1. מבוא
ב-codelab הזה תלמדו איך להשתמש ב-AlloyDB AI על ידי שילוב של חיפוש וקטורי עם הטמעות של Vertex AI. ה-Lab הזה הוא חלק מאוסף של Labs שמוקדשים לתכונות של AlloyDB AI. מידע נוסף זמין בדף AlloyDB AI בתיעוד.

דרישות מוקדמות
- הבנה בסיסית של Google Cloud Console
- מיומנויות בסיסיות בממשק שורת הפקודה וב-Google Shell
מה תלמדו
- איך פורסים אשכול AlloyDB ומכונה ראשית
- איך מתחברים ל-AlloyDB ממכונה וירטואלית ב-Google Compute Engine
- איך יוצרים מסד נתונים ומפעילים את AlloyDB AI
- איך טוענים נתונים למסד הנתונים
- איך משתמשים במודל הטמעה של Vertex AI ב-AlloyDB
- איך משפרים את התוצאה באמצעות מודל גנרטיבי של Vertex AI
- איך לשפר את הביצועים באמצעות אינדקס וקטורי
מה צריך
- חשבון Google Cloud ופרויקט Google Cloud
- דפדפן אינטרנט כמו Chrome
2. הגדרה ודרישות
הגדרת סביבה בקצב אישי
- נכנסים ל-Google Cloud Console ויוצרים פרויקט חדש או משתמשים בפרויקט קיים. אם עדיין אין לכם חשבון Gmail או חשבון Google Workspace, אתם צריכים ליצור חשבון.



- שם הפרויקט הוא השם המוצג של המשתתפים בפרויקט הזה. זו מחרוזת תווים שלא נמצאת בשימוש ב-Google APIs. תמיד אפשר לעדכן את המיקום.
- מזהה הפרויקט הוא ייחודי לכל הפרויקטים ב-Google Cloud, והוא קבוע (אי אפשר לשנות אותו אחרי שהוא מוגדר). מסוף Cloud יוצר באופן אוטומטי מחרוזת ייחודית. בדרך כלל לא צריך לדעת מה היא. ברוב ה-Codelabs, תצטרכו להפנות למזהה הפרויקט (בדרך כלל מסומן כ-
PROJECT_ID). אם אתם לא אוהבים את המזהה שנוצר, אתם יכולים ליצור מזהה אקראי אחר. אפשר גם לנסות שם משתמש משלכם ולבדוק אם הוא זמין. אי אפשר לשנות את הערך הזה אחרי השלב הזה, והוא יישאר כזה למשך הפרויקט. - לידיעתכם, יש ערך שלישי, מספר פרויקט, שחלק מממשקי ה-API משתמשים בו. במאמרי העזרה מפורט מידע נוסף על שלושת הערכים האלה.
- בשלב הבא, תצטרכו להפעיל את החיוב במסוף Cloud כדי להשתמש במשאבי Cloud או בממשקי API של Cloud. השלמת ה-codelab הזה לא תעלה לכם הרבה, אם בכלל. כדי להשבית את המשאבים ולמנוע חיובים נוספים אחרי שתסיימו את המדריך הזה, תוכלו למחוק את המשאבים שיצרתם או למחוק את הפרויקט. משתמשים חדשים ב-Google Cloud זכאים לתוכנית תקופת ניסיון בחינם בשווי 300$.
הפעלת Cloud Shell
אפשר להפעיל את Google Cloud מרחוק מהמחשב הנייד, אבל ב-codelab הזה תשתמשו ב-Google Cloud Shell, סביבת שורת פקודה שפועלת בענן.
ב-Google Cloud Console, לוחצים על סמל Cloud Shell בסרגל הכלים שבפינה הימנית העליונה:
יחלפו כמה רגעים עד שההקצאה והחיבור לסביבת העבודה יושלמו. בסיום התהליך, אמור להופיע משהו כזה:

המכונה הווירטואלית הזו כוללת את כל הכלים הדרושים למפתחים. יש בה ספריית בית בנפח מתמיד של 5GB והיא פועלת ב-Google Cloud, מה שמשפר מאוד את הביצועים והאימות ברשת. אפשר לבצע את כל העבודה ב-codelab הזה בדפדפן. לא צריך להתקין שום דבר.
3. לפני שמתחילים
הפעלת ה-API
פלט:
ב-Cloud Shell, מוודאים שמזהה הפרויקט מוגדר:
gcloud config set project [YOUR-PROJECT-ID]
מגדירים את משתנה הסביבה PROJECT_ID:
PROJECT_ID=$(gcloud config get-value project)
מפעילים את כל השירותים הנדרשים:
gcloud services enable alloydb.googleapis.com \
compute.googleapis.com \
cloudresourcemanager.googleapis.com \
servicenetworking.googleapis.com \
aiplatform.googleapis.com
הפלט הצפוי
student@cloudshell:~ (test-project-001-402417)$ gcloud config set project test-project-001-402417
Updated property [core/project].
student@cloudshell:~ (test-project-001-402417)$ PROJECT_ID=$(gcloud config get-value project)
Your active configuration is: [cloudshell-14650]
student@cloudshell:~ (test-project-001-402417)$
student@cloudshell:~ (test-project-001-402417)$ gcloud services enable alloydb.googleapis.com \
compute.googleapis.com \
cloudresourcemanager.googleapis.com \
servicenetworking.googleapis.com \
aiplatform.googleapis.com
Operation "operations/acat.p2-4470404856-1f44ebd8-894e-4356-bea7-b84165a57442" finished successfully.
מגדירים את אזור ברירת המחדל כדי להשתמש במודלים להטמעה של Vertex AI. מידע נוסף על המיקומים שבהם Vertex AI זמין בדוגמה אנחנו משתמשים באזור us-central1.
gcloud config set compute/region us-central1
4. פריסת AlloyDB
לפני שיוצרים אשכול AlloyDB, צריך להגדיר טווח כתובות IP פרטיות שזמין ב-VPC, לשימוש במכונת AlloyDB העתידית. אם אין לנו את זה, אנחנו צריכים ליצור אותו, להקצות אותו לשימוש בשירותים פנימיים של Google, ואז נוכל ליצור את האשכול ואת המופע.
יצירת טווח כתובות IP פרטיות
אנחנו צריכים להגדיר את הגישה הפרטית לשירות ב-VPC שלנו בשביל AlloyDB. ההנחה כאן היא שיש לנו רשת VPC 'ברירת מחדל' בפרויקט, והיא תשמש לכל הפעולות.
יוצרים את טווח כתובות ה-IP הפרטיות:
gcloud compute addresses create psa-range \
--global \
--purpose=VPC_PEERING \
--prefix-length=24 \
--description="VPC private service access" \
--network=default
יצירת חיבור פרטי באמצעות טווח כתובות ה-IP שהוקצה:
gcloud services vpc-peerings connect \
--service=servicenetworking.googleapis.com \
--ranges=psa-range \
--network=default
הפלט הצפוי במסוף:
student@cloudshell:~ (test-project-402417)$ gcloud compute addresses create psa-range \
--global \
--purpose=VPC_PEERING \
--prefix-length=24 \
--description="VPC private service access" \
--network=default
Created [https://www.googleapis.com/compute/v1/projects/test-project-402417/global/addresses/psa-range].
student@cloudshell:~ (test-project-402417)$ gcloud services vpc-peerings connect \
--service=servicenetworking.googleapis.com \
--ranges=psa-range \
--network=default
Operation "operations/pssn.p24-4470404856-595e209f-19b7-4669-8a71-cbd45de8ba66" finished successfully.
student@cloudshell:~ (test-project-402417)$
יצירת אשכול AlloyDB
בקטע הזה אנחנו יוצרים אשכול AlloyDB באזור us-central1.
