_depth_mm);
current += GetVisibility(uv + vec2(+2.0, -1.0) * blurriness, asset_depth_mm);
sum += current * 4.0;
current = 0.0;
current += GetVisibility(uv + vec2(-2.0, -0.0) * blurriness, asset_depth_mm);
current += GetVisibility(uv + vec2(+2.0, +0.0) * blurriness, asset_depth_mm);
current += GetVisibility(uv + vec2(+0.0, +2.0) * blurriness, asset_depth_mm);
current += GetVisibility(uv + vec2(-0.0, -2.0) * blurriness, asset_depth_mm);
sum += current * 7.0;
current = 0.0;
current += GetVisibility(uv + vec2(-1.0, -1.0) * blurriness, asset_depth_mm);
current += GetVisibility(uv + vec2(+1.0, -1.0) * blurriness, asset_depth_mm);
current += GetVisibility(uv + vec2(-1.0, +1.0) * blurriness, asset_depth_mm);
current += GetVisibility(uv + vec2(+1.0, +1.0) * blurriness, asset_depth_mm);
sum += current * 16.0;
current = 0.0;
current += GetVisibility(uv + vec2(+0.0, +1.0) * blurriness, asset_depth_mm);
current += GetVisibility(uv + vec2(-0.0, -1.0) * blurriness, asset_depth_mm);
current += GetVisibility(uv + vec2(-1.0, -0.0) * blurriness, asset_depth_mm);
current += GetVisibility(uv + vec2(+1.0, +0.0) * blurriness, asset_depth_mm);
sum += current * 26.0;
sum += GetVisibility(uv , asset_depth_mm) * 41.0;
return sum / kKernelTotalWeights;
}
替换 main() 中的以下现有代码行:
gl_FragColor.a *= GetVisibility(depth_uvs, asset_depth_mm);
替换为以下行:
gl_FragColor.a *= GetBlurredVisibilityAroundUV(depth_uvs, asset_depth_mm);
更新渲染程序以利用这一新的着色器功能。
OcclusionObjectRenderer.java
在此类的顶部添加以下成员变量:
private int occlusionBlurUniform;
private final float occlusionsBlur = 0.01f;
在 createOnGlThread 方法中添加以下代码:
// Add alongside the other calls to GLES20.glGetUniformLocation.
occlusionBlurUniform = GLES20.glGetUniformLocation(program, "u_OcclusionBlurAmount");
在 draw 方法中添加以下代码:
// Add alongside the other calls to GLES20.glUniform1f.
GLES20.glUniform1f(occlusionBlurUniform, occlusionsBlur);
| 视觉比较完成以上更改后,遮挡边界现在应该更加平滑。 |
10. 构建、运行、测试
构建和运行您的应用
- 通过 USB 插入 Android 设备。
- 依次选择 File > Build and Run。
- 另存为:ARCodeLab.apk。
- 等待应用构建并部署到您的设备中。
首次尝试将应用部署到设备时:
- 您需要允许在设备上启用 USB 调试。选择“OK”以继续。
- 系统会询问您是否允许该应用使用设备相机。您需要授予使用权限,才能继续使用 AR 功能。
测试应用
运行应用时,您可以手持设备、在空间中移动、缓慢扫描某个区域,以此测试应用的基本行为。先尝试收集至少 10 秒的数据,再从多个方向扫描该区域,然后执行下一步。
问题排查
设置 Android 设备用于开发
- 使用一根 USB 线将设备连接到开发机器。如果您要在 Windows 上开发,可能需要为设备安装相应的 USB 驱动程序。
- 执行以下步骤,在开发者选项窗口中启用 USB 调试:
- 打开设置应用。
- 如果设备使用 Android v8.0 或更高版本,请选择系统。否则,请继续执行下一步。
- 滚动到底部,然后选择关于手机。
- 滚动到底部,然后点按版本号 7 次。
- 返回上一屏幕,滚动到底部,然后点按开发者选项。
- 在开发者选项窗口中,向下滚动以找到并启用 USB 调试。
如需详细了解此流程,请访问 Google 的 Android 开发者网站。
与许可相关的构建失败
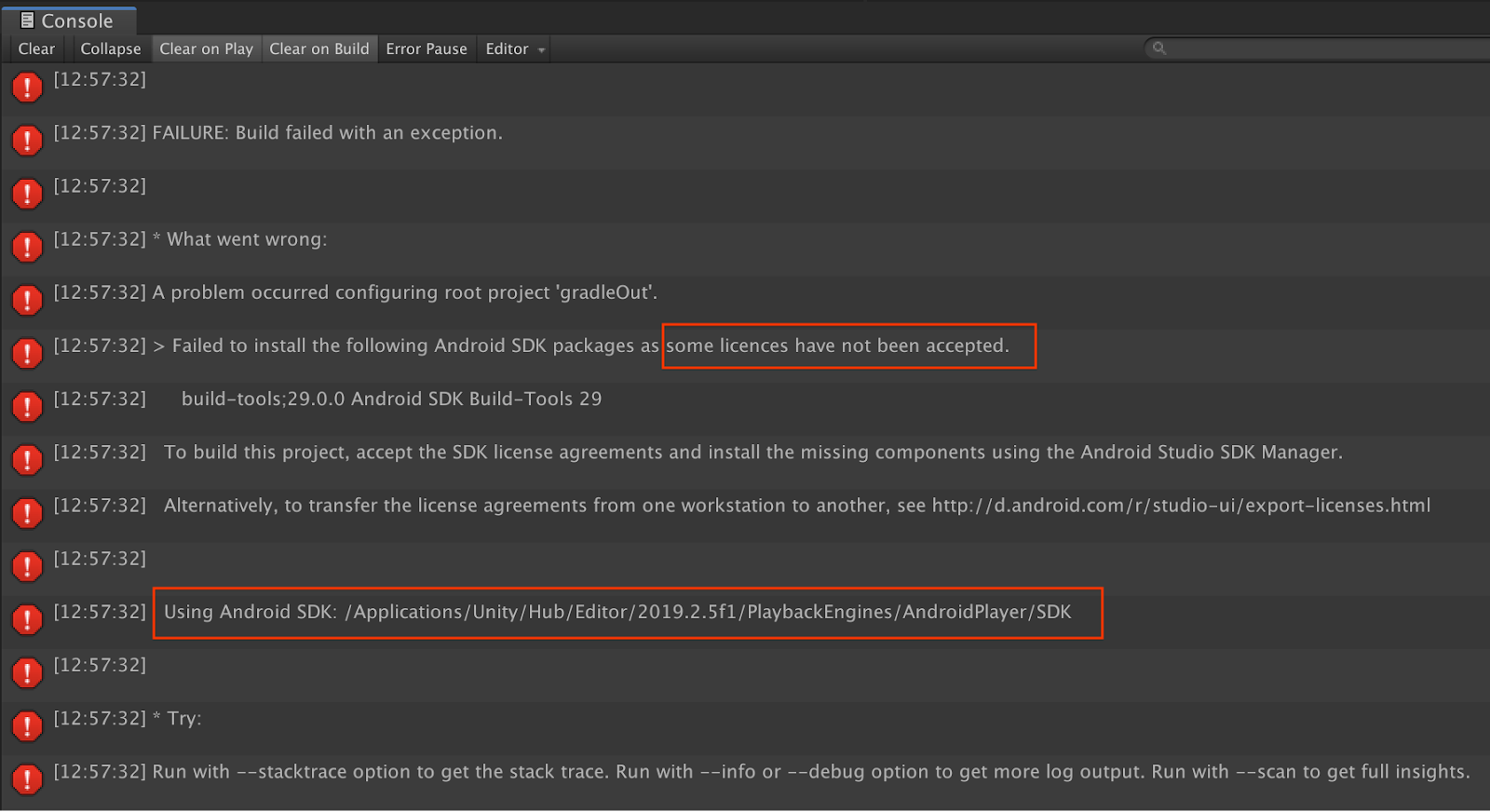
如果您遇到与许可相关的构建失败(由于尚未接受某些许可,导致安装以下 Android SDK 软件包失败),可以使用以下命令来查看和接受这些许可:
cd <path to Android SDK>
tools/bin/sdkmanager --licenses
11. 恭喜
恭喜,您已借助 Google ARCore Depth API 成功构建并运行了您的首个基于深度的增强现实应用!