מגדירים סיסמה למשתמש postgres. אתם יכולים להגדיר סיסמה משלכם או להשתמש בפונקציה אקראית כדי ליצור סיסמה
export PGPASSWORD=`openssl rand -hex 12`
הפלט הצפוי במסוף:
student@cloudshell:~ (test-project-402417)$ export PGPASSWORD=`openssl rand -hex 12`
חשוב לשמור את הסיסמה של PostgreSQL לשימוש עתידי.
echo $PGPASSWORD
תצטרכו את הסיסמה הזו בעתיד כדי להתחבר למופע בתור משתמש postgres. מומלץ לרשום את המספר או להעתיק אותו למקום כלשהו כדי שתוכלו להשתמש בו בהמשך.
הפלט הצפוי במסוף:
student@cloudshell:~ (test-project-402417)$ echo $PGPASSWORD bbefbfde7601985b0dee5723
יצירת אשכול לתקופת ניסיון בחינם
אם עדיין לא השתמשתם ב-AlloyDB, אתם יכולים ליצור אשכול לתקופת ניסיון בחינם:
מגדירים את האזור ואת שם אשכול AlloyDB. אנחנו נשתמש באזור us-central1 וב-alloydb-aip-01 כשם האשכול:
export REGION=us-central1
export ADBCLUSTER=alloydb-aip-01
מריצים את הפקודה ליצירת האשכול:
gcloud alloydb clusters create $ADBCLUSTER \
--password=$PGPASSWORD \
--network=default \
--region=$REGION \
--subscription-type=TRIAL
הפלט הצפוי במסוף:
export REGION=us-central1
export ADBCLUSTER=alloydb-aip-01
gcloud alloydb clusters create $ADBCLUSTER \
--password=$PGPASSWORD \
--network=default \
--region=$REGION \
--subscription-type=TRIAL
Operation ID: operation-1697655441138-6080235852277-9e7f04f5-2012fce4
Creating cluster...done.
יוצרים מכונת AlloyDB ראשית לאשכול באותו סשן של Cloud Shell. אם החיבור ינותק, תצטרכו להגדיר מחדש את משתני הסביבה של שם האזור והאשכול.
gcloud alloydb instances create $ADBCLUSTER-pr \
--instance-type=PRIMARY \
--cpu-count=8 \
--region=$REGION \
--cluster=$ADBCLUSTER
הפלט הצפוי במסוף:
student@cloudshell:~ (test-project-402417)$ gcloud alloydb instances create $ADBCLUSTER-pr \
--instance-type=PRIMARY \
--cpu-count=8 \
--region=$REGION \
--availability-type ZONAL \
--cluster=$ADBCLUSTER
Operation ID: operation-1697659203545-6080315c6e8ee-391805db-25852721
Creating instance...done.
יצירת אשכול AlloyDB Standard
אם זה לא אשכול ה-AlloyDB הראשון בפרויקט, ממשיכים ליצירה של אשכול רגיל.
מגדירים את האזור ואת שם אשכול AlloyDB. אנחנו נשתמש באזור us-central1 וב-alloydb-aip-01 כשם האשכול:
export REGION=us-central1
export ADBCLUSTER=alloydb-aip-01
מריצים את הפקודה ליצירת האשכול:
gcloud alloydb clusters create $ADBCLUSTER \
--password=$PGPASSWORD \
--network=default \
--region=$REGION
הפלט הצפוי במסוף:
export REGION=us-central1
export ADBCLUSTER=alloydb-aip-01
gcloud alloydb clusters create $ADBCLUSTER \
--password=$PGPASSWORD \
--network=default \
--region=$REGION
Operation ID: operation-1697655441138-6080235852277-9e7f04f5-2012fce4
Creating cluster...done.
יוצרים מכונת AlloyDB ראשית לאשכול באותו סשן של Cloud Shell. אם החיבור ינותק, תצטרכו להגדיר מחדש את משתני הסביבה של שם האזור והאשכול.
gcloud alloydb instances create $ADBCLUSTER-pr \
--instance-type=PRIMARY \
--cpu-count=2 \
--region=$REGION \
--cluster=$ADBCLUSTER
הפלט הצפוי במסוף:
student@cloudshell:~ (test-project-402417)$ gcloud alloydb instances create $ADBCLUSTER-pr \
--instance-type=PRIMARY \
--cpu-count=2 \
--region=$REGION \
--availability-type ZONAL \
--cluster=$ADBCLUSTER
Operation ID: operation-1697659203545-6080315c6e8ee-391805db-25852721
Creating instance...done.
5. התחברות ל-AlloyDB
AlloyDB נפרס באמצעות חיבור פרטי בלבד, ולכן אנחנו צריכים מכונה וירטואלית עם לקוח PostgreSQL מותקן כדי לעבוד עם מסד הנתונים.
פריסת מכונה וירטואלית ב-GCE
יוצרים מכונה וירטואלית ב-GCE באותו אזור ובאותו VPC כמו אשכול AlloyDB.
ב-Cloud Shell, מריצים את הפקודה:
export ZONE=us-central1-a
gcloud compute instances create instance-1 \
--zone=$ZONE \
--create-disk=auto-delete=yes,boot=yes,image=projects/debian-cloud/global/images/$(gcloud compute images list --filter="family=debian-12 AND family!=debian-12-arm64" --format="value(name)") \
--scopes=https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cloud-platform
הפלט הצפוי במסוף:
student@cloudshell:~ (test-project-402417)$ export ZONE=us-central1-a
student@cloudshell:~ (test-project-402417)$ export ZONE=us-central1-a
gcloud compute instances create instance-1 \
--zone=$ZONE \
--create-disk=auto-delete=yes,boot=yes,image=projects/debian-cloud/global/images/$(gcloud compute images list --filter="family=debian-12 AND family!=debian-12-arm64" --format="value(name)") \
--scopes=https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cloud-platform
Created [https://www.googleapis.com/compute/v1/projects/test-project-402417/zones/us-central1-a/instances/instance-1].
NAME: instance-1
ZONE: us-central1-a
MACHINE_TYPE: n1-standard-1
PREEMPTIBLE:
INTERNAL_IP: 10.128.0.2
EXTERNAL_IP: 34.71.192.233
STATUS: RUNNING
התקנה של Postgres Client
התקנת תוכנת הלקוח של PostgreSQL במכונה הווירטואלית שנפרסה
מתחברים ל-VM:
gcloud compute ssh instance-1 --zone=us-central1-a
הפלט הצפוי במסוף:
student@cloudshell:~ (test-project-402417)$ gcloud compute ssh instance-1 --zone=us-central1-a Updating project ssh metadata...working..Updated [https://www.googleapis.com/compute/v1/projects/test-project-402417]. Updating project ssh metadata...done. Waiting for SSH key to propagate. Warning: Permanently added 'compute.5110295539541121102' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts. Linux instance-1.us-central1-a.c.gleb-test-short-001-418811.internal 6.1.0-18-cloud-amd64 #1 SMP PREEMPT_DYNAMIC Debian 6.1.76-1 (2024-02-01) x86_64 The programs included with the Debian GNU/Linux system are free software; the exact distribution terms for each program are described in the individual files in /usr/share/doc/*/copyright. Debian GNU/Linux comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by applicable law. student@instance-1:~$
מריצים את פקודת התוכנה בתוך ה-VM:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install --yes postgresql-client
הפלט הצפוי במסוף:
student@instance-1:~$ sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install --yes postgresql-client Get:1 https://packages.cloud.google.com/apt google-compute-engine-bullseye-stable InRelease [5146 B] Get:2 https://packages.cloud.google.com/apt cloud-sdk-bullseye InRelease [6406 B] Hit:3 https://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye InRelease Get:4 https://deb.debian.org/debian-security bullseye-security InRelease [48.4 kB] Get:5 https://packages.cloud.google.com/apt google-compute-engine-bullseye-stable/main amd64 Packages [1930 B] Get:6 https://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye-updates InRelease [44.1 kB] Get:7 https://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye-backports InRelease [49.0 kB] ...redacted... update-alternatives: using /usr/share/postgresql/13/man/man1/psql.1.gz to provide /usr/share/man/man1/psql.1.gz (psql.1.gz) in auto mode Setting up postgresql-client (13+225) ... Processing triggers for man-db (2.9.4-2) ... Processing triggers for libc-bin (2.31-13+deb11u7) ...
התחברות למופע
מתחברים למופע הראשי מהמכונה הווירטואלית באמצעות psql.
בכרטיסייה של Cloud Shell שבה פתוח סשן SSH למכונה וירטואלית instance-1.
משתמשים בערך הסיסמה (PGPASSWORD) של AlloyDB שרשמתם ובמזהה האשכול של AlloyDB כדי להתחבר ל-AlloyDB מ-GCE VM:
export PGPASSWORD=<Noted password>
export PROJECT_ID=$(gcloud config get-value project)
export REGION=us-central1
export ADBCLUSTER=alloydb-aip-01
export INSTANCE_IP=$(gcloud alloydb instances describe $ADBCLUSTER-pr --cluster=$ADBCLUSTER --region=$REGION --format="value(ipAddress)")
psql "host=$INSTANCE_IP user=postgres sslmode=require"
הפלט הצפוי במסוף:
student@instance-1:~$ export PGPASSWORD=CQhOi5OygD4ps6ty student@instance-1:~$ ADBCLUSTER=alloydb-aip-01 student@instance-1:~$ REGION=us-central1 student@instance-1:~$ INSTANCE_IP=$(gcloud alloydb instances describe $ADBCLUSTER-pr --cluster=$ADBCLUSTER --region=$REGION --format="value(ipAddress)") gleb@instance-1:~$ psql "host=$INSTANCE_IP user=postgres sslmode=require" psql (15.6 (Debian 15.6-0+deb12u1), server 15.5) SSL connection (protocol: TLSv1.3, cipher: TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384, compression: off) Type "help" for help. postgres=>
סוגרים את סשן ה-psql:
exit
6. הכנת מסד נתונים
צריך ליצור מסד נתונים, להפעיל את השילוב עם Vertex AI, ליצור אובייקטים של מסד נתונים ולייבא את הנתונים.
מתן ההרשאות הנדרשות ל-AlloyDB
מוסיפים הרשאות Vertex AI לסוכן השירות של AlloyDB.
פותחים כרטיסייה נוספת ב-Cloud Shell באמצעות הסימן '+' בחלק העליון.

בכרטיסייה החדשה של Cloud Shell, מריצים את הפקודה:
PROJECT_ID=$(gcloud config get-value project)
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding $PROJECT_ID \
--member="serviceAccount:service-$(gcloud projects describe $PROJECT_ID --format="value(projectNumber)")@gcp-sa-alloydb.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \
--role="roles/aiplatform.user"
הפלט הצפוי במסוף:
student@cloudshell:~ (test-project-001-402417)$ PROJECT_ID=$(gcloud config get-value project) Your active configuration is: [cloudshell-11039] student@cloudshell:~ (test-project-001-402417)$ gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding $PROJECT_ID \ --member="serviceAccount:service-$(gcloud projects describe $PROJECT_ID --format="value(projectNumber)")@gcp-sa-alloydb.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \ --role="roles/aiplatform.user" Updated IAM policy for project [test-project-001-402417]. bindings: - members: - serviceAccount:service-4470404856@gcp-sa-alloydb.iam.gserviceaccount.com role: roles/aiplatform.user - members: ... etag: BwYIEbe_Z3U= version: 1
סוגרים את הכרטיסייה באמצעות הפקודה 'exit' בכרטיסייה:
exit
יצירת מסד נתונים
מדריך מהיר ליצירת מסד נתונים.
בסשן של המכונה הווירטואלית ב-GCE, מריצים את הפקודה:
יצירת מסד נתונים:
psql "host=$INSTANCE_IP user=postgres" -c "CREATE DATABASE quickstart_db"
הפלט הצפוי במסוף:
student@instance-1:~$ psql "host=$INSTANCE_IP user=postgres" -c "CREATE DATABASE quickstart_db" CREATE DATABASE student@instance-1:~$
הפעלת השילוב של Vertex AI
מפעילים את האינטגרציה של Vertex AI ואת התוספים pgvector במסד הנתונים.
במכונה הווירטואלית ב-GCE מריצים את הפקודה:
psql "host=$INSTANCE_IP user=postgres dbname=quickstart_db" -c "CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS google_ml_integration CASCADE"
psql "host=$INSTANCE_IP user=postgres dbname=quickstart_db" -c "CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS vector"
הפלט הצפוי במסוף:
student@instance-1:~$ psql "host=$INSTANCE_IP user=postgres dbname=quickstart_db" -c "CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS google_ml_integration CASCADE" psql "host=$INSTANCE_IP user=postgres dbname=quickstart_db" -c "CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS vector" CREATE EXTENSION CREATE EXTENSION student@instance-1:~$
ייבוא נתונים
מורידים את הנתונים המוכנים ומייבאים אותם למסד הנתונים החדש.
במכונה הווירטואלית ב-GCE מריצים את הפקודה:
gsutil cat gs://cloud-training/gcc/gcc-tech-004/cymbal_demo_schema.sql |psql "host=$INSTANCE_IP user=postgres dbname=quickstart_db"
gsutil cat gs://cloud-training/gcc/gcc-tech-004/cymbal_products.csv |psql "host=$INSTANCE_IP user=postgres dbname=quickstart_db" -c "\copy cymbal_products from stdin csv header"
gsutil cat gs://cloud-training/gcc/gcc-tech-004/cymbal_inventory.csv |psql "host=$INSTANCE_IP user=postgres dbname=quickstart_db" -c "\copy cymbal_inventory from stdin csv header"
gsutil cat gs://cloud-training/gcc/gcc-tech-004/cymbal_stores.csv |psql "host=$INSTANCE_IP user=postgres dbname=quickstart_db" -c "\copy cymbal_stores from stdin csv header"
הפלט הצפוי במסוף:
student@instance-1:~$ gsutil cat gs://cloud-training/gcc/gcc-tech-004/cymbal_demo_schema.sql |psql "host=$INSTANCE_IP user=postgres dbname=quickstart_db" SET SET SET SET SET set_config ------------ (1 row) SET SET SET SET SET SET CREATE TABLE ALTER TABLE CREATE TABLE ALTER TABLE CREATE TABLE ALTER TABLE CREATE TABLE ALTER TABLE CREATE SEQUENCE ALTER TABLE ALTER SEQUENCE ALTER TABLE ALTER TABLE ALTER TABLE student@instance-1:~$ gsutil cat gs://cloud-training/gcc/gcc-tech-004/cymbal_products.csv |psql "host=$INSTANCE_IP user=postgres dbname=quickstart_db" -c "\copy cymbal_products from stdin csv header" COPY 941 student@instance-1:~$ gsutil cat gs://cloud-training/gcc/gcc-tech-004/cymbal_inventory.csv |psql "host=$INSTANCE_IP user=postgres dbname=quickstart_db" -c "\copy cymbal_inventory from stdin csv header" COPY 263861 student@instance-1:~$ gsutil cat gs://cloud-training/gcc/gcc-tech-004/cymbal_stores.csv |psql "host=$INSTANCE_IP user=postgres dbname=quickstart_db" -c "\copy cymbal_stores from stdin csv header" COPY 4654 student@instance-1:~$
7. חישוב הטמעות
אחרי ייבוא הנתונים, נתוני המוצרים נמצאים בטבלה cymbal_products, נתוני המלאי שמציגים את מספר המוצרים הזמינים בכל חנות נמצאים בטבלה cymbal_inventory, ורשימת החנויות נמצאת בטבלה cymbal_stores. אנחנו צריכים לחשב את נתוני הווקטור על סמך תיאורים של המוצרים שלנו, ונשתמש לשם כך בפונקציה embedding. נשתמש בפונקציה כדי לבצע אינטגרציה עם Vertex AI, לחשב נתוני וקטור על סמך תיאורי המוצרים שלנו ולהוסיף אותם לטבלה. במסמכי התיעוד יש מידע נוסף על הטכנולוגיה שבה נעשה שימוש.
יצירת עמודת הטמעה
מתחברים למסד הנתונים באמצעות psql ויוצרים עמודה וירטואלית עם נתוני הווקטור באמצעות פונקציית ההטמעה בטבלה cymbal_products. פונקציית ההטמעה מחזירה נתוני וקטור מ-Vertex AI על סמך הנתונים שסופקו מעמודת product_description.
psql "host=$INSTANCE_IP user=postgres dbname=quickstart_db"
בסשן psql, אחרי שמתחברים למסד הנתונים, מריצים את הפקודה:
ALTER TABLE cymbal_products ADD COLUMN embedding vector(768) GENERATED ALWAYS AS (embedding('text-embedding-005',product_description)) STORED;
הפקודה תיצור את העמודה הווירטואלית ותאכלס אותה בנתוני וקטורים.
הפלט הצפוי במסוף:
student@instance-1:~$ psql "host=$INSTANCE_IP user=postgres dbname=quickstart_db"
psql (13.11 (Debian 13.11-0+deb11u1), server 14.7)
WARNING: psql major version 13, server major version 14.
Some psql features might not work.
SSL connection (protocol: TLSv1.3, cipher: TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384, bits: 256, compression: off)
Type "help" for help.
quickstart_db=> ALTER TABLE cymbal_products ADD COLUMN embedding vector(768) GENERATED ALWAYS AS (embedding('text-embedding-004',product_description)) STORED;
ALTER TABLE
quickstart_db=>
8. הרצת חיפוש דמיון
עכשיו אפשר להריץ את החיפוש באמצעות חיפוש דמיון שמבוסס על ערכים וקטוריים שחושבו עבור התיאורים, ועל הערך הווקטורי שמתקבל עבור הבקשה.
אפשר להריץ את שאילתת ה-SQL מממשק שורת הפקודה של psql, או לחלופין מ-AlloyDB Studio. יכול להיות שפלט מורכב עם כמה שורות ייראה טוב יותר ב-AlloyDB Studio.
התחברות ל-AlloyDB Studio
בפרקים הבאים, אפשר להריץ ב-AlloyDB Studio את כל פקודות ה-SQL שדורשות חיבור למסד הנתונים. כדי להריץ את הפקודה, צריך לפתוח את ממשק מסוף האינטרנט של אשכול AlloyDB על ידי לחיצה על המופע הראשי.

אחר כך לוחצים על AlloyDB Studio בצד ימין:

בוחרים במסד הנתונים quickstart_db, במשתמש postgres ומזינים את הסיסמה שרשמתם כשיצרתם את האשכול. לאחר מכן לוחצים על הלחצן 'אימות'.

ממשק AlloyDB Studio ייפתח. כדי להריץ את הפקודות במסד הנתונים, לוחצים על הכרטיסייה Editor 1 (עורך 1) בצד שמאל.

ייפתח ממשק שבו אפשר להריץ פקודות SQL

אם אתם מעדיפים להשתמש ב-psql משורת הפקודה, אתם יכולים לפעול לפי השלבים החלופיים ולהתחבר למסד הנתונים מתוך סשן ה-SSH של המכונה הווירטואלית, כמו שמתואר בפרקים הקודמים.
הרצת חיפוש דמיון מ-psql
אם החיבור למסד הנתונים נותק, צריך להתחבר אליו שוב באמצעות psql או AlloyDB Studio.
מתחברים למסד הנתונים:
psql "host=$INSTANCE_IP user=postgres dbname=quickstart_db"
מריצים שאילתה כדי לקבל רשימה של מוצרים זמינים שקשורים באופן הכי הדוק לבקשה של לקוח. הבקשה שאנחנו מעבירים ל-Vertex AI כדי לקבל את ערך הווקטור היא: "What kind of fruit trees grow well here?" (אילו עצי פרי גדלים כאן היטב?).
זו השאילתה שאפשר להריץ כדי לבחור את 10 הפריטים הראשונים שהכי מתאימים לבקשה שלנו:
SELECT
cp.product_name,
left(cp.product_description,80) as description,
cp.sale_price,
cs.zip_code,
(cp.embedding <=> embedding('text-embedding-005','What kind of fruit trees grow well here?')::vector) as distance
FROM
cymbal_products cp
JOIN cymbal_inventory ci on
ci.uniq_id=cp.uniq_id
JOIN cymbal_stores cs on
cs.store_id=ci.store_id
AND ci.inventory>0
AND cs.store_id = 1583
ORDER BY
distance ASC
LIMIT 10;
והנה הפלט הצפוי:
quickstart_db=> SELECT
cp.product_name,
left(cp.product_description,80) as description,
cp.sale_price,
cs.zip_code,
(cp.embedding <=> embedding('text-embedding-005','What kind of fruit trees grow well here?')::vector) as distance
FROM
cymbal_products cp
JOIN cymbal_inventory ci on
ci.uniq_id=cp.uniq_id
JOIN cymbal_stores cs on
cs.store_id=ci.store_id
AND ci.inventory>0
AND cs.store_id = 1583
ORDER BY
distance ASC
LIMIT 10;
product_name | description | sale_price | zip_code | distance
-------------------------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------+------------+----------+---------------------
Cherry Tree | This is a beautiful cherry tree that will produce delicious cherries. It is an d | 75.00 | 93230 | 0.43922018972266397
Meyer Lemon Tree | Meyer Lemon trees are California's favorite lemon tree! Grow your own lemons by | 34 | 93230 | 0.4685112926118228
Toyon | This is a beautiful toyon tree that can grow to be over 20 feet tall. It is an e | 10.00 | 93230 | 0.4835677149651668
California Lilac | This is a beautiful lilac tree that can grow to be over 10 feet tall. It is an d | 5.00 | 93230 | 0.4947204525907498
California Peppertree | This is a beautiful peppertree that can grow to be over 30 feet tall. It is an e | 25.00 | 93230 | 0.5054166905547247
California Black Walnut | This is a beautiful walnut tree that can grow to be over 80 feet tall. It is a d | 100.00 | 93230 | 0.5084219510932597
California Sycamore | This is a beautiful sycamore tree that can grow to be over 100 feet tall. It is | 300.00 | 93230 | 0.5140519790508755
Coast Live Oak | This is a beautiful oak tree that can grow to be over 100 feet tall. It is an ev | 500.00 | 93230 | 0.5143126438081371
Fremont Cottonwood | This is a beautiful cottonwood tree that can grow to be over 100 feet tall. It i | 200.00 | 93230 | 0.5174774727252058
Madrone | This is a beautiful madrona tree that can grow to be over 80 feet tall. It is an | 50.00 | 93230 | 0.5227400803389093
9. שיפור התשובה
אפשר לשפר את התשובה לאפליקציית לקוח באמצעות תוצאת השאילתה, ולהכין פלט משמעותי באמצעות תוצאות השאילתה שסופקו כחלק מההנחיה למודל השפה הבסיסי הגנרטיבי של Vertex AI.
כדי לעשות את זה, אנחנו מתכננים ליצור קובץ JSON עם התוצאות מחיפוש הווקטורים, ואז להשתמש בקובץ ה-JSON שנוצר כתוספת להנחיה למודל LLM של טקסט ב-Vertex AI כדי ליצור פלט משמעותי. בשלב הראשון אנחנו יוצרים את ה-JSON, אחר כך בודקים אותו ב-Vertex AI Studio ובשלב האחרון משלבים אותו בהצהרת SQL שאפשר להשתמש בה באפליקציה.
יצירת פלט בפורמט JSON
משנים את השאילתה כדי ליצור את הפלט בפורמט JSON ולהחזיר רק שורה אחת להעברה אל Vertex AI
הנה דוגמה לשאילתה:
WITH trees as (
SELECT
cp.product_name,
left(cp.product_description,80) as description,
cp.sale_price,
cs.zip_code,
cp.uniq_id as product_id
FROM
cymbal_products cp
JOIN cymbal_inventory ci on
ci.uniq_id=cp.uniq_id
JOIN cymbal_stores cs on
cs.store_id=ci.store_id
AND ci.inventory>0
AND cs.store_id = 1583
ORDER BY
(cp.embedding <=> embedding('text-embedding-005','What kind of fruit trees grow well here?')::vector) ASC
LIMIT 1)
SELECT json_agg(trees) FROM trees;
וכאן מופיע קובץ ה-JSON הצפוי בפלט:
[{"product_name":"Cherry Tree","description":"This is a beautiful cherry tree that will produce delicious cherries. It is an d","sale_price":75.00,"zip_code":93230,"product_id":"d536e9e823296a2eba198e52dd23e712"}]
הפעלת ההנחיה ב-Vertex AI Studio
אפשר להשתמש ב-JSON שנוצר כדי לספק אותו כחלק מההנחיה למודל טקסט של AI גנרטיבי ב-Vertex AI Studio
פותחים את Vertex AI Studio ב-Cloud Console.
אם לא השתמשתם בו בעבר, יכול להיות שתתבקשו לאשר את תנאי השימוש. לוחצים על הלחצן 'הסכמה והמשך'.
כותבים את ההנחיה בממשק.
יכול להיות שתתבקשו להפעיל ממשקי API נוספים, אבל אפשר להתעלם מהבקשה. אנחנו לא צריכים עוד ממשקי API כדי לסיים את שיעור ה-Lab.
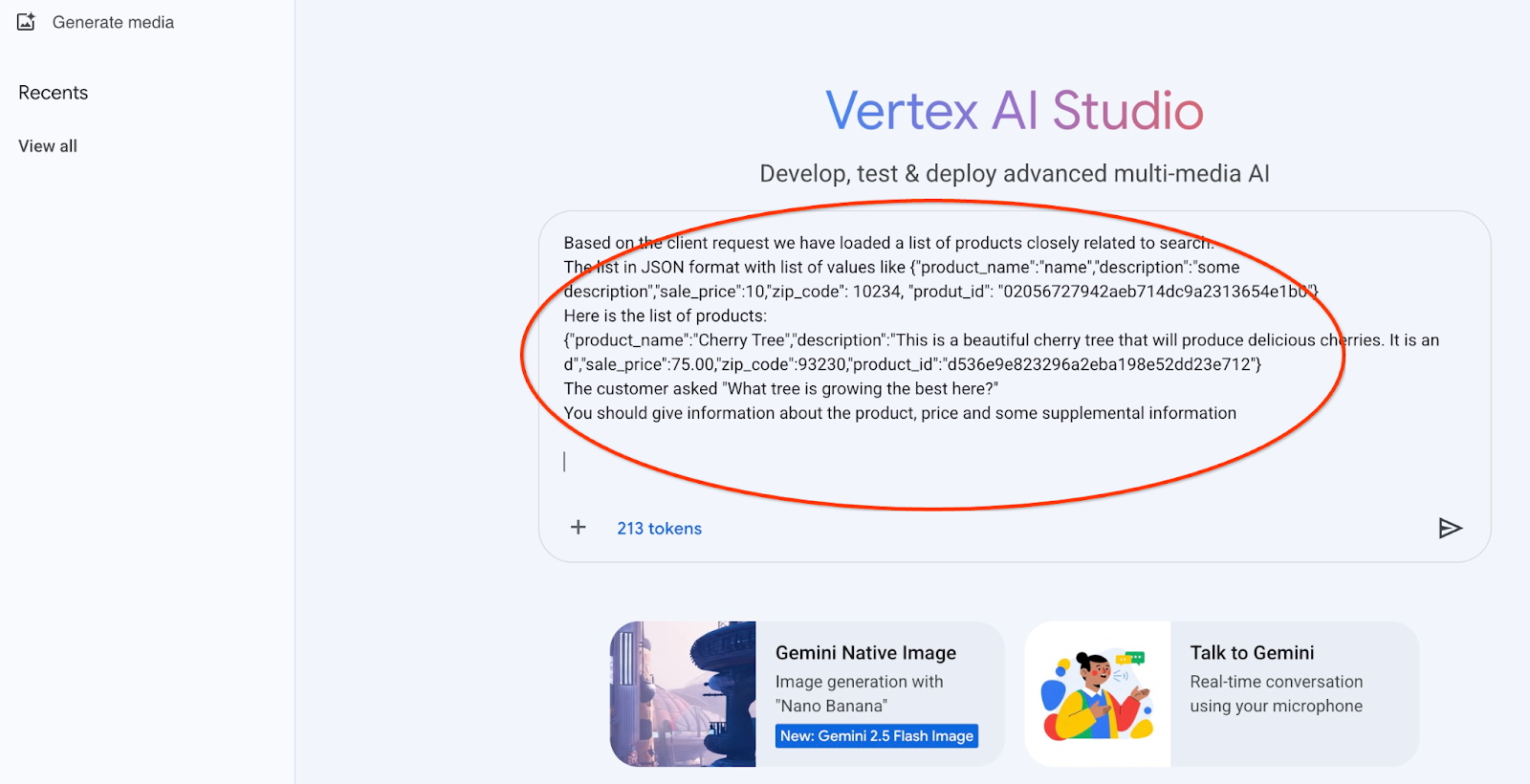
זו ההנחיה שבה נשתמש עם פלט ה-JSON של השאילתה הראשונה לגבי העצים:
אתה יועץ ידידותי שעוזר למצוא מוצר על סמך הצרכים של הלקוח.
על סמך בקשת הלקוח, טענו רשימה של מוצרים שקשורים קשר הדוק לחיפוש.
רשימה בפורמט JSON עם רשימת ערכים כמו {"product_name":"name","description":"some description","sale_price":10,"zip_code": 10234, "produt_id": "02056727942aeb714dc9a2313654e1b0"}
הנה רשימת המוצרים:
{"product_name":"Cherry Tree","description":"This is a beautiful cherry tree that will produce delicious cherries. It is an d","sale_price":75.00,"zip_code":93230,"product_id":"d536e9e823296a2eba198e52dd23e712"}
הלקוח שאל "What tree is growing the best here?"
צריך לספק מידע על המוצר, המחיר ומידע נוסף
זו התוצאה כשמריצים את ההנחיה עם ערכי ה-JSON שלנו ועם המודל gemini-2.5-flash-light:
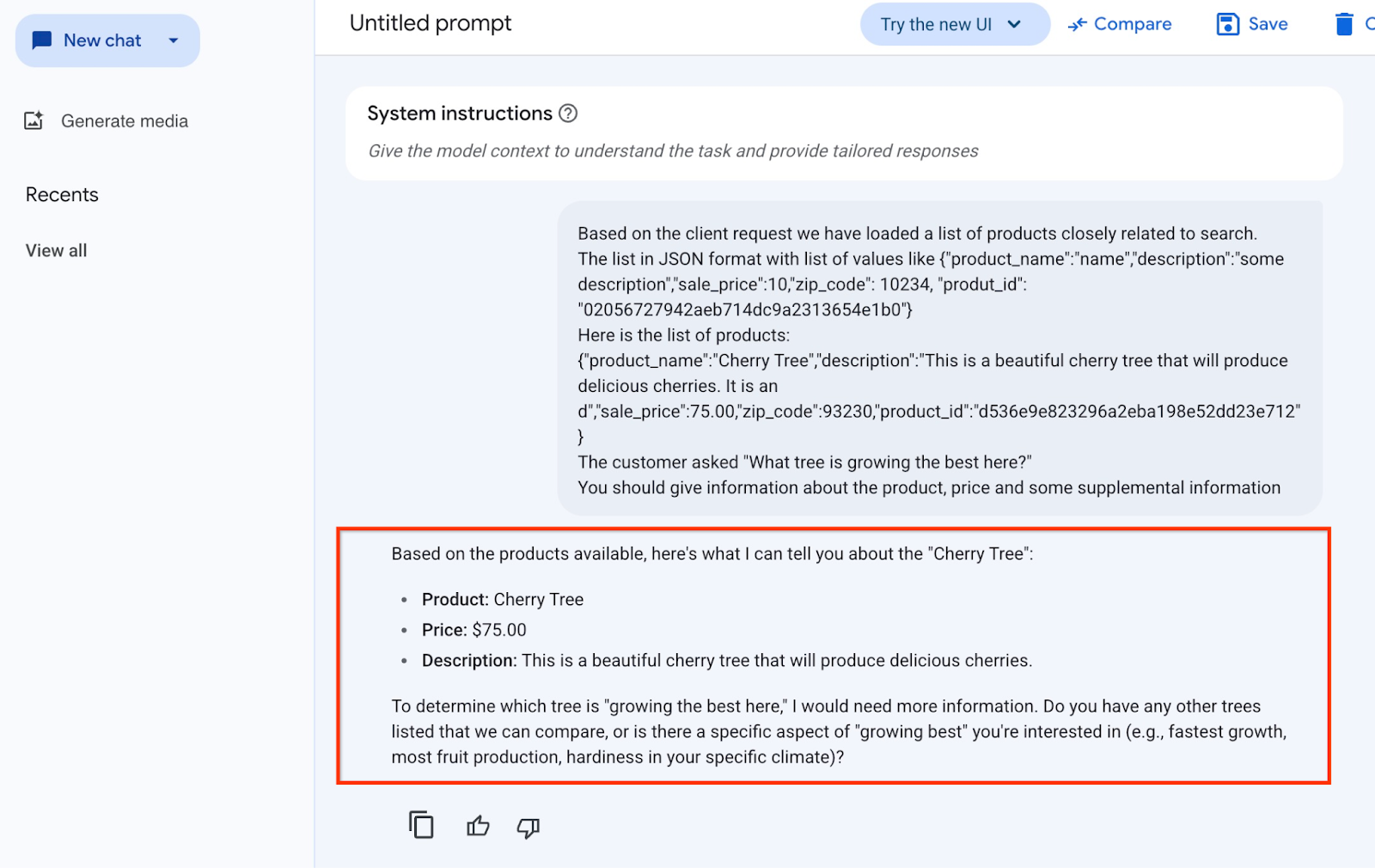
התשובה שקיבלנו מהמודל בדוגמה הזו מופיעה בהמשך. שימו לב שהתשובה עשויה להיות שונה כי המודל והפרמטרים משתנים עם הזמן:
"על סמך המוצרים הזמינים, הנה מה שאני יכול לספר לך על 'עץ הדובדבן':
מוצר: עץ דובדבן
מחיר: 75.00$
תיאור: זהו עץ דובדבן יפהפה שיניב דובדבנים טעימים.
כדי לקבוע איזה עץ 'צומח הכי טוב כאן', אצטרך לקבל מידע נוסף. יש עוד עצים ברשימה שאפשר להשוות ביניהם, או שיש היבט ספציפי של 'הצמיחה הכי טובה' שמעניין אותך (למשל, הצמיחה הכי מהירה, הכי הרבה פירות, עמידות באקלים הספציפי שלך)?"
הרצת ההנחיה ב-PSQL
אנחנו יכולים להשתמש בשילוב של AlloyDB AI עם Vertex AI כדי לקבל את אותה תשובה ממודל גנרטיבי באמצעות SQL ישירות במסד הנתונים. אבל כדי להשתמש במודל gemini-1.5-flash, קודם צריך לרשום אותו.
מאמתים את התוסף google_ml_integration. הגרסה צריכה להיות 1.4.2 ומעלה.
מתחברים למסד הנתונים quickstart_db מ-psql כמו שמוצג למעלה (או משתמשים ב-AlloyDB Studio) ומריצים את הפקודה:
SELECT extversion from pg_extension where extname='google_ml_integration';
בודקים את דגל מסד הנתונים google_ml_integration.enable_model_support.
show google_ml_integration.enable_model_support;
הפלט הצפוי מהסשן של psql הוא 'on':
postgres=> show google_ml_integration.enable_model_support; google_ml_integration.enable_model_support -------------------------------------------- on (1 row)
אם מופיעה האפשרות 'כבוי', צריך להגדיר את דגל מסד הנתונים google_ml_integration.enable_model_support ל'מופעל'. כדי לעשות זאת, אפשר להשתמש בממשק של מסוף האינטרנט של AlloyDB או להריץ את פקודת gcloud הבאה.
PROJECT_ID=$(gcloud config get-value project)
REGION=us-central1
ADBCLUSTER=alloydb-aip-01
gcloud beta alloydb instances update $ADBCLUSTER-pr \
--database-flags google_ml_integration.enable_model_support=on \
--region=$REGION \
--cluster=$ADBCLUSTER \
--project=$PROJECT_ID \
--update-mode=FORCE_APPLY
הפעלת הפקודה ברקע נמשכת כ-3-5 דקות. לאחר מכן תוכלו לאמת מחדש את הסימון.
לשאילתה שלנו אנחנו צריכים שני מודלים. הראשון הוא המודל text-embedding-005 שכבר נמצא בשימוש, והשני הוא אחד ממודלי Gemini הגנריים של Google.
אנחנו מתחילים עם מודל הטמעת טקסט. כדי לרשום את הרצת המודל ב-psql או ב-AlloyDB Studio, מריצים את הקוד הבא:
CALL
google_ml.create_model(
model_id => 'text-embedding-005',
model_provider => 'google',
model_qualified_name => 'text-embedding-005',
model_type => 'text_embedding',
model_auth_type => 'alloydb_service_agent_iam',
model_in_transform_fn => 'google_ml.vertexai_text_embedding_input_transform',
model_out_transform_fn => 'google_ml.vertexai_text_embedding_output_transform');
המודל הבא שצריך לרשום הוא gemini-2.0-flash-001, שישמש ליצירת הפלט הידידותי למשתמש.
CALL
google_ml.create_model(
model_id => 'gemini-2.5-flash',
model_request_url => 'publishers/google/models/gemini-2.5-flash:streamGenerateContent',
model_provider => 'google',
model_auth_type => 'alloydb_service_agent_iam');
תמיד אפשר לבדוק את רשימת המודלים הרשומים על ידי בחירת מידע מהתצוגה google_ml.model_info_view.
select model_id,model_type from google_ml.model_info_view;
פלט לדוגמה
quickstart_db=> select model_id,model_type from google_ml.model_info_view;
model_id | model_type
-------------------------+----------------
textembedding-gecko | text_embedding
textembedding-gecko@001 | text_embedding
text-embedding-005 | text_embedding
gemini-2.5-flash | generic
(4 rows)
עכשיו אפשר להשתמש ב-JSON שנוצר בשאילתת משנה כדי לספק אותו כחלק מההנחיה למודל טקסט של AI גנרטיבי באמצעות SQL.
בסשן של psql או AlloyDB Studio למסד הנתונים, מריצים את השאילתה
WITH trees AS (
SELECT
cp.product_name,
cp.product_description AS description,
cp.sale_price,
cs.zip_code,
cp.uniq_id AS product_id
FROM
cymbal_products cp
JOIN cymbal_inventory ci ON
ci.uniq_id = cp.uniq_id
JOIN cymbal_stores cs ON
cs.store_id = ci.store_id
AND ci.inventory>0
AND cs.store_id = 1583
ORDER BY
(cp.embedding <=> embedding('text-embedding-005',
'What kind of fruit trees grow well here?')::vector) ASC
LIMIT 1),
prompt AS (
SELECT
'You are a friendly advisor helping to find a product based on the customer''s needs.
Based on the client request we have loaded a list of products closely related to search.
The list in JSON format with list of values like {"product_name":"name","product_description":"some description","sale_price":10}
Here is the list of products:' || json_agg(trees) || 'The customer asked "What kind of fruit trees grow well here?"
You should give information about the product, price and some supplemental information' AS prompt_text
FROM
trees),
response AS (
SELECT
json_array_elements(google_ml.predict_row( model_id =>'gemini-2.5-flash',
request_body => json_build_object('contents',
json_build_object('role',
'user',
'parts',
json_build_object('text',
prompt_text)))))->'candidates'->0->'content'->'parts'->0->'text' AS resp
FROM
prompt)
SELECT
string_agg(resp::text,
' ')
FROM
response;
וכאן מופיע הפלט הצפוי. הפלט שיתקבל עשוי להיות שונה בהתאם לגרסת המודל ולפרמטרים שלו:
"Hello there! I can certainly help you with finding a great fruit tree for your area.\n\nBased on what grows well, we have a wonderful **Cherry Tree** that could be a perfect fit!\n\nThis beautiful cherry tree is an excellent choice for producing delicious cherries right in your garden. It's an deciduous tree that typically" " grows to about 15 feet tall. Beyond its fruit, it offers lovely aesthetics with dark green leaves in the summer that transition to a beautiful red in the fall, making it great for shade and privacy too.\n\nCherry trees generally prefer a cool, moist climate and sandy soil, and they are best suited for USDA Zones" " 4-9. Given the zip code you're inquiring about (93230), which is typically in USDA Zone 9, this Cherry Tree should thrive wonderfully!\n\nYou can get this magnificent tree for just **$75.00**.\n\nLet me know if you have any other questions!" "
10. יצירת אינדקס וקטורי
מערך הנתונים שלנו קטן יחסית, וזמן התגובה תלוי בעיקר באינטראקציה עם מודלים של AI. אבל כשמדובר במיליוני וקטורים, החלק של חיפוש הווקטורים יכול לתפוס חלק משמעותי מזמן התגובה שלנו ולהעמיס על המערכת. כדי לשפר את זה, אנחנו יכולים לבנות אינדקס על הווקטורים שלנו.
יצירת אינדקס ScaNN
כדי ליצור את אינדקס SCANN, צריך להפעיל עוד תוסף. התוסף alloydb_scann מספק לנו ממשק לעבודה עם אינדקס וקטור מסוג ANN באמצעות אלגוריתם Google ScaNN.
CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS alloydb_scann;
הפלט אמור להיראות כך:
quickstart_db=> CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS alloydb_scann; CREATE EXTENSION Time: 27.468 ms quickstart_db=>
עכשיו אפשר ליצור את האינדקס. בדוגמה הבאה, השארתי את רוב הפרמטרים כברירת מחדל וסיפקתי רק מספר מחיצות (num_leaves) לאינדקס:
CREATE INDEX cymbal_products_embeddings_scann ON cymbal_products
USING scann (embedding cosine)
WITH (num_leaves=31, max_num_levels = 2);
מידע על שינוי פרמטרים של אינדקס זמין במסמכי התיעוד.
הפלט אמור להיראות כך:
quickstart_db=> CREATE INDEX cymbal_products_embeddings_scann ON cymbal_products USING scann (embedding cosine) WITH (num_leaves=31, max_num_levels = 2); CREATE INDEX quickstart_db=>
השוואת תשובות
עכשיו אפשר להריץ את שאילתת החיפוש הווקטורי במצב EXPLAIN ולוודא שהאינדקס שימש לחיפוש.
EXPLAIN (analyze)
WITH trees as (
SELECT
cp.product_name,
left(cp.product_description,80) as description,
cp.sale_price,
cs.zip_code,
cp.uniq_id as product_id
FROM
cymbal_products cp
JOIN cymbal_inventory ci on
ci.uniq_id=cp.uniq_id
JOIN cymbal_stores cs on
cs.store_id=ci.store_id
AND ci.inventory>0
AND cs.store_id = 1583
ORDER BY
(cp.embedding <=> embedding('text-embedding-005','What kind of fruit trees grow well here?')::vector) ASC
LIMIT 1)
SELECT json_agg(trees) FROM trees;
הפלט הצפוי (הושמטו פרטים לצורך הבהרה):
... Aggregate (cost=16.59..16.60 rows=1 width=32) (actual time=2.875..2.877 rows=1 loops=1) -> Subquery Scan on trees (cost=8.42..16.59 rows=1 width=142) (actual time=2.860..2.862 rows=1 loops=1) -> Limit (cost=8.42..16.58 rows=1 width=158) (actual time=2.855..2.856 rows=1 loops=1) -> Nested Loop (cost=8.42..6489.19 rows=794 width=158) (actual time=2.854..2.855 rows=1 loops=1) -> Nested Loop (cost=8.13..6466.99 rows=794 width=938) (actual time=2.742..2.743 rows=1 loops=1) -> Index Scan using cymbal_products_embeddings_scann on cymbal_products cp (cost=7.71..111.99 rows=876 width=934) (actual time=2.724..2.724 rows=1 loops=1) Order By: (embedding <=> '[0.008864171,0.03693164,-0.024245683,-0.00355923,0.0055611245,0.015985578,...<redacted>...5685,-0.03914233,-0.018452475,0.00826032,-0.07372604]'::vector) -> Index Scan using walmart_inventory_pkey on cymbal_inventory ci (cost=0.42..7.26 rows=1 width=37) (actual time=0.015..0.015 rows=1 loops=1) Index Cond: ((store_id = 1583) AND (uniq_id = (cp.uniq_id)::text)) ...
מהפלט אפשר לראות בבירור שהשאילתה השתמשה ב-Index Scan באמצעות cymbal_products_embeddings_scann ב-cymbal_products.
ואם מריצים את השאילתה בלי explain:
WITH trees as (
SELECT
cp.product_name,
left(cp.product_description,80) as description,
cp.sale_price,
cs.zip_code,
cp.uniq_id as product_id
FROM
cymbal_products cp
JOIN cymbal_inventory ci on
ci.uniq_id=cp.uniq_id
JOIN cymbal_stores cs on
cs.store_id=ci.store_id
AND ci.inventory>0
AND cs.store_id = 1583
ORDER BY
(cp.embedding <=> embedding('text-embedding-005','What kind of fruit trees grow well here?')::vector) ASC
LIMIT 1)
SELECT json_agg(trees) FROM trees;
הפלט אמור להיראות כך:
[{"product_name":"Meyer Lemon Tree","description":"Meyer Lemon trees are California's favorite lemon tree! Grow your own lemons by ","sale_price":34,"zip_code":93230,"product_id":"02056727942aeb714dc9a2313654e1b0"}]
אנחנו רואים שהתוצאה שונה מעט, ובמקום עץ הדובד שהופיע בראש תוצאות החיפוש שלנו בלי אינדקס, מופיעה האפשרות השנייה – עץ לימון מאייר. לכן, המדד מספק לנו נתונים על הביצועים, אבל הוא עדיין מדויק מספיק כדי להניב תוצאות טובות.
אפשר לנסות אינדקסים שונים שזמינים לווקטורים, ודוגמאות נוספות של שילוב עם langchain זמינות בדף התיעוד.
11. ניקוי הסביבה
בסיום שיעור ה-Lab, צריך להשמיד את המכונות ואת האשכול של AlloyDB.
מחיקת אשכול AlloyDB וכל המכונות
אם השתמשתם בגרסת הניסיון של AlloyDB. אל תמחקו את אשכול הניסיון אם אתם מתכננים לבדוק מעבדות ומשאבים אחרים באמצעות אשכול הניסיון. לא תוכלו ליצור אשכול ניסיון נוסף באותו פרויקט.
האפשרות force משמידה את האשכול וגם מוחקת את כל המופעים ששייכים לאשכול.
ב-Cloud Shell, מגדירים את משתני הפרויקט והסביבה אם התנתקתם וכל ההגדרות הקודמות אבדו:
gcloud config set project <your project id>
export REGION=us-central1
export ADBCLUSTER=alloydb-aip-01
export PROJECT_ID=$(gcloud config get-value project)
מחיקת האשכול:
gcloud alloydb clusters delete $ADBCLUSTER --region=$REGION --force
הפלט הצפוי במסוף:
student@cloudshell:~ (test-project-001-402417)$ gcloud alloydb clusters delete $ADBCLUSTER --region=$REGION --force All of the cluster data will be lost when the cluster is deleted. Do you want to continue (Y/n)? Y Operation ID: operation-1697820178429-6082890a0b570-4a72f7e4-4c5df36f Deleting cluster...done.
מחיקת גיבויים של AlloyDB
מחיקת כל הגיבויים של AlloyDB באשכול:
for i in $(gcloud alloydb backups list --filter="CLUSTER_NAME: projects/$PROJECT_ID/locations/$REGION/clusters/$ADBCLUSTER" --format="value(name)" --sort-by=~createTime) ; do gcloud alloydb backups delete $(basename $i) --region $REGION --quiet; done
הפלט הצפוי במסוף:
student@cloudshell:~ (test-project-001-402417)$ for i in $(gcloud alloydb backups list --filter="CLUSTER_NAME: projects/$PROJECT_ID/locations/$REGION/clusters/$ADBCLUSTER" --format="value(name)" --sort-by=~createTime) ; do gcloud alloydb backups delete $(basename $i) --region $REGION --quiet; done Operation ID: operation-1697826266108-60829fb7b5258-7f99dc0b-99f3c35f Deleting backup...done.
עכשיו אפשר להרוס את המכונה הווירטואלית
מחיקת מכונה וירטואלית ב-GCE
ב-Cloud Shell, מריצים את הפקודה:
export GCEVM=instance-1
export ZONE=us-central1-a
gcloud compute instances delete $GCEVM \
--zone=$ZONE \
--quiet
הפלט הצפוי במסוף:
student@cloudshell:~ (test-project-001-402417)$ export GCEVM=instance-1
export ZONE=us-central1-a
gcloud compute instances delete $GCEVM \
--zone=$ZONE \
--quiet
Deleted
12. מזל טוב
כל הכבוד, סיימתם את ה-Codelab.
מה למדנו
- איך פורסים אשכול AlloyDB ומכונה ראשית
- איך מתחברים ל-AlloyDB ממכונה וירטואלית ב-Google Compute Engine
- איך יוצרים מסד נתונים ומפעילים את AlloyDB AI
- איך טוענים נתונים למסד הנתונים
- איך משתמשים במודל הטמעה של Vertex AI ב-AlloyDB
- איך משפרים את התוצאה באמצעות מודל גנרטיבי של Vertex AI
- איך לשפר את הביצועים באמצעות אינדקס וקטורי
13. סקר
פלט:

